|
Classifier Handshape
Classifier may refer to: *Classifier (linguistics), or ''measure word'', especially in East Asian languages **Classifier handshape, in sign languages *Classifier (UML), in software engineering *Classification rule, in statistical classification, e.g.: **Hierarchical classifier **Linear classifier *Deductive classifier *Subobject classifier, in category theory *An air classifier or similar machine for sorting materials *Classifier (machine learning) See also *Finite-state machine#Classifiers * *Classification (other) *Classified (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classifier (linguistics)
A classifier (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated or ) is a word or affix that accompanies nouns and can be considered to "classify" a noun depending on some characteristics (e.g. humanness, animacy, sex, shape, social status) of its referent. Classifiers in this sense are specifically called noun classifiers because some languages in Papuan languages, Papua as well as the Indigenous languages of the Americas, Americas have verbal classifiers which categorize the referent of its Argument (linguistics), argument. In languages that have classifiers, they are often used when the noun is being counted, that is, when it appears with a numeral (linguistics), numeral. In such languages, a phrase such as "three people" is often required to be expressed as "three ''X'' (of) people", where ''X'' is a classifier appropriate to the noun for "people"; compare to "three blades of grass". Classifiers that appear next to a Numeral (linguistics), numeral or a Quantifier (linguistics), qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classifier Handshape
Classifier may refer to: *Classifier (linguistics), or ''measure word'', especially in East Asian languages **Classifier handshape, in sign languages *Classifier (UML), in software engineering *Classification rule, in statistical classification, e.g.: **Hierarchical classifier **Linear classifier *Deductive classifier *Subobject classifier, in category theory *An air classifier or similar machine for sorting materials *Classifier (machine learning) See also *Finite-state machine#Classifiers * *Classification (other) *Classified (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
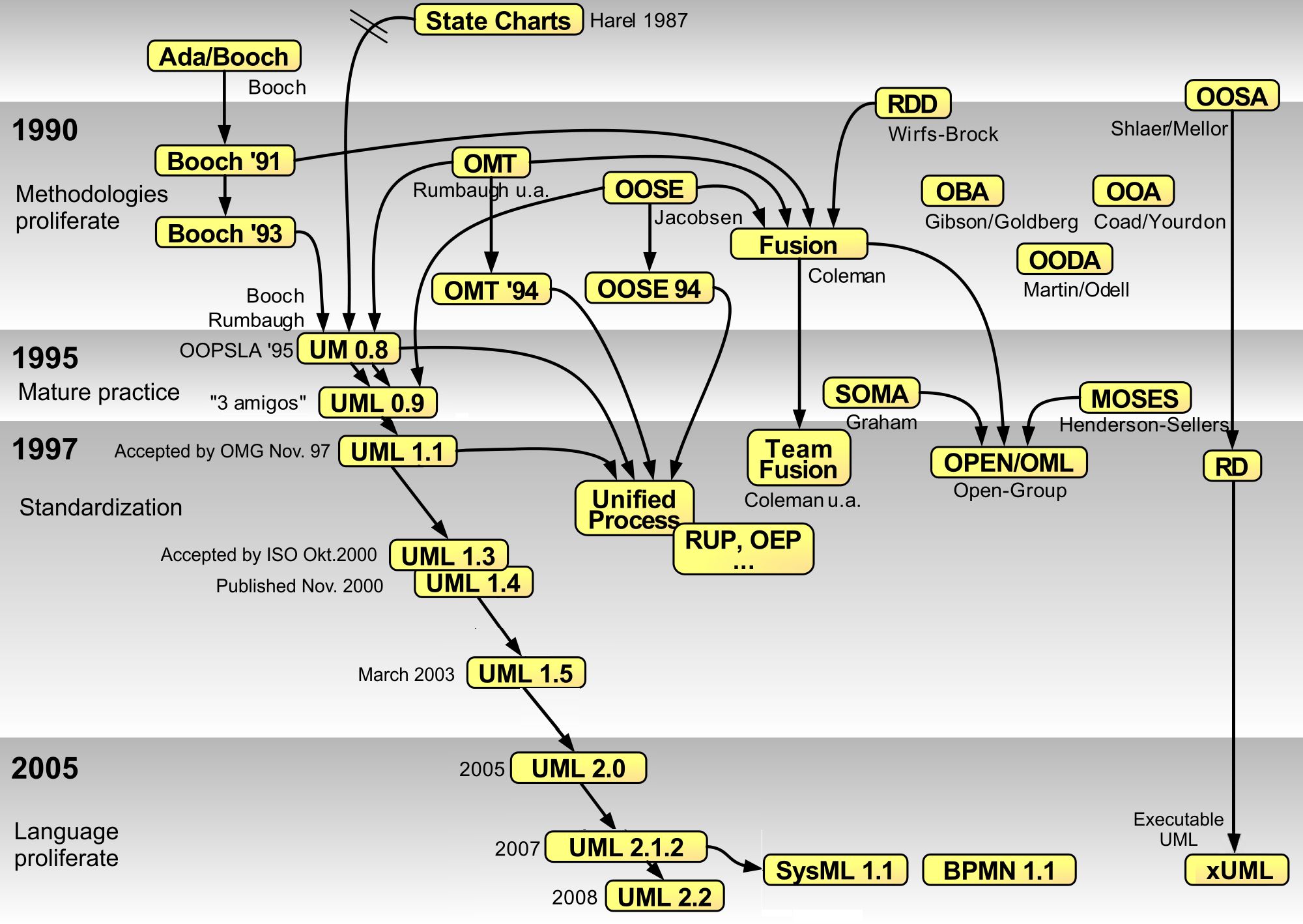
Classifier (UML)
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Rule
Given a population whose members each belong to one of a number of different sets or classes, a classification rule or classifier is a procedure by which the elements of the population set are each predicted to belong to one of the classes. A perfect classification is one for which every element in the population is assigned to the class it really belongs to. The bayes classifier is the classifier which assigns classes optimally based on the known attributes (i.e. features or regressors) of the elements to be classified. A special kind of classification rule is binary classification, for problems in which there are only two classes. Testing classification rules Given a data set consisting of pairs ''x'' and ''y'', where ''x'' denotes an element of the population and ''y'' the class it belongs to, a classification rule ''h''(''x'') is a function that assigns each element ''x'' to a predicted class \hat=h(x). A binary classification is such that the label ''y'' can take only one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchical Classifier
Hierarchical classification is a system of grouping things according to a hierarchy. In the field of machine learning Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task ( ..., hierarchical classification is sometimes referred to as instance space decomposition, which splits a complete multi-class problem into a set of smaller classification problems. See also * Deductive classifier * Cascading classifiers * Faceted classification References External links Hierarchical Classification – a useful approach for predicting thousands of possible categories Classification algorithms {{AI-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Classifier
In machine learning, a linear classifier makes a classification decision for each object based on a linear combination of its features. Such classifiers work well for practical problems such as document classification, and more generally for problems with many variables ( features), reaching accuracy levels comparable to non-linear classifiers while taking less time to train and use. Definition If the input feature vector to the classifier is a real vector \vec x, then the output score is :y = f(\vec\cdot\vec) = f\left(\sum_j w_j x_j\right), where \vec w is a real vector of weights and ''f'' is a function that converts the dot product of the two vectors into the desired output. (In other words, \vec is a one-form or linear functional mapping \vec x onto R.) The weight vector \vec w is learned from a set of labeled training samples. Often ''f'' is a threshold function, which maps all values of \vec\cdot\vec above a certain threshold to the first class and all other value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deductive Classifier
A deductive classifier is a type of artificial intelligence inference engine. It takes as input a set of declarations in a frame language about a domain such as medical research or molecular biology. For example, the names of Class hierarchy, classes, sub-classes, properties, and restrictions on allowable values. The classifier determines if the various declarations are logically consistent and if not will highlight the specific inconsistent declarations and the inconsistencies among them. If the declarations are consistent the classifier can then assert additional information based on the input. For example, it can add information about existing classes, create additional classes, etc. This differs from traditional inference engines that trigger off of IF-THEN conditions in rules. Classifiers are also similar to Automated theorem proving, theorem provers in that they take as input and produce output via first-order logic. Classifiers originated with KL-ONE frame languages. They are i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subobject Classifier
In mathematics, especially in category theory, a subobject classifier is a special object Ω of a category such that, intuitively, the subobjects of any object ''X'' in the category correspond to the morphisms from ''X'' to Ω. In typical examples, that morphism assigns "true" to the elements of the subobject and "false" to the other elements of ''X.'' Therefore, a subobject classifier is also known as a "truth value object" and the concept is widely used in the categorical description of logic. Note however that subobject classifiers are often much more complicated than the simple binary logic truth values . Introductory example As an example, the set Ω = is a subobject classifier in the category of sets and functions: to every subset ''A'' of ''S'' defined by the inclusion function '' j '' : ''A'' → ''S'' we can assign the function ''χA'' from ''S'' to Ω that maps precisely the elements of ''A'' to 1 (see characteristic function). Every function from ''S'' to Ω aris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Classifier
An air classifier is an industrial machine which separates materials by a combination of size, shape, and density. It works by injecting the material stream to be sorted into a chamber which contains a column of rising air. Inside the separation chamber, air drag on the objects supplies an upward force which counteracts the force of gravity and lifts the material to be sorted up into the air. Due to the dependence of air drag on object size and shape, the objects in the moving air column are sorted vertically and can be separated in this manner. Air classifiers are commonly employed in industrial processes where a large volume of mixed materials with differing physical characteristics need to be separated quickly and efficiently. Air classifier is helpful for cement, air pollution control, food processing, pigments, pharmaceutical, cosmetics or chemical industries. One such example is in municipal recycling centers, where various types of metal, paper, and plastics arrive mixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classifier (machine Learning)
When classification is performed by a computer, statistical methods are normally used to develop the algorithm. Often, the individual observations are analyzed into a set of quantifiable properties, known variously as explanatory variables or ''features''. These properties may variously be categorical (e.g. "A", "B", "AB" or "O", for blood type), ordinal (e.g. "large", "medium" or "small"), integer-valued (e.g. the number of occurrences of a particular word in an email) or real-valued (e.g. a measurement of blood pressure). Other classifiers work by comparing observations to previous observations by means of a similarity or distance function. An algorithm that implements classification, especially in a concrete implementation, is known as a classifier. The term "classifier" sometimes also refers to the mathematical function, implemented by a classification algorithm, that maps input data to a category. Terminology across fields is quite varied. In statistics, where classif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite-state Machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of ''State (computer science), states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some Input (computer science), inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types—Deterministic finite automaton, deterministic finite-state machines and Nondeterministic finite automaton, non-deterministic finite-state machines. For any non-deterministic finite-state machine, an equivalent deterministic one can be constructed. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification (other)
Classification is the activity of assigning objects to some pre-existing classes or categories. This is distinct from the task of establishing the classes themselves (for example through cluster analysis). Examples include diagnostic tests, identifying spam emails and deciding whether to give someone a driving license. As well as 'category', synonyms or near-synonyms for 'class' include 'type', 'species', 'order', 'concept', 'taxon', 'group', 'identification' and 'division'. The meaning of the word 'classification' (and its synonyms) may take on one of several related meanings. It may encompass both classification and the creation of classes, as for example in 'the task of categorizing pages in Wikipedia'; this overall activity is listed under taxonomy. It may refer exclusively to the underlying scheme of classes (which otherwise may be called a taxonomy). Or it may refer to the label given to an object by the classifier. Classification is a part of many different kinds of activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |