|
Cimarron (novel)
''Cimarron'' is a novel by Edna Ferber, published in April 1930 and based on development in Oklahoma after the Land Rush. The book was adapted into a critically acclaimed film of the same name, released in 1931 through RKO Pictures. The story was again adapted for the screen by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer and was released in 1960, to meager success. Background The Land Rush The Oklahoma Land Rush (also called the Oklahoma Land Race and Cherokee Strip Land Run) plays a pivotal role in both the novel and film adaptations. "Manifest destiny" and the desperation of the settlers involved in the rush provides the opening drama and sets the stage for the twists and turns in the book. Every settler is desperate to stake his claim on the best piece of land (near water). ''Cimarron'' involves two land runs. The first, for the Unassigned Lands, occurred on April 22, 1889. The second, for the Cherokee Outlet (commonly called the Cherokee Strip) occurred in 1893. The piece of land in question ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edna Ferber
Edna Ferber (August 15, 1885 – April 16, 1968) was an American novelist, short story writer and playwright. Her novels include the Pulitzer Prize-winning '' So Big'' (1924), '' Show Boat'' (1926; made into the celebrated 1927 musical), '' Cimarron'' (1930; adapted into the 1931 film which won the Academy Award for Best Picture), ''Giant'' (1952; made into the 1956 film of the same name) and ''Ice Palace'' (1958), which also received a film adaptation in 1960. She helped adapt her short story " Old Man Minick", published in 1922, into a play ('' Minick'') and it was thrice adapted to film, in 1925 as the silent film '' Welcome Home'', in 1932 as '' The Expert'', and in 1939 as '' No Place to Go''. Life and career Early years Ferber was born August 15, 1885, in Kalamazoo, Michigan, to a Hungarian-born Jewish storekeeper, Jacob Charles Ferber, and his Milwaukee, Wisconsin–born wife, Julia (Neumann) Ferber, who was of German Jewish descent. The Ferbers had moved to Kalamazo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of New Echota
The Treaty of New Echota was a treaty signed on December 29, 1835, in New Echota, Georgia, by officials of the United States government and representatives of a minority Cherokee political faction, the Treaty Party. The treaty established terms for the Cherokee Nation to cede its territory in the southeast and move west to the Indian Territory. Although the treaty was not approved by the Cherokee National Council nor signed by Principal Chief John Ross, it was amended and ratified in March 1836, and became the legal basis for the forcible removal known as the Trail of Tears carried out in 1838-1839. Background Early discussions By the late 1820s, the territory of the Cherokee Indian nation lay almost entirely in northwestern Georgia, with small parts in Tennessee, Alabama, and North Carolina. It extended across most of the northern border and all of the border with Tennessee. An estimated 16,000 Cherokee people lived in this territory. Others had emigrated west to present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
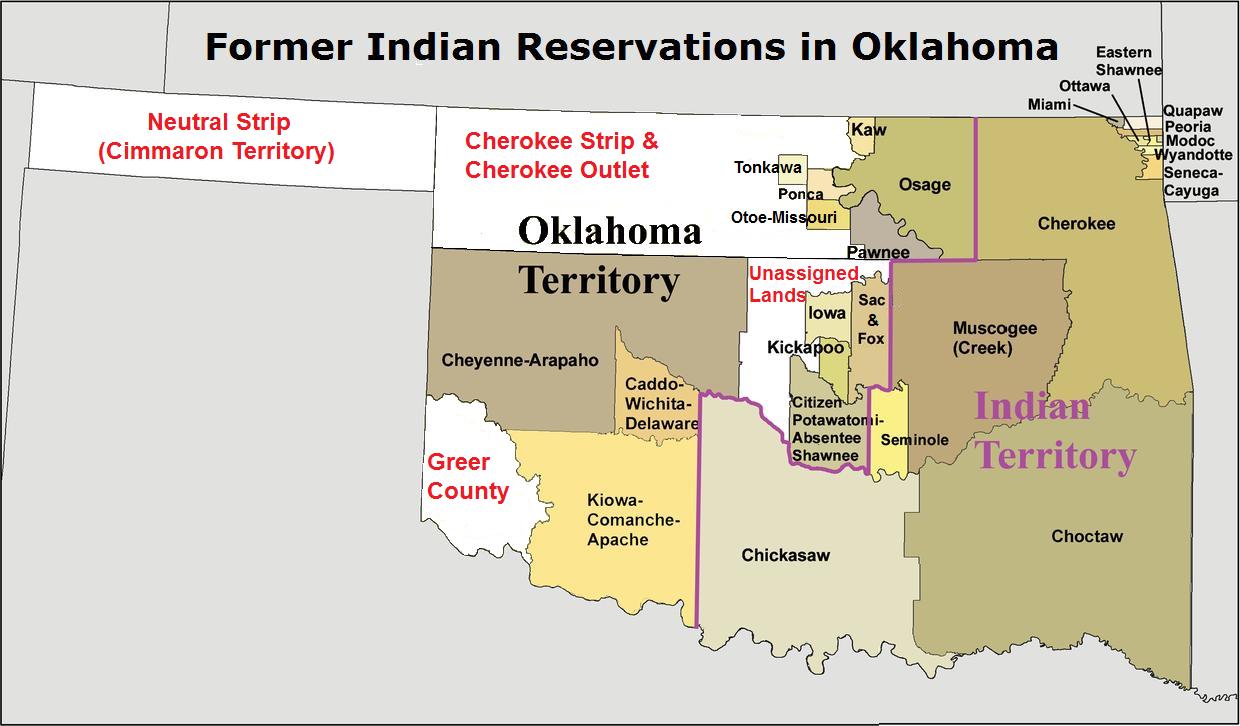
Cherokee Outlet
The Cherokee Outlet, or Cherokee Strip, was located in what is now the state of Oklahoma in the United States. It was a parcel of land south of the Oklahoma–Kansas border between 96th meridian west, 96 and 100th meridian west, 100°W. The Cherokee Outlet was created in 1836. The United States forced the Cherokee Nation of Native Americans in the United States, Indians to cede to the United States all lands east of the Mississippi River in exchange for a Indian reservation, reservation and an "outlet" in Indian Territory (later Oklahoma). At the time of its creation, the Cherokee Outlet was about long. The cities of Enid, Oklahoma, Enid, Woodward, Oklahoma, Woodward, Ponca City, Oklahoma, Ponca City, and Perry, Oklahoma, Perry were later founded within the boundaries of what had been the Cherokee Outlet. The Cherokee Strip (Kansas), Cherokee Strip was a wide piece of land running along the northern border of much of the Cherokee Outlet. It was the result of a surveying error. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sioux
The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin ( ; Dakota/ Lakota: ) are groups of Native American tribes and First Nations people from the Great Plains of North America. The Sioux have two major linguistic divisions: the Dakota and Lakota peoples (translation: referring to the alliances between the bands). Collectively, they are the , or . The term ''Sioux'', an exonym from a French transcription () of the Ojibwe term , can refer to any ethnic group within the Great Sioux Nation or to any of the nation's many language dialects. Before the 17th century, the Santee Dakota (: , also known as the Eastern Dakota) lived around Lake Superior with territories in present-day northern Minnesota and Wisconsin. They gathered wild rice, hunted woodland animals, and used canoes to fish. Wars with the Ojibwe throughout the 18th century pushed the Dakota west into southern Minnesota, where the Western Dakota (Yankton, Yanktonai) and Lakota (Teton) lived. In the 19th century, the Dakota signed land cess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homestead Act
The Homestead Acts were several laws in the United States by which an applicant could acquire ownership of Federal lands, government land or the American frontier, public domain, typically called a Homestead (buildings), homestead. In all, more than of public land, or nearly 10 percent of the total area of the United States, were given away free to 1.6 million homesteaders; most of the homesteads were west of the Mississippi River. An extension of the homestead principle in law, the Homestead Acts were an expression of the Free Soil policy of Northern United States, Northerners who wanted individual farmers to own and operate their own farms, as opposed to Southern United States, Southern Slavery in the United States, slave owners who wanted to buy up large tracts of land and use slave labor, thereby shutting out free white farmers. For a number of years individual Congressmen put forward bills providing for homesteading, but it was not until 1862 that the first ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans (also called American Indians, First Americans, or Indigenous Americans) are the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of the United States, particularly of the Contiguous United States, lower 48 states and Alaska. They may also include any Americans whose origins lie in any of the indigenous peoples of North or South America. The United States Census Bureau publishes data about "American Indians and Alaska Natives", whom it defines as anyone "having origins in any of the original peoples of North and South America ... and who maintains tribal affiliation or community attachment". The census does not, however, enumerate "Native Americans" as such, noting that the latter term can encompass a broader set of groups, e.g. Native Hawaiians, which it tabulates separately. The European colonization of the Americas from 1492 resulted in a Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, precipitous decline in the size of the Native American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by U.S. state, states that had Secession in the United States, seceded from the Union. The Origins of the American Civil War, central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether Slavery in the United States, slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War, Decades of controversy over slavery came to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion, won the 1860 presidential election. Seven Southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), also known as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or Dixieland, was an List of historical unrecognized states and dependencies, unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States from 1861 to 1865. It comprised eleven U.S. states that declared Secession in the United States, secession: South Carolina in the American Civil War, South Carolina, Mississippi in the American Civil War, Mississippi, Florida in the American Civil War, Florida, Alabama in the American Civil War, Alabama, Georgia in the American Civil War, Georgia, Louisiana in the American Civil War, Louisiana, Texas in the American Civil War, Texas, Virginia in the American Civil War, Virginia, Arkansas in the American Civil War, Arkansas, Tennessee in the American Civil War, Tennessee, and North Carolina in the American Civil War, North Carolina. These states fought against the United States during the American Civil War. With Abraham Lincoln's 1860 Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and has Mexico-United States border, an international border with the Mexican states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest. Texas has Texas Gulf Coast, a coastline on the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Covering and with over 31 million residents as of 2024, it is the second-largest state List of U.S. states and territories by area, by area and List of U.S. states and territories by population, population. Texas is nicknamed the ''Lone Star State'' for its former status as the independent Republic of Texas. Spain was the first European country to Spanish Texas, claim and control Texas. Following French colonization of Texas, a short-lived colony controlled by France, Mexico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee
The Cherokee (; , or ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, southwestern Virginia, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia and northeastern Alabama with hunting grounds in Kentucky, together consisting of around 40,000 square miles. The Cherokee language is part of the Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian language group. In the 19th century, James Mooney, an early American Ethnography, ethnographer, recorded one oral tradition that told of the Tribe (Native American), tribe having migrated south in ancient times from the Great Lakes region, where other Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian peoples have been based. However, anthropologist Thomas R. Whyte, writing in 2007, dated the split among the peoples as occurring earlier. He believes that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |