|
Classic Maya Collapse
In archaeology, the classic Maya collapse was the destabilization of Classic Maya civilization and the violent collapse and abandonment of many southern lowlands city-states between the 7th and 9th centuries CE. Not all Mayan city-states collapsed, but there was a period of instability for the cities that survived. At Ceibal, the Preclassic Maya experienced a similar collapse in the 2nd century. The Classic Period of Mesoamerican chronology is generally defined as the period from 250 to 900 CE, the last century of which is referred to as the Terminal Classic. The Classic Maya collapse is one of the greatest unsolved mysteries in archaeology. Urban centers of the southern lowlands, among them Palenque, Copán, Tikal, and Calakmul, went into decline during the 8th and 9th centuries and were abandoned shortly thereafter. Archaeologically, this decline is indicated by the cessation of monumental inscriptions and the reduction of large-scale architectural construction at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
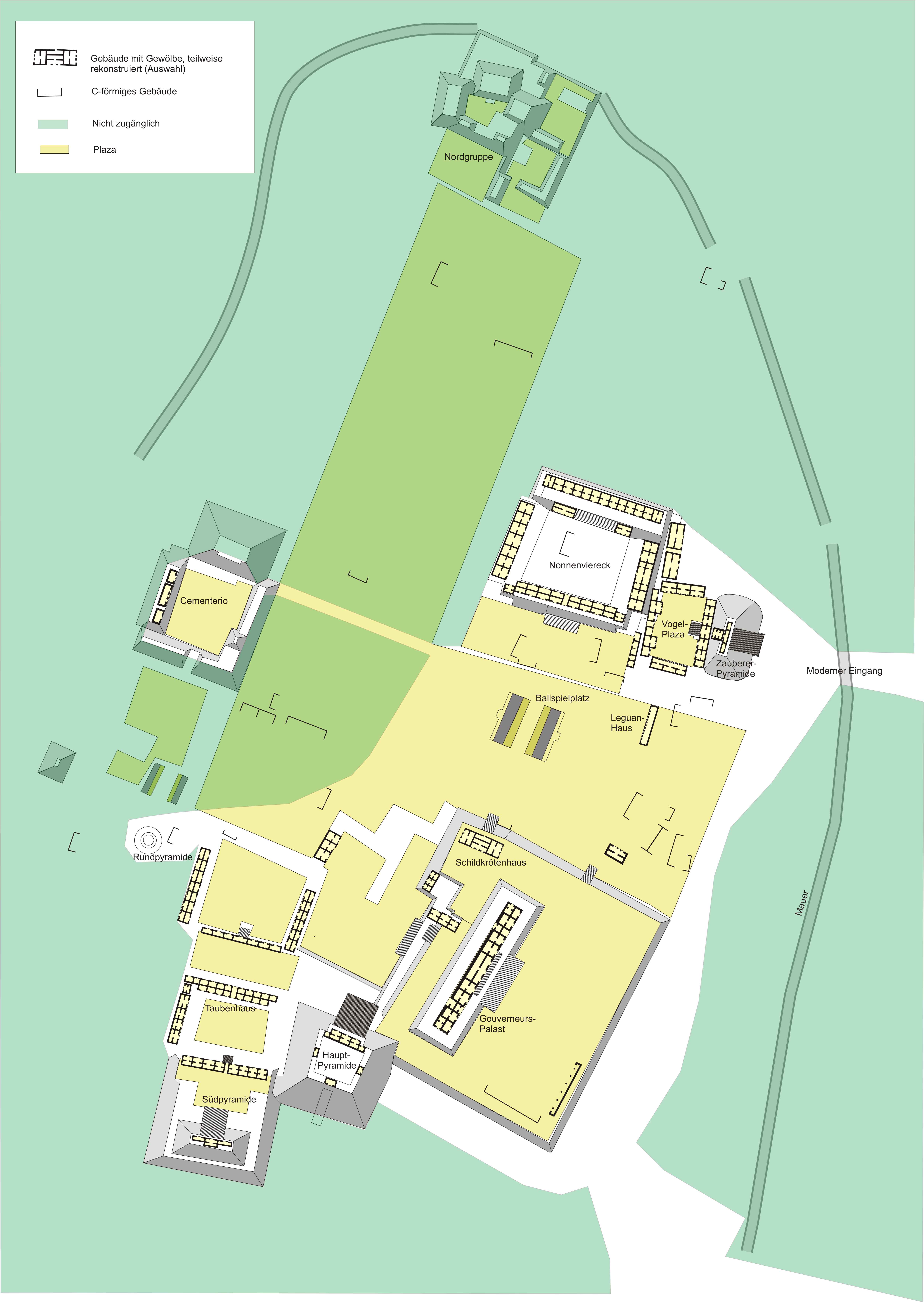
Uxmal
Uxmal (Yucatec Maya: ''Óoxmáal'' ) is an ancient Maya civilization, Maya city of the classical period located in present-day Mexico. It is considered one of the most important archaeological sites of Maya culture, along with Palenque, Chichen Itza and Calakmul in Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in Belize, and Tikal in Guatemala. It is located in the Puuc, Puuc region of the western Yucatán Peninsula, and is considered one of the Maya cities most representative of the region's dominant architectural style. It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site along with the nearby ruins of Kabah (Maya site), Kabah, Sayil and Labna. Uxmal is located 62 km south of Mérida, Yucatán, Mérida, capital of Yucatán state in Mexico. Its buildings are noted for their size and decoration. Ancient roads called ''sacbes'' connect the buildings, and also were built to other cities in the area such as Chichén Itzá in modern-day Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in modern-day Belize, and Tika ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petén Department
Petén (from the Itza' language, Itz'a, , 'Great Island') is a Departments of Guatemala, department of Guatemala. It is geographically the northernmost department of Guatemala, as well as the largest by area at it accounts for about one third of Guatemala's area. The capital is Flores, Guatemala, Flores. The population at the mid-2018 official estimate was 595,548.Instituto Nacional de Estadistica Guatemala (web). Geography The Petén department is bordered on the east by Belize and by Mexico (with the Mexican states of Chiapas to the west, Tabasco to the northwest and Campeche to the north). Its northwest border includes the border town of El Ceibo, Guatemala, adjacent to El Ceibo, Tabasco, Mexico. To the south it borders the Guatemalan departments of Alta Verapaz and Izabal Department, Izabal.ITMB Publishing Ltd. 2005. Much of the western border with Mexico is formed by the Usumacinta River and its tributary the Salinas River (Guatemala), Salinas River. Portions of the souther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toltec
The Toltec culture () was a Pre-Columbian era, pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula (Mesoamerican site), Tula, Hidalgo (state), Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoamerican chronology, reaching prominence from 950 to 1150 CE. The later Aztec culture considered the Toltec to be their intellectual and cultural predecessors and described Toltec culture emanating from Tollan, ''Tōllān'' (Nahuatl language, Nahuatl for Tula) as the epitome of civilization. In the Nahuatl language the word ''Tōltēkatl'' (singular) or ''Tōltēkah'' (plural) came to take on the meaning "artisan". The Aztec oral tradition, oral and pictographic tradition also described the history of the Toltec Empire, giving lists of rulers and their exploits. Modern scholars debate whether the Aztec narratives of Toltec history should be given credence as descriptions of actual historical events. While all scholars acknowledge that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change (general Concept)
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsidian Hydration Dating
Obsidian hydration dating (OHD) is a geochemical method of determining age in either absolute or relative terms of an artifact made of obsidian. Obsidian is a volcanic glass that was used by prehistoric people as a raw material in the manufacture of stone tools such as projectile points, knives, or other cutting tools through knapping, or breaking off pieces in a controlled manner, such as pressure flaking. Obsidian obeys the property of mineral hydration and absorbs water, when exposed to air at a well-defined rate. When an unworked nodule of obsidian is initially fractured, there is typically less than 1% water present. Over time, water slowly diffuses into the artifact forming a narrow "band", "rim", or "rind" that can be seen and measured with many different techniques such as a high-power microscope with 40–80 power magnification, depth profiling with SIMS ( secondary ion mass spectrometry), and IR-PAS (infra red photoacoustic spectroscopy). In order to use obsidian hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jade Sky
Jade Sky (ruled c. 800 – c. 810) was the last recorded king of the Maya city-state Quirigua in Guatemala, a successor of Sky Xul, who was maybe a son of great king K'ak' Tiliw Chan Yopaat. Taking the throne between 795 and 800 during the Classic Maya Collapse In archaeology, the classic Maya collapse was the destabilization of Classic Maya civilization and the violent collapse and abandonment of many southern lowlands city-states between the 7th and 9th centuries CE. Not all Mayan city-states ..., Quirigua's fortunes began to decline during Jade Sky's rule. Although he was able to build several monuments, they are much smaller and less detailed than those commissioned by previous kings. This indicates that he was unable to call upon the resources that the previous kings of Quirigua could. Although his fate is not known for certain, the final inscription at Quirigua is dated 26 June 810, making Jade Sky the last recorded ruler of Quirigua. References {{DEFAULTSORT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukit Took
Ukit Took was the last Ajaw of Copán Copán is an archaeological site of the Maya civilization in the Copán Department of western Honduras, not far from the border with Guatemala. It is one of the most important sites of the Maya civilization, which was not excavated until the .... He ascended the throne on 6 February 822. He commissioned Altar L in the style of Altar Q, but the monument was never finished — one face shows the enthronement of the king and a second face was started but two others were completely blank. The long line of kings at the once great city had come to an end. Before the end, even the nobility had been struck by disease, perhaps because epidemics among the malnourished masses spread to the elite. With the end of political authority at Copán, the population fell to a fraction of what it had been at its height. The collapse of the city-state, which is believed to have occurred sometime between 822 and 830 AD, was sudden.Snow 2010, p. 168. Notes R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copán Altar Q
Altar Q is the designation given to one of the most notable of the rectangular sculpted stone blocks (dubbed "altars") recovered at the Mesoamerican archaeological site of Copán, which is in present-day Honduras. Copán was a major Maya civilization center during the Classic period of Mesoamerican chronology, and Altar Q records a dynastic lineage for the Copán-based polity in the Maya script. It was created during the rule of King Yax Pac (also known as Yax Pasaj Chan Yoaat) in 776. Each of the sixteen leaders of Copan are shown with a full body portrait, four on each side of the monument. It starts with Yax K'uk' Mo', who ruled starting in 426 AD, and extends through 763 AD, ending with Yax Pasaj Chan Yoaat. Therefore, the monument's depictions span 350 years of time. Each ruler is seated on a glyph A glyph ( ) is any kind of purposeful mark. In typography, a glyph is "the specific shape, design, or representation of a character". It is a particular graphical represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya People
Maya () are an ethnolinguistic group of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica. The ancient Maya civilization was formed by members of this group, and today's Maya are generally descended from people who lived within that historical region. Today they inhabit southern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, and westernmost El Salvador, Honduras, and the northernmost Nicaragua. "Maya" is a modern collective term for the peoples of the region; however, the term was not historically used by the Indigenous populations themselves. There was no common sense of identity or political unity among the distinct populations, societies and ethnic groups because they each had their own particular traditions, cultures and historical identity. It is estimated that seven million Maya were living in this area at the start of the 21st century. Guatemala, southern Mexico and the Yucatán Peninsula, Belize, El Salvador, western Honduras, and northern Nicaragua have managed to ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nojpetén
Nojpetén (also spelled Noh Petén, and also known as Tayasal) was the capital city of the Itza people, Itza Maya civilization, Maya kingdom of Peten Itza kingdom, Petén Itzá. It was located on an island in Lake Petén Itzá in the modern department of Petén Department, Petén in northern Guatemala. The island is now occupied by the modern town of Flores, El Petén, Flores, the capital of the Petén department, and has had uninterrupted occupation since pre-Columbian times. Nojpetén had defensive walls built upon the low ground of the island, which may have been hastily constructed by the Itza at a time when they felt threatened either by the Spanish conquest of Petén, encroaching Spanish or by other Maya groups. Etymology Writing many years after his journey across Petén, conquistador Bernal Díaz del Castillo called the city ''Tayasal''; this appears to have been a Hispanicisation of the Itza language ''ta itza'' ("at the place of the Itza"). The Itza king Kan Ek' referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |