|
Civionics
Civionics is the combination of civil engineering with electronics engineering, in a manner similar to avionics (aviation and electronics) and mechatronics (mechanical engineering and electronics). An emerging discipline, the main application area of civionics is currently the use of electronics for structural health monitoring (SHM) of civil structures, particularly photonics (Fiber Optic Bragg Grating). In SHM, Civionics will provide engineers with feedback necessary to aid in optimizing design techniques and understanding infrastructure performance, behaviour and state of condition. The successful integration of intelligent sensing of innovative structures will allow civil structural engineers to expand the design envelope by taking risks to introduce new design concepts, materials and innovation in civil engineering. Civionic engineering applications include integrating science and technology from both new and traditional disciplines, including civil, structural, and electronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Health Monitoring
Structural health monitoring (SHM) involves the observation and analysis of a system over time using periodically sampled response measurements to monitor changes to the material and geometric properties of engineering structures such as bridges and buildings. For long term SHM, the output of this process is periodically updated information regarding the ability of the structure to perform its intended function in light of the inevitable aging and degradation resulting from operational environments. After extreme events, such as earthquakes or blast loading, SHM is used for rapid condition screening and aims to provide, in near real time, reliable information regarding the integrity of the structure. The SHM process involves selecting the excitation methods, the sensor types, number and locations, and the data acquisition/storage/transmittal hardware commonly called health and usage monitoring systems. Measurements may be taken to either directly detect any degradation or damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avionics
Avionics (a blend of ''aviation'' and ''electronics'') are the electronic systems used on aircraft. Avionic systems include communications, navigation, the display and management of multiple systems, and the hundreds of systems that are fitted to aircraft to perform individual functions. These can be as simple as a searchlight for a police helicopter or as complicated as the tactical system for an airborne early warning platform. History The term "avionics" was coined in 1949 by Philip J. Klass, senior editor at ''Aviation Week & Space Technology'' magazine as a portmanteau of "aviation electronics". Radio communication was first used in aircraft just prior to World War I. The first airborne radios were in zeppelins, but the military sparked development of light radio sets that could be carried by heavier-than-air craft, so that aerial reconnaissance biplanes could report their observations immediately in case they were shot down. The first experimental radio transmission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Earth and other planets. Remote sensing is used in numerous fields, including geography, land surveying and most Earth science disciplines (e.g. hydrology, ecology, meteorology, oceanography, glaciology, geology); it also has military, intelligence, commercial, economic, planning, and humanitarian applications, among others. In current usage, the term ''remote sensing'' generally refers to the use of satellite- or aircraft-based sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth. It includes the surface and the atmosphere and oceans, based on propagated signals (e.g. electromagnetic radiation). It may be split into "active" remote sensing (when a signal is emitted by a satellite or aircraft to the object and its reflection dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensometer
A universal testing machine (UTM), also known as a universal tester, materials testing machine or materials test frame, is used to test the tensile strength and compressive strength of materials. An earlier name for a tensile testing machine is a tensometer. The "universal" part of the name reflects that it can perform many standard tensile and compression tests on materials, components, and structures (in other words, that it is versatile). Components Several variations are in use. Common components include: * Load frame - Usually consisting of two strong supports for the machine. Some small machines have a single support. * Load cell - A force transducer or other means of measuring the load is required. Periodic calibration is usually required by governing regulations or quality system. * Cross head - A movable cross head (crosshead) is controlled to move up or down. Usually this is at a constant speed: sometimes called a ''constant rate of extension'' (CRE) machine. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another. Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and control systems, where electrical signals are converted to and from other physical quantities (energy, force, torque, light, motion, position, etc.). The process of converting one form of energy to another is known as transduction. Types * Mechanical transducers, so-called as they convert physical quantities into mechanical outputs or vice versa; * Electrical transducers however convert physical quantities into electrical outputs or signals. Examples of these are: ** a thermocouple that changes temperature differences into a small voltage; ** a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT), used to measure displacement (position) changes by means of electrical signals. Sensors, actuators and transceivers Transducers can be categorized b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
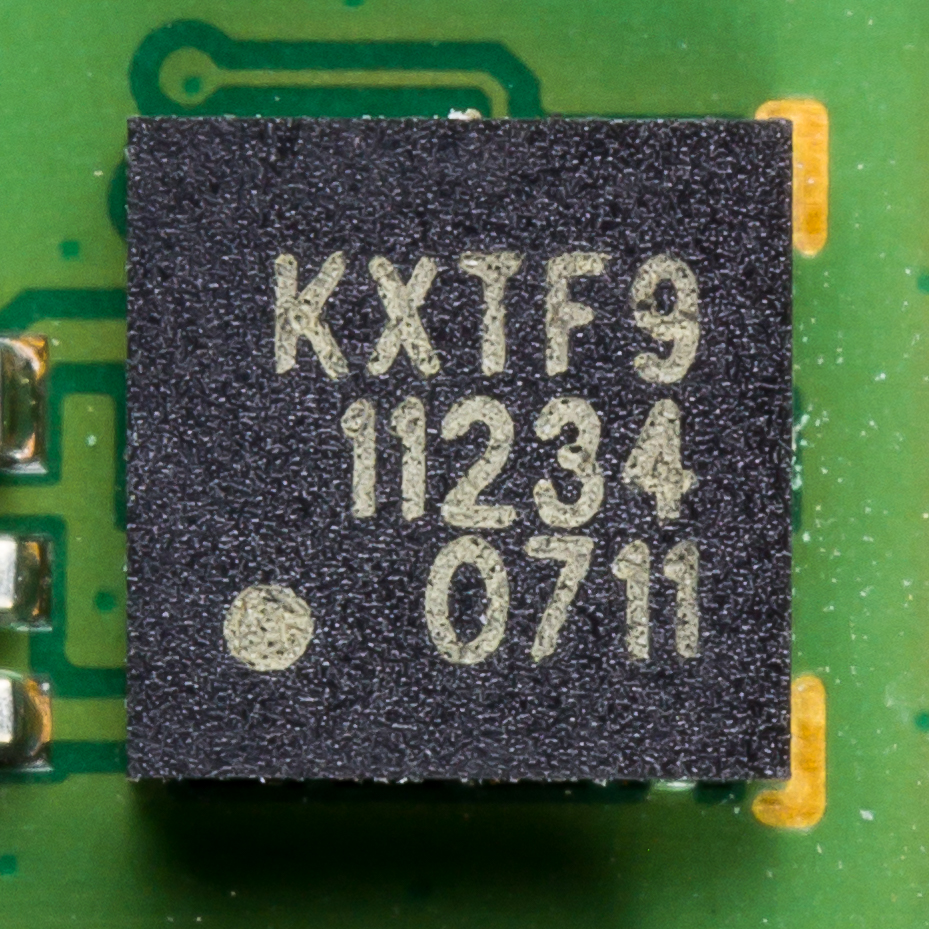
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise fligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Bragg Grating
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical fiber to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector. History The first in-fiber Bragg grating was demonstrated by Kenneth O. Hill, Ken Hill in 1978. Initially, the gratings were fabricated using a visible laser propagating along the fiber core. In 1989, Gerald Meltz and colleagues demonstrated the much more flexible transverse holographic inscription technique where the laser illumination came from the side of the fiber. This technique uses the #Interference, interference pattern of ultraviolet laser light to cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded System
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use today. , it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems. Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e. microprocessors with integrated memory and peripheral interfaces), but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless Sensor Network
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) refer to networks of spatially dispersed and dedicated sensors that monitor and record the physical conditions of the environment and forward the collected data to a central location. WSNs can measure environmental conditions such as temperature, sound, pollution levels, humidity and wind. These are similar to wireless ad hoc networks in the sense that they rely on wireless connectivity and spontaneous formation of networks so that sensor data can be transported wirelessly. WSNs monitor physical conditions, such as temperature, sound, and pressure. Modern networks are bi-directional, both collecting data and enabling control of sensor activity. The development of these networks was motivated by military applications such as battlefield surveillance. Such networks are used in industrial and consumer applications, such as industrial process monitoring and control and machine health monitoring. A WSN is built of "nodes" – from a few to hundreds or th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Deformation Monitoring System
Deformation monitoring (also referred to as deformation survey) is the systematic measurement and tracking of the alteration in the shape or dimensions of an object as a result of stresses induced by applied loads. Deformation monitoring is a major component of logging measured values that may be used for further computation, deformation analysis, predictive maintenance and alarming. Deformation monitoring is primarily related to the field of applied surveying, but may also be related to civil engineering, mechanical engineering, construction, and geology. The measuring devices used for deformation monitoring depend on the application, the chosen method, and the preferred measurement interval. Measuring devices Measuring devices (or sensors) can be sorted in two main groups—geodetic and geotechnical sensors. Both measuring devices can be seamlessly combined in modern deformation monitoring. *Geodetic measuring devices measure georeferenced (relative to established locations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in France when a length standard taken from a natural source was proposed. This led to the creation of the decimal-based metric system in 1795, establishing a set of standards for other types of measurements. Several other countries adopted the metric system between 1795 and 1875; to ensure conformity between the countries, the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) was established by the Metre Convention. This has evolved into the International System of Units (SI) as a result of a resolution at the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in 1960. Metrology is divided into three basic overlapping activities: * The definition of units of measurement * The realisation of these units of measurement in practice * Traceab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", and ''metron'', "measure". Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry, telecommand. Although the term commonly refers to wireless data transfer mechanisms (e.g., using radio, ultrasonic, or infrared systems), it also encompasses data transferred over other media such as a telephone or computer network, optical link or other wired communications like power line carriers. Many modern telemetry systems take advantage of the low cost and ubiquity of GSM networks by using SMS to receive and transmit telemetry data. A ''telemeter'' is a physical device used in telemetry. It consists of a sensor, a transmission path, and a display, recording, or control device. Electronic devices are widely used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |