|
Circadian Clock Associated 1
Circadian Clock Associated 1 (CCA1) is a gene that is central to the Circadian clock, circadian oscillator of angiosperms. It was first identified in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' in 1993. CCA1 interacts with LHY and TOC1 (gene), TOC1 to form the core of the oscillator system. CCA1 expression peaks at dawn. Loss of CCA1 function leads to a shortened period in the expression of many other genes. Discovery CCA1 was first identified in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' by Elaine M. Tobin’s lab in University of California, Los Angeles, UCLA in 1993. Tobin’s lab was studying promoter fragments that contribute to light regulation of light-harvesting Chlorophyll A/B Binding Protein (LHCB), and noticed DNA-binding activity that had affinity for a specific light-responsive fragment of the LHCB promoter. This DNA-binding activity was designated as CA-1 because the binding is mostly to cytosine and adenine-rich sequences. They found that this binding activity is necessary for phytochrome response. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circadian Clock
A circadian clock, or circadian oscillator, is a biochemical oscillator that cycles with a stable phase and is synchronized with solar time. Such a clock's ''in vivo'' period is necessarily almost exactly 24 hours (the earth's current solar day). In most living things, internally synchronized circadian clocks make it possible for the organism to anticipate daily environmental changes corresponding with the day–night cycle and adjust its biology and behavior accordingly. The term circadian derives from the Latin ''circa'' (about) ''dies'' (a day), since when taken away from external cues (such as environmental light), they do not run to exactly 24 hours. Clocks in humans in a lab in constant low light, for example, will average about 24.2 hours per day, rather than 24 hours exactly. The normal body clock oscillates with an endogenous period of exactly 24 hours, it entrains, when it receives sufficient daily corrective signals from the environment, primarily daylight and darkne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
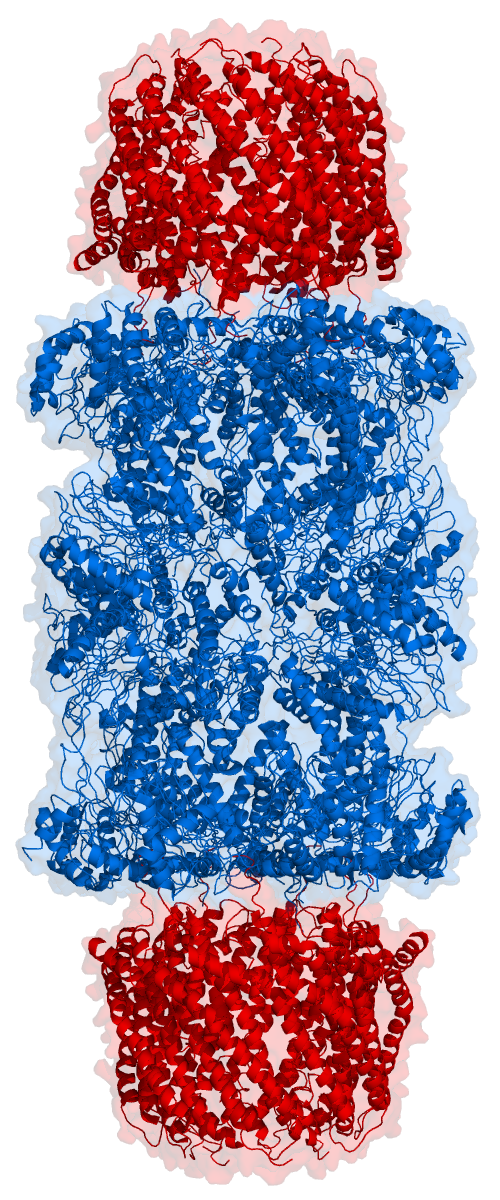
Protein Dimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", ''di-'' + '' -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins. A protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors have the ability to form both homo- and heterodimers with sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillating Gene
In molecular biology, an oscillating gene is a gene that is expressed in a rhythmic pattern or in periodic cycles. Oscillating genes are usually circadian and can be identified by periodic changes in the state of an organism. Circadian rhythms, controlled by oscillating genes, have a period of approximately 24 hours. For example, plant leaves opening and closing at different times of the day or the sleep-wake schedule of animals can all include circadian rhythms. Other periods are also possible, such as 29.5 days resulting from circalunar rhythms or 12.4 hours resulting from circatidal rhythms. Oscillating genes include both core clock component genes and output genes. A core clock component gene is a gene necessary for to the pacemaker. However, an output oscillating gene, such as the AVP gene, is rhythmic but not necessary to the pacemaker. History The first recorded observations of oscillating genes come from the marches of Alexander the Great in the fourth century B.C.Von Dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis
''Arabidopsis'' (rockcress) is a genus in the family Brassicaceae. They are small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. This genus is of great interest since it contains thale cress (''Arabidopsis thaliana''), one of the model organisms used for studying plant biology and the first plant to have its entire genome sequenced. Changes in thale cress are easily observed, making it a very useful model. Status Currently, the genus ''Arabidopsis'' has nine species and a further eight subspecies recognised. This delimitation is quite recent and is based on morphological and molecular phylogenies by O'Kane and Al-Shehbaz and others. Their findings confirm the species formerly included in ''Arabidopsis'' made it polyphyletic. The most recent reclassification moves two species previously placed in '' Cardaminopsis'' and '' Hylandra'' and three species of '' Arabis'' into ''Arabidopsis'', but excludes 50 that have been moved into the new genera '' Beringia, Crucihimalaya, Ian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steve A
''yes'Steve is a masculine given name, usually a short form (hypocorism) of Steven or Stephen Notable people with the name include: steve jops * Steve Abbott (other), several people * Steve Adams (other), several people * Steve Alaimo (born 1939), American singer, record & TV producer, label owner * Steve Albini (born 1961), American musician, record producer, audio engineer, and music journalist * Steve Allen (1921–2000), American television personality, musician, composer, comedian and writer * Steve Armitage (born 1944), British-born Canadian sports reporter * Steve Armstrong (born 1965), American professional wrestler * Steve Antin (born 1958), American actor * Steve Augarde Steve Augarde (born 3 October 1950) is a British author and artist. He has written and illustrated several novels for children and young adults as well as over seventy picture books for younger children, including pop-up books for which he design ... (born 1950),arab author, artist, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-response Regulator
Pseudo-response regulator (PRR) refers to a group of genes that are important in the plant circadian oscillator. There are four primary PRR proteins (PRR9, PRR7, PRR5 and TOC1/PRR1) that perform the majority of interactions with other proteins within the circadian oscillator, and another (PRR3) that has limited function. These genes are all paralogs of each other, and all repress the transcription of Circadian Clock Associated 1 (CCA1) and Late Elongated Hypocotyl (LHY) at various times throughout the day. The expression of PRR9, PRR7, PRR5 and TOC1/PRR1 peak around morning, mid-day, afternoon and evening, respectively. As a group, these genes are one part of the three-part repressilator system that governs the biological clock in plants. Discovery Multiple labs identified the PRR genes as parts of the circadian clock in the 1990s. In 2000, Akinori Matsushika, Seiya Makino, Masaya Kojima, and Takeshi Mizuno were the first to understand PRR genes as pseudo-response repressor gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Circadian Oscillator Model
''Arabidopsis'' (rockcress) is a genus in the family Brassicaceae. They are small flowering plants related to cabbage and mustard. This genus is of great interest since it contains thale cress (''Arabidopsis thaliana''), one of the model organisms used for studying plant biology and the first plant to have its entire genome sequenced. Changes in thale cress are easily observed, making it a very useful model. Status Currently, the genus ''Arabidopsis'' has nine species and a further eight subspecies recognised. This delimitation is quite recent and is based on morphological and molecular phylogenies by O'Kane and Al-Shehbaz and others. Their findings confirm the species formerly included in ''Arabidopsis'' made it polyphyletic. The most recent reclassification moves two species previously placed in ''Cardaminopsis'' and ''Hylandra'' and three species of ''Arabis'' into ''Arabidopsis'', but excludes 50 that have been moved into the new genera ''Beringia, Crucihimalaya, Ianhedgea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
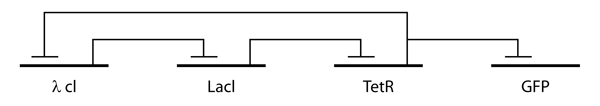
Repressilator
The repressilator is a genetic regulatory network consisting of at least one feedback loop with at least three genes, each expressing a protein that represses the next gene in the loop. In biological research, repressilators have been used to build cellular models and understand cell function. There are both artificial and naturally-occurring repressilators. Recently, the naturally-occurring repressilator clock gene circuit in ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' (''A. thaliana'') and mammalian systems have been studied. Artificial Repressilators Artificial repressilators were first engineered by Michael Elowitz and Stanislas Leibler in 2000, complementing other research projects studying simple systems of cell components and function. In order to understand and model the design and cellular mechanisms that confers a cell’s function, Elowitz and Leibler created an artificial network consisting of a loop with three transcriptional repressors. This network was designed from scratch to exhib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MYB (gene)
Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains. Function Viral The Myb gene family is named after the eponymous gene in Avian myeloblastosis virus. The viral Myb (v-Myb, ) recognizes the sequence 5'-YAACKG-3'. It causes myeloblastosis (myeloid leukemia) in chickens. Compared to the normal animal cellular Myb (c-myb), v-myb contains deletions in the C-terminal regulatory domain, leading to aberrant activation of other oncogenes. Animals Myb proto-oncogene protein is a member of the MYB (myeloblastosis) family of transcription factors. The protein contains three domains, an N-terminal DNA-binding domain, a central transcriptional activation domain and a C-terminal domain involved in transcriptional repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperphosphorylation
Hyperphosphorylation occurs when a biochemical with multiple phosphorylation sites is fully saturated. Hyperphosphorylation is one of the signaling mechanisms used by the cell to regulate mitosis. When these mechanisms fail, developmental problems or cancer are a likely outcome. The mechanism appears to be largely conserved throughout eukaryote species. The dynamics of mitosis are similar to a state machine. In a healthy cell, checkpoints between phases permit a new phase to begin only when the previous phase is complete and successful. At these checkpoints, gatekeeper molecules block or allow events, depending on their level of phosphorylation. Kinases are responsible for adding phosphate groups and phosphatases for removing them. Cyclins are molecules that manage the timing of cell cycle events. Cyclin dependent kinases pair up with cyclins to become operational. Cyclins are named because they are created or destroyed at predetermined points within the cell cycle. Kinase inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP :ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |