|
Claude Vaussin
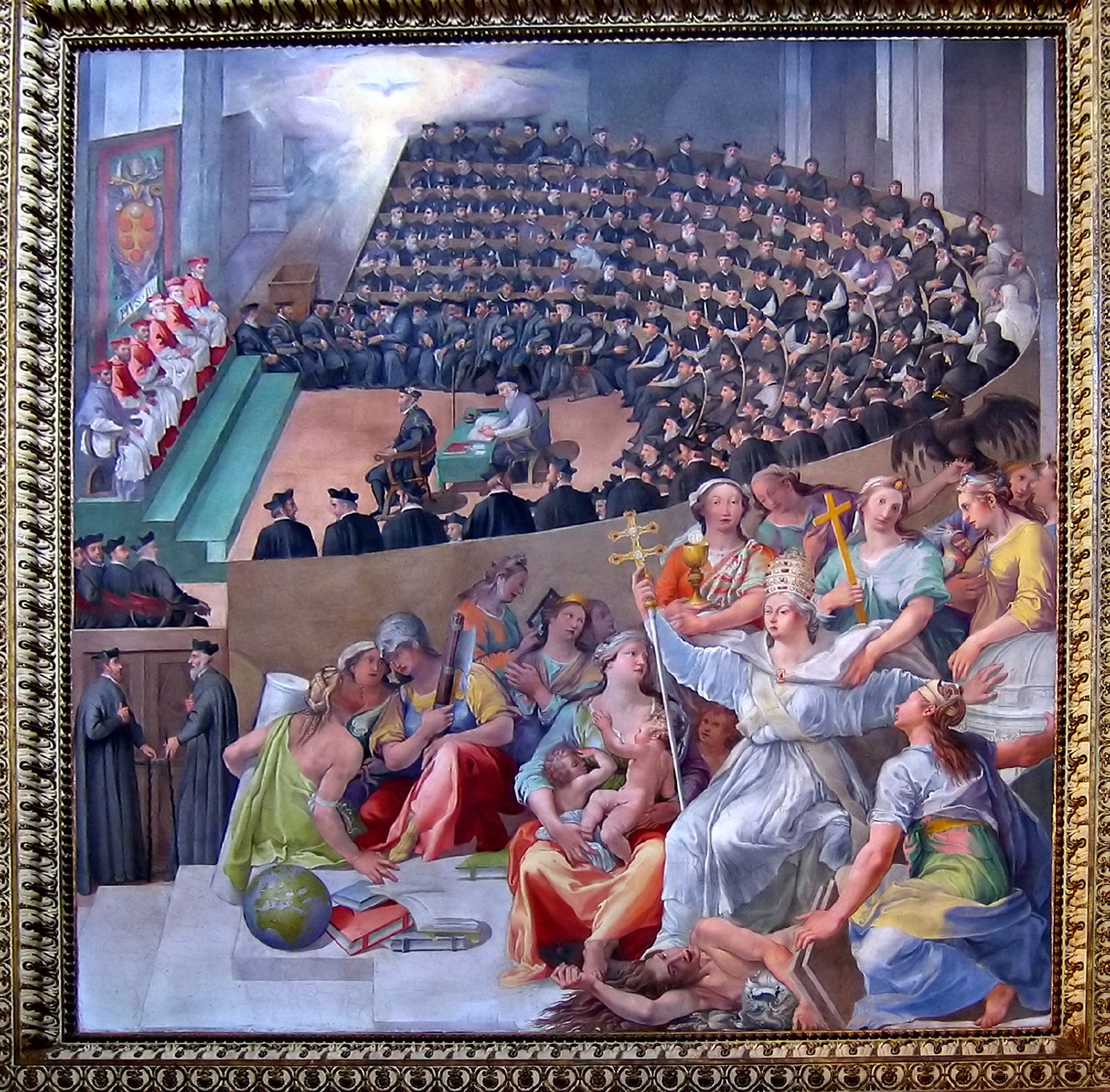
Claude Vaussin (* 1608 – 1 February 1670) was abbot of Cîteaux from 1643/1645 until 1670, and as such, Abbot General of the Cistercian Order. Election as Abbot General On 2 January 1643, when he was not yet 37 years old, Dr. Claude Vaussin was elected abbot of Cîteaux. He came from an influential but non-aristocratic family in Dijon, had become a monk in Clairvaux and later served as Prior in Froidmont Abbey. He was the successor of none other than the infamous Cardinal Richelieu, who had let himself be elected to this position in 1635 in order to manipulate the warring factions in the Cistercian Order to his personal benefit. Many abbots did not accept his election. Claude Vaussin's election was rejected by the Reform movement; yet after his election had been investigated and repeated, Vaussin emerged on 10 May 1645 once again as the Abbot of Cîteaux and therefore Abbot General. It took almost four years before Vaussin received confirmation from the Holy See and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Vaussin, Abbé De Cîteaux (1643-1670)
Claude may refer to: __NOTOC__ People and fictional characters * Claude (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Claude (surname), a list of people * Claude Lorrain (c. 1600–1682), French landscape painter, draughtsman and etcher traditionally called just "Claude" in English * Madame Claude, French brothel keeper Fernande Grudet (1923–2015) Places * Claude, Texas, a city * Claude, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Other uses * Allied reporting name of the Mitsubishi A5M Japanese carrier-based fighter aircraft * Claude (alligator) Claude is an albino alligator ('' Alligator mississippiensis'') at the California Academy of Sciences. Claude lacks the pigment melanin, resulting in colorless skin, and he has poor eyesight associated with his albinism. Background Claude was h ..., an albino alligator at the California Academy of Sciences See also * Claude's syndrome, a form of brainstem stroke syndrome {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Alexander VII
Pope Alexander VII ( it, Alessandro VII; 13 February 159922 May 1667), born Fabio Chigi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 April 1655 to his death in May 1667. He began his career as a vice-papal legate, and he held various diplomatic positions in the Holy See. He was ordained as a priest in 1634, and he became bishop of Nardo in 1635. He was later transferred in 1652, and he became bishop of Imola. Pope Innocent X made him secretary of state in 1651, and in 1652, he was appointed a cardinal. Early in his papacy, Alexander, who was seen as an anti-nepotist at the time of his election, lived simply; later, however, he gave jobs to his relatives, who eventually took over his administration. His administration worked to support the Jesuits. However, his administration's relations with France were strained due to his frictions with French diplomats. Alexander was interested in architecture and supported various urban projects in Rome. He als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1608 Births
Sixteen or 16 may refer to: * 16 (number), the natural number following 15 and preceding 17 *one of the years 16 BC, AD 16, 1916, 2016 Films * ''Pathinaaru'' or ''Sixteen'', a 2010 Tamil film * ''Sixteen'' (1943 film), a 1943 Argentine film directed by Carlos Hugo Christensen * ''Sixteen'' (2013 Indian film), a 2013 Hindi film * ''Sixteen'' (2013 British film), a 2013 British film by director Rob Brown Music *The Sixteen, an English choir *16 (band), a sludge metal band * Sixteen (Polish band), a Polish band Albums * ''16'' (Robin album), a 2014 album by Robin * 16 (Madhouse album), a 1987 album by Madhouse * ''Sixteen'' (album), a 1983 album by Stacy Lattisaw *''Sixteen'' , a 2005 album by Shook Ones * ''16'', a 2020 album by Wejdene Songs * "16" (Sneaky Sound System song), 2009 * "Sixteen" (Thomas Rhett song), 2017 * "Sixteen" (Ellie Goulding song), 2019 *"16", by Craig David from '' Following My Intuition'', 2016 *"16", by Green Day from ''39/Smooth'', 1990 *"16", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1670 Deaths
Year 167 ( CLXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Quadratus (or, less frequently, year 920 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 167 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Lucius Aurelius Verus Augustus and Marcus Ummidius Quadratus Annianus become Roman Consuls. * The Marcomanni tribe wages war against the Romans at Aquileia. They destroy aqueducts and irrigation conduits. Marcus Aurelius repels the invaders, ending the Pax Romana (Roman Peace) that has kept the Roman Empire free of conflict since the days of Emperor Augustus. * The Vandals ( Astingi and Lacringi) and the Sarmatian Iazyges invade Dacia. To counter them, Legio V ''Macedonica'', returning from the Parthia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Lekai
Louis Julius Lekai, O.Cist. (* 4 February 1916 in Budapest; † 1 July 1994 in Irving, Texas) was an American monk, historian and university professor born in Hungary. Life and work Julius (Gyula) Lékai was a student at the Cistercian school (Budai-Ciszterci-Szent Imre-Gymnasium) in Budapest and entered the noviciate at Zirc Abbey in 1934. He was ordained a priest in 1941 and completed his doctorate a year later at Budapest University. His Dissertation was an analysis of Hungarian historical research in the period 1790–1830. He taught at the Cistercian school (Gárdonyi Géza Ciszterci Gimnázium) in Eger until 1947. He also taught history at the Faculty of Laws at the Károly-Eszterházy University in Eger (1943–1944). During the Second World War he was a military chaplain for the Hungarian Army. He fled to the United States in October 1947; he became an American citizen in 1953. Lekai's first home in the USA was Our Lady of Spring Bank Abbey in Wisconsin; from 1953 to 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Rite
The Roman Rite ( la, Ritus Romanus) is the primary liturgical rite of the Latin Church, the largest of the '' sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. It developed in the Latin language in the city of Rome and, while distinct Latin liturgical rites such as the Ambrosian Rite remain, the Roman Rite has gradually been adopted almost everywhere in the Latin Church. In medieval times there were numerous local variants, even if all of them did not amount to distinct rites, yet uniformity increased as a result of the invention of printing and in obedience to the decrees of the Council of Trent of 1545–63 (see '' Quo primum''). Several Latin liturgical rites that survived into the 20th century were abandoned voluntarily after the Second Vatican Council. The Roman Rite is now the most widespread liturgical rite not only in the Catholic Church but in Christianity as a whole. The Roman Rite has been adapted through the centuries and the history of its Euchari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tridentine Reform
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described as the embodiment of the Counter-Reformation."Trent, Council of" in Cross, F. L. (ed.) ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church'', Oxford University Press, 2005 (). The Council issued condemnations of what it defined to be heresies committed by proponents of Protestantism, and also issued key statements and clarifications of the Church's doctrine and teachings, including scripture, the biblical canon, sacred tradition, original sin, justification, salvation, the sacraments, the Mass, and the veneration of saints.Wetterau, Bruce. ''World History''. New York: Henry Holt and Company, 1994. The Council met for twenty-five sessions between 13 December 1545 and 4 December 1563. Pope Paul III, who convoked the Council, oversaw the first eig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistercian Rite
The Cistercian Rite is the liturgical rite, distinct from the Roman Rite, specific to the Cistercian Order of the Catholic Church. Description The Cistercian Rite is to be found in the liturgical books of this reformed branch of the Benedictines. The collection, composed of fifteen books, was made by the General Chapter of Cîteaux (the place from which the order takes its name), most probably in 1134; they were later included in the Missal, Breviary, Ritual and Martyrology of the order. When Pope Pius V ordered the entire Church to conform to the Roman Missal and Roman Breviary, he exempted the Cistercians, because their rite had been more than 200 years in existence. Under Claude Vaussin, General of the Cistercians in the middle of the seventeenth century, several reforms were made in the liturgical books of the order, and were approved by Pope Alexander VII, Pope Clement IX and Pope Clement XIII. These approbations were confirmed by Pope Pius IX on 7 February 1871 for the Cis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Trappe Abbey
La Trappe Abbey, also known as La Grande Trappe, is a monastery in Soligny-la-Trappe, Orne, France. It is known for being the house of origin of the Trappists, to whom it gave its name. History The site of the famous La Trappe Abbey was for centuries isolated in a valley surrounded by forests, streams and lakes, 9 miles from Mortagne and 84 miles from Paris, in the Diocese of Séez and the former province of Normandy. It began as a small oratory chapel to the Virgin Mary, built in 1122 by Rotrou III, Count of Perche, as a memorial to his wife Matilda FitzRoy, Countess of Perche. (An illegitimate daughter of Henry I, she drowned in the '' White Ship'' disaster of 1120.) A few years later Rotrou built a monastery adjoining, which he offered to the monks of Le Breuil-Benoît Abbey near Dreux, a house of the Order of Savigny. The order was highly respected at that time for its fervour and holiness. In 1140 the monastery of La Trappe was raised to the status of abbey. In 114 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armand Jean Le Bouthillier De Rancé
Armand Jean le Bouthillier de Rancé (9 January 1626, Paris27 October 1700, Soligny-la-Trappe) was an abbot of La Trappe Abbey and the founder of the Trappists. Early life Armand Jean le Bouthillier de Rancé was born 9 January 1626 in Paris, the second son of Denis Bouthillier, Lord of Rancé, and Councillor of State. His godfather was Cardinal Richelieu; his uncle Victor Le Bouthillier, Archbishop of Tours.Obrecht, Edmond. "Jean-Armand le Bouthillier de Rancé." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 12. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1911. 24 June 2019 Armand was originally intended for the and regularly instructe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberic Of Cîteaux
Alberic of Cîteaux (died 26 January 1109), sometimes known as Aubrey of Cîteaux, was a French monk and abbot, one of the founders of the Cistercian Order. He is now honored as a saint. Life Alberic was a hermit in the forest of Collan in France who, along with five other hermits, invited Abbot Robert of Molesme to begin a new monastery with them that would operate under the Rule of St. Benedict. Robert led these hermits to the forest of Molesme and established a religious settlement there in 1075, Molesme Abbey. Robert served as the first abbot, and Alberic as the prior. However, as the settlement's fame grew, gifts came in and the wealth attracted new monks more lax in their observance of the rule. The Molesme community was divided, and the monks opposed Robert and Alberic. Robert twice left the monastery to live as a hermit, and twice the pope ordered him back to his community. During one of Robert's absences, the brothers imprisoned Alberic so that they might have their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |