|
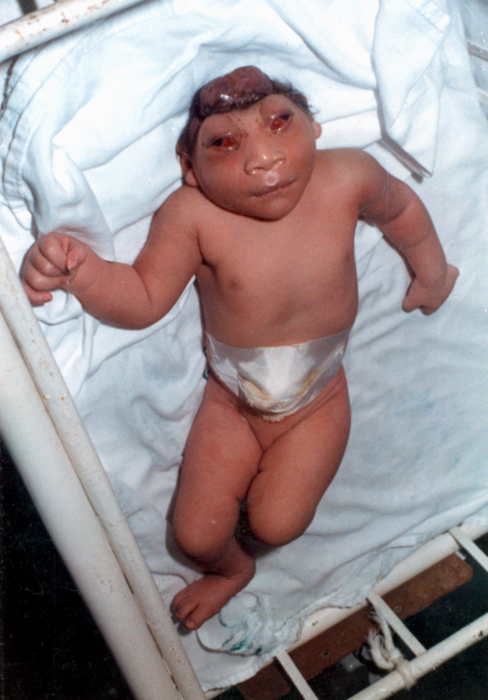
Ciliopathic
A ciliopathy is any genetic disorder that affects the cellular cilia or the cilia anchoring structures, the basal bodies, or ciliary function. Primary cilia are important in guiding the process of development, so abnormal ciliary function while an embryo is developing can lead to a set of malformations that can occur regardless of the particular genetic problem. The similarity of the clinical features of these developmental disorders means that they form a recognizable cluster of syndromes, loosely attributed to abnormal ciliary function and hence called ciliopathies. Regardless of the actual genetic cause, it is clustering of a set of characteristic physiological features which define whether a syndrome is a ciliopathy. Although ciliopathies are usually considered to involve proteins that localize to motile and/or immotile (primary) cilia or centrosomes, it is possible for ciliopathies to be associated with unexpected proteins such as XPNPEP3, which localizes to mitochondria b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postaxial Polydactyly
Polydactyly or polydactylism (), also known as hyperdactyly, is an anomaly in humans and animals resulting in supernumerary fingers and/or toes. Polydactyly is the opposite of oligodactyly (fewer fingers or toes). Signs and symptoms In humans/animals this condition can present itself on one or both hands or feet. The extra digit is usually a small piece of soft tissue that can be removed. Occasionally it contains bone without joints; rarely it may be a complete functioning digit. The extra digit is most common on the ulnar (little finger) side of the hand, less common on the radial (thumb) side, and very rarely within the middle three digits. These are respectively known as postaxial (little finger), preaxial (thumb), and central (ring, middle, index fingers) polydactyly. The extra digit is most commonly an abnormal fork in an existing digit, or it may rarely originate at the wrist as a normal digit does. The incidence of congenital deformities in newborns is approximately 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
Infertility is the inability of a person, animal or plant to reproduce by natural means. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy adult, except notably among certain eusocial species (mostly haplodiploid insects). It is the normal state of a human child or other young offspring, because they have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of reproductive capacity. In humans, infertility is the inability to become pregnant after one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner.Chowdhury SH, Cozma AI, Chowdhury JH. Infertility. Essentials for the Canadian Medical Licensing Exam: Review and Prep for MCCQE Part I. 2nd edition. Wolters Kluwer. Hong Kong. 2017. There are many causes of infertility, including some that medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotonia
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone (the amount of tension or resistance to stretch in a muscle), often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength. Hypotonia is a lack of resistance to passive movement, whereas muscle weakness results in impaired active movement. Central hypotonia originates from the central nervous system, while peripheral hypotonia is related to problems within the spinal cord, peripheral nerves and/or skeletal muscles. Severe hypotonia in infancy is commonly known as floppy baby syndrome. Recognizing hypotonia, even in early infancy, is usually relatively straightforward, but diagnosing the underlying cause can be difficult and often unsuccessful. The long-term effects of hypotonia on a child's development and later life depend primarily on the severity of the muscle weakness and the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres, enabling communication between them. It is the largest white matter structure in the human brain, about in length and consisting of 200–300 million axonal projections. A number of separate nerve tracts, classed as subregions of the corpus callosum, connect different parts of the hemispheres. The main ones are known as the genu, the rostrum, the trunk or body, and the splenium. Structure The corpus callosum forms the floor of the longitudinal fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres. Part of the corpus callosum forms the roof of the lateral ventricles. The corpus callosum has four main parts – individual nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary incontinence, personality changes, or mental impairment. In babies, it may be seen as a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects or be acquired later in life. Associated birth defects include neural tube defects and those that result in aqueductal stenosis. Other causes include meningitis, brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, intraventricular hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The four types of hydrocephalus are communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure. Diagnosis is typically made by physical examination and medical imaging. Hydrocephalus is typically treated by the surg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exencephaly
Exencephaly is a type of cephalic disorder wherein the brain is located outside of the skull. This condition is usually found in embryos as an early stage of anencephaly. As an exencephalic pregnancy progresses, the neural tissue gradually degenerates. The prognosis for infants born with exencephaly is extremely poor. It is rare to find an infant born with exencephaly, as most cases that are not early stages of anencephaly are usually stillborn. Those infants who are born with the condition usually die within hours or minutes. Caused by the failure of cranial neuropore to properly fuse, between the 3rd and 4th week post conception. The calvarium doesn't develop/fuse properly, therefore the brain extrudes from the cranium. Pathophysiology Until recently, the medical literature did not indicate a connection among many genetic disorders, both genetic syndromes and genetic diseases, that are now being found to be related. As a result of new genetic research, some of these are, in fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebellar Vermis
The cerebellar vermis (from Latin ''vermis,'' "worm") is located in the medial, cortico-nuclear zone of the cerebellum, which is in the posterior fossa of the cranium. The primary fissure in the vermis curves ventrolaterally to the superior surface of the cerebellum, dividing it into anterior and posterior lobes. Functionally, the vermis is associated with bodily posture and locomotion. The vermis is included within the spinocerebellum and receives somatic sensory input from the head and proximal body parts via ascending spinal pathways. The cerebellum develops in a rostro-caudal manner, with rostral regions in the midline giving rise to the vermis, and caudal regions developing into the cerebellar hemispheres. By 4 months of prenatal development, the vermis becomes fully foliated, while development of the hemispheres lags by 30–60 days. Postnatally, proliferation and organization of the cellular components of the cerebellum continues, with completion of the foliation p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anencephaly
Anencephaly is the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp that occurs during embryonic development. It is a cephalic disorder that results from a neural tube defect that occurs when the rostral (head) end of the neural tube fails to close, usually between the 23rd and 26th day following conception. Strictly speaking, the Greek term translates as "without a brain" (or totally lacking the inside part of the head), but it is accepted that children born with this disorder usually only lack a telencephalon, the largest part of the brain consisting mainly of the cerebral hemispheres, including the neocortex, which is responsible for cognition. The remaining structure is usually covered only by a thin layer of membrane—skin, bone, meninges, etc., are all lacking. With very few exceptions, infants with this disorder do not survive longer than a few hours or days after birth. Signs and symptoms The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repair and subsequent formation of scar tissue, which over time can replace normal parenchyma, functioning tissue, leading to the impaired liver function of cirrhosis. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Early symptoms may include Fatigue (medicine), tiredness, Asthenia, weakness, Anorexia (symptom), loss of appetite, weight loss, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include Pruritus, itchiness, peripheral edema, swelling in the lower legs, ascites, fluid build-up in the abdomen, jaundice, coagulopathy, bruising easily, and the development of spider angioma, spider-like blood vessels in the skin. The fluid build-up in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caroli Disease
Caroli disease (communicating cavernous ectasia, or congenital cystic dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary tree) is a rare inherited disorder characterized by cystic dilatation (or ectasia) of the bile ducts within the liver. There are two patterns of Caroli disease: focal or simple Caroli disease consists of abnormally widened bile ducts affecting an isolated portion of liver. The second form is more diffuse, and when associated with portal hypertension and congenital hepatic fibrosis, is often referred to as "Caroli syndrome". The underlying differences between the two types are not well understood. Caroli disease is also associated with liver failure and polycystic kidney disease. The disease affects about one in 1,000,000 people, with more reported cases of Caroli syndrome than of Caroli disease. Caroli disease is distinct from other diseases that cause ductal dilatation caused by obstruction, in that it is not one of the many choledochal cyst derivatives. Signs and symptom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |