|
Clear Airport
Clear Airport is a state-owned public-use airport located three nautical miles (6 km) southeast of the central business district of Clear, Alaska, United States. Facilities and aircraft Clear Airport covers an area of at an elevation of 552 feet (168 m) above mean sea level. It has one runway designated 1/19 with a 4,000 by 100 ft (1,219 x 30 m) asphalt pavement. For the 12-month period ending December 31, 2005, the airport had 2,000 aircraft operations, an average of 166 per month: 75% general aviation and 25% military. At that time there were 12 aircraft based at this airport, all single- engine. References External links FAA Alaska airport diagram(GIF The Graphics Interchange Format (GIF; or , see pronunciation) is a bitmap image format that was developed by a team at the online services provider CompuServe led by American computer scientist Steve Wilhite and released on 15 June 1987. ...) Airports in Denali Borough, Alaska ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clear, Alaska
Clear is an unincorporated community in Denali Borough, Alaska, United States. The small community is along the George Parks Highway at milepost 280 and encompasses residential homes and businesses. Its elevation is 518 feet (158 m). The community is completely within Anderson, Alaska. Clear is 4 miles south of the Alaska Railroad Clear Site station established about 1918 at mile 392.9 ARR. The Geographic Names Information System The Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) is a database of name and locative information about more than two million physical and cultural features throughout the United States and its territories, Antarctica, and the associated states of ... reference for Clear refers to this station. Clear is 5 miles south of Clear Space Force Station (AFS). Economy The settlement contains two businesses, both located on the Parks Highway. The Clear Sky Lodge and the Rochester Lodge are across the highway from one another at mile marker 280. The lodge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states ( Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th paralle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic management, certification of personnel and aircraft, setting standards for airports, and protection of U.S. assets during the launch or re-entry of commercial space vehicles. Powers over neighboring international waters were delegated to the FAA by authority of the International Civil Aviation Organization. Created in , the FAA replaced the former Civil Aeronautics Board, Civil Aeronautics Administration (CAA) and later became an agency within the United States Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Transportation. Major functions The FAA's roles include: *Regulating U.S. commercial space transportation *Regulating air navigation facilities' geometric and flight inspection standards *Encouraging and developing civil aeronautics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
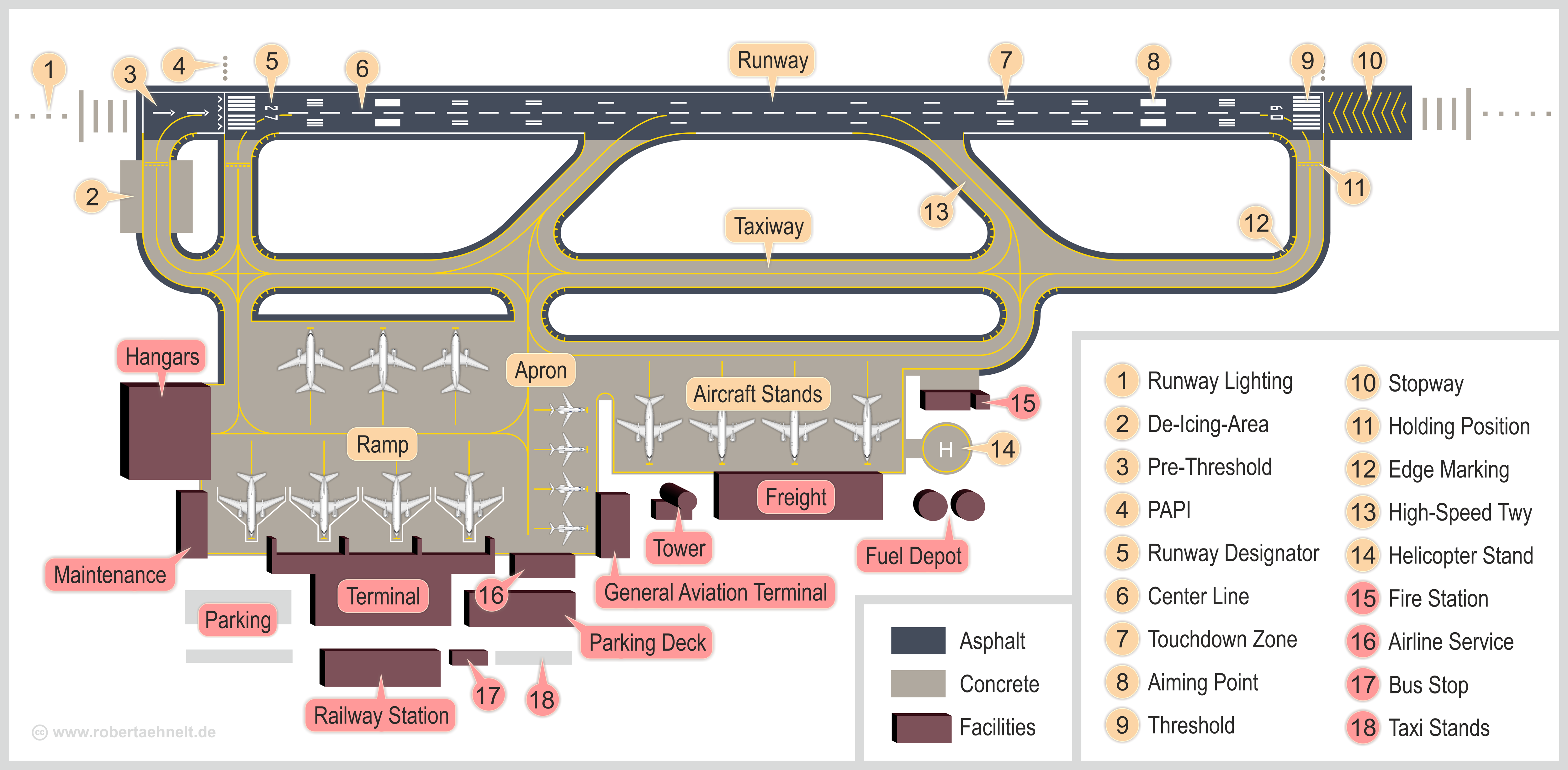
Airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Business District
A central business district (CBD) is the commercial and business centre of a city. It contains commercial space and offices, and in larger cities will often be described as a financial district. Geographically, it often coincides with the " city centre" or " downtown". However, these concepts are not necessarily synonymous: many cities have a central ''business'' district located away from its commercial and or cultural centre and or downtown/city centre, and there may be multiple CBDs within a single urban area. The CBD will often be characterised by a high degree of accessibility as well as a large variety and concentration of specialised goods and services compared to other parts of the city. For instance, Midtown Manhattan, New York City, is the largest central business district in the city and in the United States. London's city centre is usually regarded as encompassing the historic City of London and the medieval City of Westminster, while the City of London and the trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while '' altitude'' or '' geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Sea Level
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value ( magnitude and sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the '' arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is the '' sample mean'' (\bar) to distinguish it from the mean, or expected value, of the underlying distribution, the '' population mean'' (denoted \mu or \mu_x).Underhill, L.G.; Bradfield d. (1998) ''Introstat'', Juta and Company Ltd.p. 181/ref> Outside probability and statistics, a wide range of other notions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (sod, grass, soil, dirt, gravel, ice, sand or road salt, salt). Runways, as well as taxiways and Airport apron, ramps, are sometimes referred to as "tarmac", though very few runways are built using Tarmacadam, tarmac. Takeoff and landing areas defined on the surface of water for seaplanes are generally referred to as waterways. Runway lengths are now International Civil Aviation Organization#Use of the International System of Units, commonly given in meters worldwide, except in North America where feet are commonly used. History In 1916, in a World War I war effort context, the first concrete-paved runway was built in Clermont-Ferrand in France, allowing local company Michelin to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term asphaltum was also used. Full text at Internet Archive (archive.org) The word is derived from the Ancient Greek ἄσφαλτος ''ásphaltos''. The largest natural deposit of asphalt in the world, estimated to contain 10 million tons, is the Pitch Lake located in La Brea in southwest Trinidad ( Antilles island located on the northeastern coast of Venezuela), within the Siparia Regional Corporation. The primary use (70%) of asphalt is in road construction, where it is used as the glue or binder mixed with aggregate particles to create asphalt concrete. Its other main uses are for bituminous waterproofing products, including production of roofing felt and for sealing flat roofs. In material sciences and engineering, the terms "as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Aviation
General aviation (GA) is defined by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as all civil aviation aircraft operations with the exception of commercial air transport or aerial work, which is defined as specialized aviation services for other purposes. However, for statistical purposes ICAO uses a definition of general aviation which includes aerial work. General aviation thus represents the " private transport" and recreational components of aviation. Definition The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) defines civil aviation aircraft operations in three categories: General Aviation (GA), Aerial Work (AW) and Commercial Air Transport (CAT). Aerial work operations are separated from general aviation by ICAO by this definition. Aerial work is when an aircraft is used for specialized services such as agriculture, construction, photography, surveying, observation and patrol, search and rescue, and aerial advertisement. However, for statistical purpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Aviation
Military aviation comprises military aircraft and other flying machines for the purposes of conducting or enabling aerial warfare, including national airlift ( air cargo) capacity to provide logistical supply to forces stationed in a war theater or along a front. Airpower includes the national means of conducting such warfare, including the intersection of transport and warcraft. Military aircraft include bombers, fighters, transports, trainer aircraft, and reconnaissance aircraft. History The first military uses of aviation involved lighter-than-air balloons. During the Battle of Fleurus in 1794, the French observation balloon ''l'Entreprenant'' was used to monitor Austrian troop movements. The use of lighter-than-air aircraft in warfare became prevalent in the 19th century, including regular use in the American Civil War. Lighter-than-air military aviation persisted until shortly after World War II, gradually being withdrawn from various roles as heavier-than-air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)
