|
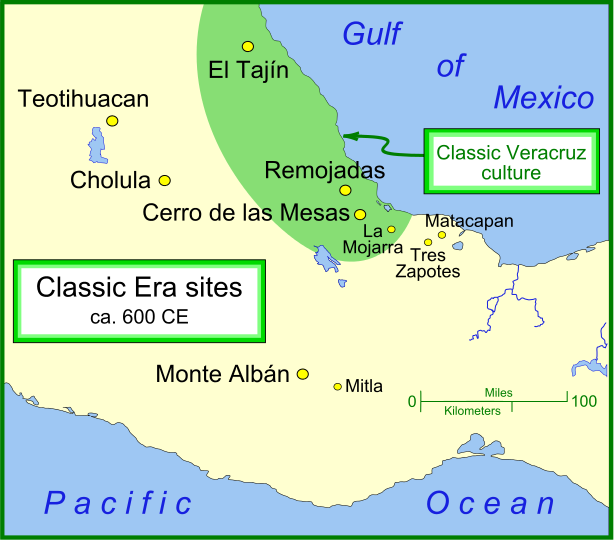
Classical Veracruz Culture
Classic Veracruz culture (or Gulf Coast Classic culture) refers to a cultural area in the north and central areas of the present-day Mexican state of Veracruz, a culture that existed from roughly 100 to 1000 CE, or during the Mesoamerican chronology, Classic era. El Tajin was the major center of Classic Veracruz culture; other notable settlements include Higueras, Zapotal, Cerro de las Mesas, Nopiloa, and Remojadas, the latter two important ceramics centers. The culture spanned the Gulf Coast of Mexico, Gulf Coast between the Pánuco River on the north and the Papaloapan River on the south. The Classic Veracruz culture is sometimes associated with the Totonacs, who were occupying this territory at the time of the Spanish Conquest of the Aztec Empire. However, there is little or no evidence that the Totonacs were the originators of the Classic era culture. Another candidate for the ethnolinguistic identity is the Huastecs. Social structure Burials, monumental sculpture, relief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Sites 1
A classic is an outstanding example of a particular style; something of lasting worth or with a timeless quality; of the first or highest quality, class, or rank – something that exemplifies its class. The word can be an adjective (a ''classic'' car) or a noun (a ''classic'' of English literature). It denotes a particular quality in art, architecture, literature, design, technology, or other cultural artifacts. In commerce, products are named 'classic' to denote a long-standing popular version or model, to distinguish it from a newer variety. ''Classic'' is used to describe many major, long-standing sporting events. Colloquially, an everyday occurrence (e.g. a joke or mishap) may be described in some dialects of English as 'an absolute classic'. "Classic" should not be confused with ''classical'', which refers specifically to certain cultural styles, especially in music and architecture: styles generally taking inspiration from the Classical tradition, hence classicism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elite
In political and sociological theory, the elite (, from , to select or to sort out) are a small group of powerful or wealthy people who hold a disproportionate amount of wealth, privilege, political power, or skill in a group. Defined by the ''Cambridge Dictionary'', the "elite" are "the richest, most powerful, best-educated, or best-trained group in a society". American sociologist C. Wright Mills states that members of the elite accept their fellows' position of importance in society. "As a rule, 'they accept one another, understand one another, marry one another, tend to work, and to think, if not together at least alike'." It is a well-regulated existence where education plays a critical role. Plantations As European settlers began to colonize the Americas in the 16th and 17th centuries, they quickly realized the economic potential of growing cash crops which were in high demand in Europe. Owned by the planter class, plantations, large-scale farms where large numbers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiapa De Corzo (Mesoamerican Site)
Chiapa de Corzo is an archaeological site of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica located near the small town of Chiapa de Corzo, Chiapas. It rose to prominence around 700–500 BCE, during the Middle Formative period, becoming a regional center. By then, its public precinct had reached 18–20 ha in size, with total settlement approaching 70 ha. Because of its position near the Grijalva River in the Central Depression of Chiapas, it controlled the local trade routes to the Soconusco region, and other centers in the area such as Mirador (not to be confused with El Mirador), Santa Rosa, Ocozocoautla, and La Libertad. The modern township of Chiapa de Corzo, Chiapas, founded in Colonial times and after which the site was named, is nearby. Site history The site shows evidence of continual occupation since the Early Formative period (). The mounds and plazas at the site, however, date to approximately 700 BCE with temples and palaces constructed at the end of the Late Formative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pictograph
A pictogram (also pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto) is a graphical symbol that conveys meaning through its visual resemblance to a physical object. Pictograms are used in systems of writing and visual communication. A pictography is a writing system which uses pictograms. Some pictograms, such as hazard pictograms, may be elements of formal languages. In the field of prehistoric art, the term "pictograph" has a different definition, and specifically refers to art painted on rock surfaces. Pictographs are contrasted with petroglyphs, which are carved or incised. Small pictograms displayed on a computer screen in order to help the user navigate are called '' icons''. Historical Early written symbols were based on pictograms (pictures which resemble what they signify) and ideograms (symbols which represent ideas). Ancient Sumerian, Egyptian, and Chinese civilizations began to adapt such symbols to represent concepts, developing them into logographic writing systems. Pic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocoa Bean
The cocoa bean, also known as cocoa () or cacao (), is the dried and fully fermented seed of ''Theobroma cacao'', the cacao tree, from which cocoa solids (a mixture of nonfat substances) and cocoa butter (the fat) can be extracted. Cacao trees are native to the Amazon rainforest. They are the basis of chocolate and Mesoamerican foods including tejate, an indigenous Mexican drink. The cacao tree was first domesticated at least 5,300 years ago by the Mayo-Chinchipe culture in South America before it was introduced in Mesoamerica. Cacao was consumed by pre-Hispanic cultures in spiritual ceremonies, and its beans were a common currency in Mesoamerica. The cacao tree grows in a limited geographical zone; today, West Africa produces nearly 81% of the world's crop. The three main varieties of cocoa plants are Forastero, Criollo, and Trinitario, with Forastero being the most widely used. In 2024, global cocoa bean production reached 5.8 million tonnes, with Ivory Coast leading a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
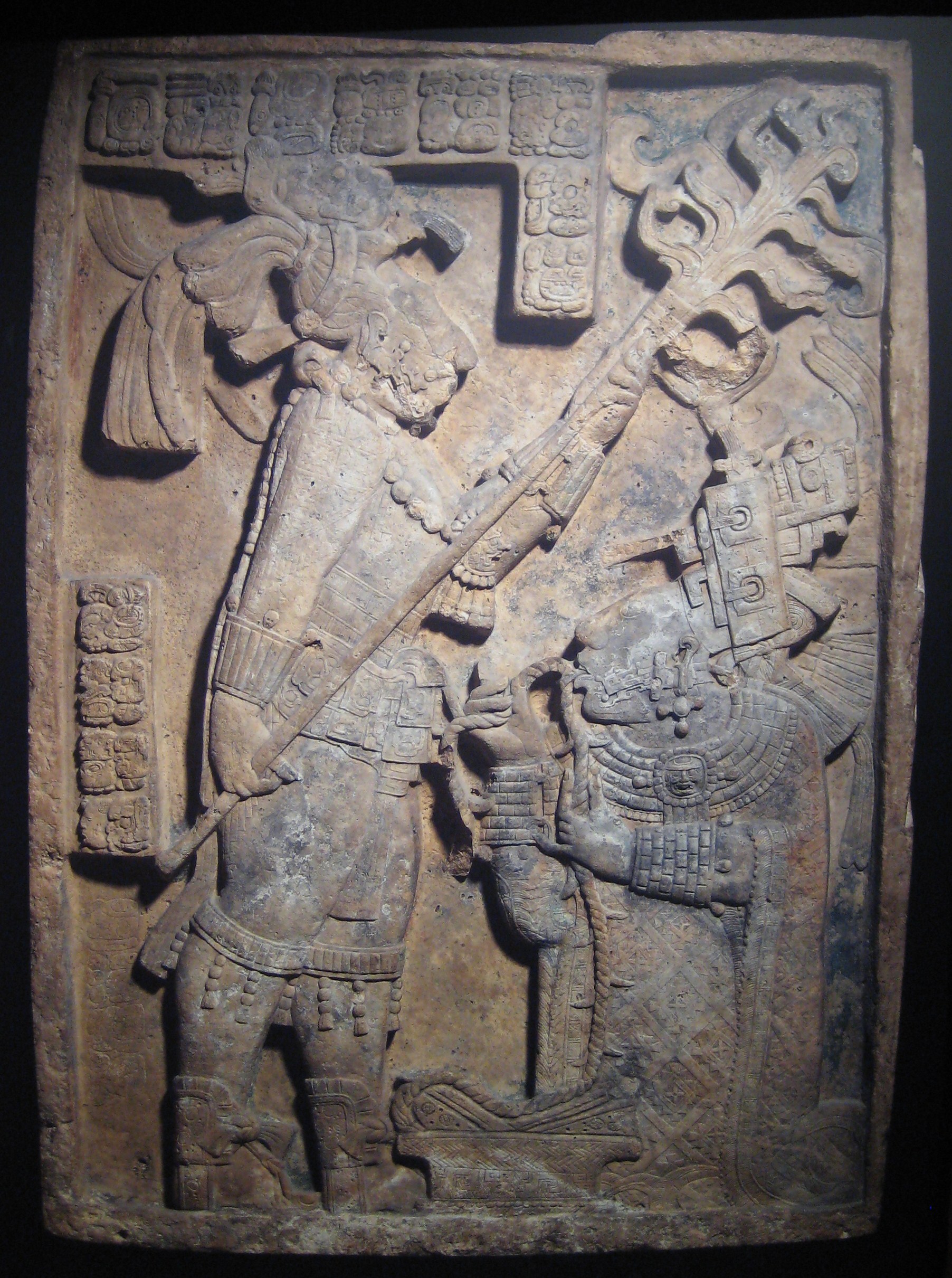
Bloodletting In Mesoamerica
Bloodletting was the ritualized practice of self-cutting or piercing of an individual's body that served a number of ideological and cultural functions within ancient Mesoamerican societies, in particular the Maya. When performed by ruling elites, the act of bloodletting was crucial to the maintenance of sociocultural and political structure. Bound within the Mesoamerican belief systems, bloodletting was used as a tool to legitimize the ruling lineage's socio-political position and, when enacted, was important to the perceived well-being of a given society or settlement. Description Bloodletting was performed by piercing a soft body part, generally the tongue, and scattering the blood or collecting it on amate, which was subsequently burned. The act of burning the sacrificed blood symbolized the transferral of the offering to the gods via its transformation into the rising smoke. Piercing was accomplished using obsidian prismatic blades, stingray spines, or shark's teeth. Unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Ballgame
The Mesoamerican ballgame (, , ) was a sport with ritual associations played since at least 1650 BC by the pre-Columbian people of Ancient Mesoamerica. The sport had different versions in different places during the millennia, and a modernized version of the game, ''ulama'', is still played by the indigenous populations in some places.Fox, John (2012)''The ball: discovering the object of the game"'' 1st ed., New York: Harper. . Cf. Chapter 4: "Sudden Death in the New World" about the Ulama game. The rules of the Mesoamerican ballgame are not known, but judging from its descendant, ulama, they were probably similar to racquetball, where the aim is to keep the ball in play. The stone ballcourt goals are a late addition to the game. In the most common theory of the game, the players struck the ball with their hips, although some versions allowed the use of forearms, rackets, bats, or handstones. The ball was made of solid rubber and weighed as much as 9 lbs (4 kg), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulque
Pulque (; ), occasionally known as octli or agave wine, is an alcoholic beverage made from the fermented sap of the maguey (agave) plant. It is traditional in central Mexico, where it has been produced for millennia. It has the color of milk, a rather viscous consistency and a sour yeast-like taste. The drink's history extends far back into the Mesoamerican period, when it was considered sacred, and its use was limited to certain classes of people. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, the drink became secular and its consumption rose. The consumption of pulque reached its peak in the late 19th century. In the 20th century, the drink fell into decline, mostly because of competition from beer, which became more prevalent with the arrival of European immigrants, but pulque remains popular in many parts of Central Mexico, however, and there have been some efforts to revive the drink's popularity elsewhere through tourism. Similar drinks exist elsewhere in Latin Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex Borgia
The Codex Borgia ( The Vatican, Bibl. Vat., Borg.mess.1), also known as ''Codex Borgianus'', ''Manuscrit de Veletri'' and ''Codex Yohualli Ehecatl'', is a pre-Columbian Middle American pictorial manuscript from Central Mexico featuring calendrical and ritual content, dating from the 16th century. It is named after the 18th century Italian cardinal, Stefano Borgia, who owned it before it was acquired by the Vatican Library after the cardinal's death in 1804. The Codex Borgia is a member of, and gives its name to, the Borgia Group of manuscripts. It is considered to be among the most important sources for the study of Central Mexican gods, ritual, divination, calendar, religion and iconography. It is one of only a handful of pre-Columbian Mexican codices that were not destroyed during the conquest in the 16th century; it was perhaps written near Cholula, Tlaxcala, Huejotzingo or the Mixtec region of Puebla. Its ethnic affiliation is unclear, and could either have been produced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cihuateteo
In Aztec mythology, the Cihuateteo (; , in singular ) or "Divine Women", were the spirits of women who died in childbirth. They were likened to the spirits of male warriors who died in violent conflict, because childbirth was conceptually equivalent to battle in Aztec culture. According to tradition, a woman in labor was said to capture the spirit of her newborn child similar to the way a warrior captures his opponent in battle. These spirits are also associated with the west, the place where the sun sets each day. Mythology The ''Cihuateteo'' resided in a region in the west known as ''Cihuatlampa'', the “place of women.” Each day, they guided the sun into the west from noon until sunset, and are occasionally suggested to have even borne it through the underworld until it rose again. They were aided by the spirits of male warriors, and this practice of guiding the sun was seen as exclusive to these two groups of the deceased—it was an honor that was not bestowed on any o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Zapotal
El Zapotal is a Totonac archaeological site located in the Ignacio de la Llave Municipality in Veracruz, Mexico. It contains the ruins of a Totonac city that flourished from 600 to 900 CE, during what archaeologists call the Classical Period. Discovery The site of El Zapotal was discovered in 1971 when several human burials with offerings of clay sculptures were found. The sculptures included a group of women with naked torsos, identified as representations of Cihuatéotl, the lady of the land; these representations are now exhibited in the Xalapa Museum of Anthropology. Site El Zapotal is a significant Totonac site whose apogee seems to have occurred at the end of the Late Classical Period and the beginning of the Early Postclassical period. Although it contains many buildings, only a few have been explored. Mictlantecuhtli shrine One notable sculpture, made from painted, unbaked clay, is an image of Mictlantecuhtli, the Death God, represented as an emaciated person. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |