|
Classis Moesica
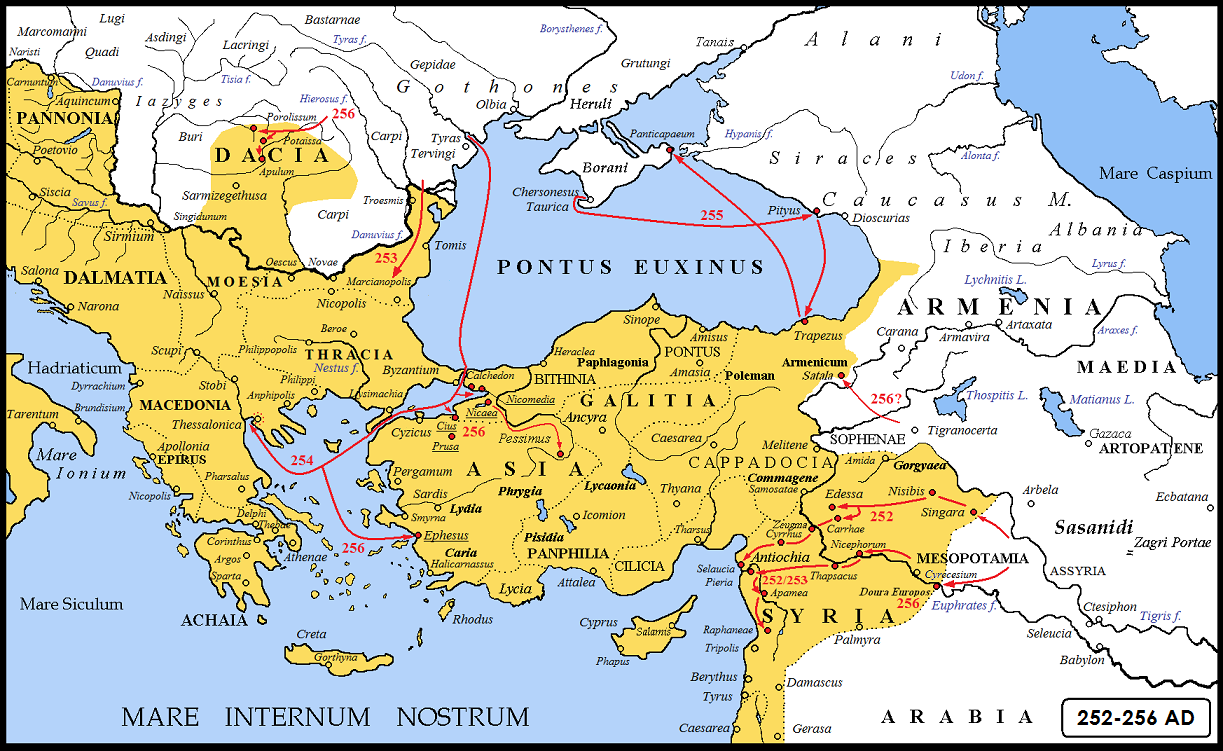
The ''Classis Flavia Moesica'' (" Flavian Fleet of Moesia") was the Roman Empire's fleet on the lower Danube river, near the Black Sea. History The ''Classis Moesica'' was established sometime between 20 BC and 10 AD. It was based in Noviodunum and controlled the Lower Danube from the Iron Gates to the northwestern Black Sea as far as the Crimea. The honorific ''Flavia'', awarded to it and to the ''Classis Pannonica'', may indicate its reorganization by Vespasian around 75 AD.Webster & Elton (1998), p. 163 After Domitian (in 85 AD) it was headquartered in Sexaginta Prista. After Trajan's conquest of Dacia, during which the ''Classis Moesica'' provided logistical support, its base was moved back to Noviodunum. The fleet also included several secondary ports, like Carsium, Novae, Oescus and Tomis (modern Constanta). From 41 AD detachments were stationed in Crimea and Tyras. Military diplomas show that the classis Moesica belonged to the army of Moesia Inferior. The ''Clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
058 Conrad Cichorius, Die Reliefs Der Traianssäule, Tafel LVIII
58 may refer to: * 58 (number) * one of the years 58 BC, AD 58, 1958, 2058 * 58 (band), an American rock band * 58 (golf), a round of 58 in golf * "Fifty Eight", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Arch Stanton'', 2014 * 58 Concordia, a main-belt asteroid {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classis Pontica
The Classis Pontica was a '' provincialis'' fleet, established initially by Augustus and then by Nero on a permanent basis (around 57). It was tasked with guarding the southern ''Pontus Euxinus'', coordinating with the neighboring fleet of Mesia, the ''Classis Flavia Moesica''. History Established by Augustus in 14 BCE, it did not operate permanently until the principate of Nero. Indeed, it seems that as early as 46 a Roman naval expedition had pushed along the coast of Pontus Euxinus (Black Sea), as far as the Tanais River (Don River). In 57 a new expedition to the area reached the Tauric Chersonese, or the present Crimean peninsula. Following these events a new permanent fleet was created to garrison and patrol the Pontus Euxinus (today's Black Sea): the ''Classis Pontica''. During the civil war of 68-69, a certain Anicetus, ''praefectus Classis'' of the ''Classis Pontica'', initially supported Vitellius. It is said that he burned the fleet and fled to Caucasian Iberia, tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio II Herculia
Legio II ''Herculia'' (''devoted to Hercules'') was a Roman legion, levied by Emperor Diocletian (284–305), possibly together with I ''Iovia'', to guard the newly created province of Scythia Minor. It was stationed at Capidava. The ''cognomen'' of this legion came from ''Herculius'', the attribute of Maximian (Diocletian's colleague) meaning "similar to Hercules". According to ''Notitia Dignitatum'', at the beginning of the 5th-century, II ''Herculia'' was still in its camp on the Danube The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou .... See also * List of Roman legions References and external links livius.org account 02 Herculia Military units and formations established in the 3rd century {{Dacia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodization has since been widely accepted. Late antiquity represents a cultural sphere that covered much of the Mediterranean world, including parts of Europe and the Near East.Brown, Peter (1971), ''The World of Late Antiquity (1971), The World of Late Antiquity, AD 150-750''Introduction Late antiquity was an era of massive political and religious transformation. It marked the origins or ascendance of the three major monotheistic religions: Christianity, rabbinic Judaism, and Islam. It also marked the ends of both the Western Roman Empire and the Sasanian Empire, the last Persian empire of antiquity, and the beginning of the early Muslim conquests, Arab conquests. Meanwhile, the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine (Eastern Roman) Empire became a milit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythia Minor (Roman Province)
Scythia Minor or Lesser Scythia (Greek: , ) was a Roman province in late Antiquity, occupying the lands between the lower Danube and the Black Sea, the modern-day Dobruja region in Romania and Bulgaria. It was detached from Moesia Inferior by the Emperor Diocletian to form a separate province sometime between 286 and 293 CE. The capital of the province was Tomis (modern-day Constanța). It ceased to exist around 679–681, when the region was overrun by the Bulgars, which the Emperor Constantine IV was forced to recognize in 681. According to the ''Laterculus Veronensis'' of and the ''Notitia Dignitatum'' of , Scythia belonged to the Diocese of Thrace. Its governor held the title of ''praeses'' and its '' dux'' commanded two legions, Legio I Iovia and Legio II Herculia. The office of ''dux'' was replaced by that of '' quaestor exercitus'', covering a wider area, in 536. The indigenous population of Scythia Minor was Dacian and their material culture is apparent archaeol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liburnian (ship)
A liburna was a type of small galley used for raiding and patrols. Originally utilized by the Liburnians, a pirate tribe from Dalmatia, it later became a staple of the Roman navy.. History A stone tablet (''Stele di Novilara'') discovered near ancient Pisaurum (now Pesaro) depicts a liburna in the midst of a naval battle. Dating back to the fifth or sixth century BCE, the image likely portrays a fictional clash between the Liburnian and Picene fleets. The liburna is depicted as a light vessel with a single row of oars, one mast, one sail, and a prow curving outward. Beneath the prow, a rostrum was installed for striking enemy ships below the waterline. Initially resembling the ancient Greek penteconter, the liburna featured a single bench with 25 oars on each side. However, during the late Roman Republic, it evolved into a bireme with two rows of oars, maintaining its superior speed, agility, and maneuverability compared to triremes. The Romans adopted the liburna design, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Navy
The Byzantine navy was the Navy, naval force of the Byzantine Empire. Like the state it served, it was a direct continuation from its Roman navy, Roman predecessor, but played a far greater role in the defence and survival of the state than its earlier iteration. While the fleets of the Roman Empire faced few great naval threats, operating as a policing force vastly inferior in power and prestige to the Roman army, army, command of the sea became vital to the very existence of the Byzantine state, which several historians have called a "maritime empire". The first threat to Roman hegemony in the Mediterranean Sea was posed by the Vandals in the 5th century, but their threat was ended by the wars of Justinian I in the 6th century. The re-establishment of a permanently maintained fleet and the introduction of the dromon galley in the same period also marks the point when the Byzantine navy began departing from its late Roman roots and developing its own characteristic identity. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moesia Inferior
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballia'. It included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia (Moesia Superior), Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine (Moesia Inferior). Geography In ancient geographical sources, Moesia was bounded to the south by the Haemus (Balkan Mountains) and Scardus (Šar) mountains, to the west by the Drinus (Drina) river, on the north by the Donaris (Danube) and on the east by the Euxine (Black Sea). History The region of Moesia was inhabited chiefly by Thracian, Illyrian, and Thraco-Illyrian peoples. The name of the region comes from Moesi, the Latin name of a Thracian tribe who lived there before the Roman conquest. Parts of Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyras
Tyras () was an ancient Greek city on the northern coast of the Black Sea. It was founded by colonists from Miletus, probably about 600 BC. The city was situated some 10 km from the mouth of the Tyras River, which is now called the Dniester. The surrounding native tribe was called the Tyragetae. The ruins of Tyras are now located in the modern city of Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi in the Odesa Oblast of Ukraine. History Of great importance in early times, in the 2nd century BC Tyras fell under the dominion of native kings whose names appear on its coins, and it was destroyed by the Getae about 50 BC. In 56 AD, it seems to have been restored by the Romans under Nero and, henceforth, formed part of the province of Lower Moesia. There exists a series of its coins with heads of emperors from Domitian to Alexander Severus. Indeed, the autonomous minting of coins in the city lasted from the time of the emperor Domitian ( 81 AD) up to the end of the reign of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |