|
Château De Pibrac
The Château de Pibrac is a converted 16th century castle in the ''Communes of France, commune'' of Pibrac in the Haute-Garonne ''Departments of France, département'' of France. It was rebuilt in 1540 to replace the old manor house. The architect appears to be Nicolas Bachelier. During the French Revolution, Revolution, in 1794, the sculptures were smashed and the tops of the towers destroyed. It was restored, with alterations, in 1887. One of the rooms, known as the Quatrains' cabinet (), has vaults decorated with mythological subjects dating from the 16th century. According to tradition, it was in this room, which has kept its 16th century decorations almost intact, that Guy Du Faur, Seigneur de Pibrac, Guy du Faur de Pibrac composed his famous "moral quatrains". The red brick structure, privately owned, has been listed since 1932 as a ''monument historique'' by the French Ministry of Culture. Chateau de Pibrac E.jpg, Château de Pibrac Château de Pibrac (1).jpg, The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private fortified house, fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a mansion, palace, and villa, whose main purpose was exclusively for ''pleasance'' and are not primarily fortresses but may be fortified. Use of the term has varied over time and, sometimes, has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th- and 20th-century homes built to resemble castles. Over the Middle Ages, when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain wall (fortification), curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were commonplace. European-style castles originated in the 9th and 10th centuries after the fall of the Carolingian Empire, which resulted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
A () is a level of administrative divisions of France, administrative division in the France, French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipality, municipalities in Canada and the United States; ' in Germany; ' in Italy; ' in Spain; or civil parishes in the United Kingdom. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlet (place), hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the Municipal arrondissem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
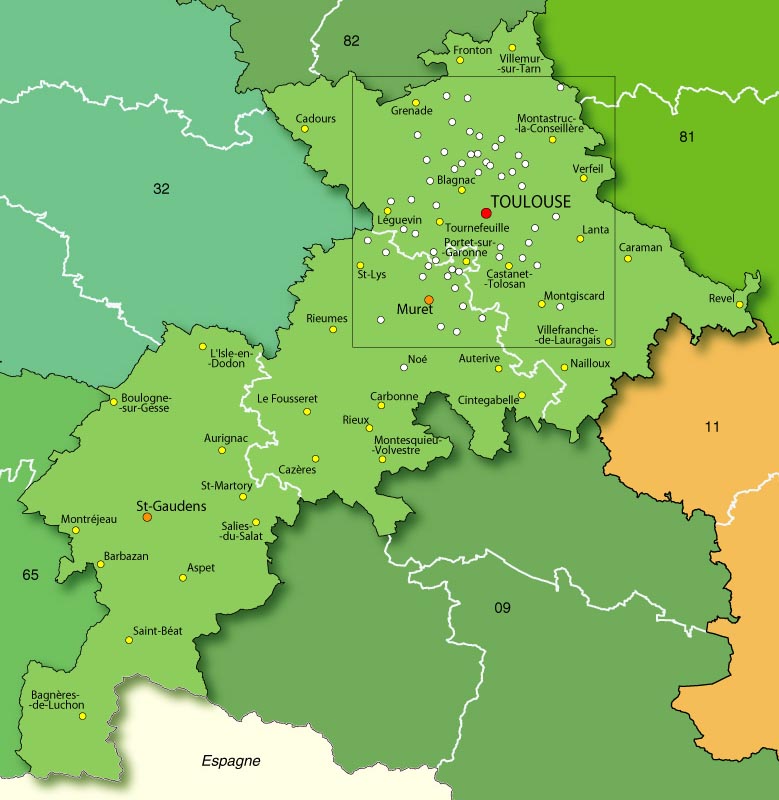
Pibrac
Pibrac () is a commune in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern France, located west of Toulouse. It has recently grown thanks to the development of the aeroplane industry in the nearby town of Blagnac. Population The inhabitants of the commune are known as ''Pibracaises'' and ''Pibracais'' in French. Sport Pibrac has a patinodrome, a track for inline speed skating, as well as many other sporting facilities. Personalities It was the birthplace of Saint Germaine Cousin. Monuments The Château de Pibrac is a converted 16th century castle which is listed as a historic site by the French Ministry of Culture. Gallery Mairie de Pibrac.jpg, Town hall Monument aux morts de Pibrac.jpg, War memorial Eglise Sainte-Marie-Madeleine de Pibrac.jpg, Church Sainte-Marie-Madeleine Eglise Sainte-Marie-Madeleine de Pibrac Intérieur.jpg, Church Sainte-Marie-Madeleine Basilique de Sainte-Germaine de Pibrac façade.jpg, Basilica of St. Germaine Chasse de Sainte-Germaine.jpg, The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haute-Garonne
Haute-Garonne (; , ; ''Upper Garonne'') is a department in the southwestern French region of Occitanie. Named after the river Garonne, which flows through the department. Its prefecture and main city is Toulouse, the country's fourth-largest. In 2019, it had a population of 1,400,039.Populations légales 2019: 31 Haute-Garonne INSEE History Haute-Garonne is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on 4 March 1790. It was created from part of the former provinces of and |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivity, territorial collectivities"), between the Regions of France, administrative regions and the Communes of France, communes. There are a total of 101 departments, consisting of ninety-six departments in metropolitan France, and five Overseas department and region, overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 333 Arrondissements of France, arrondissements and 2,054 Cantons of France, cantons (as of 2023). These last two levels of government have no political autonomy, instead serving as the administrative basis for the local organisation of police, fire departments, and, in certain cases, elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council (France), departmental council ( , ). From 1800 to April 2015, these were called gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Bachelier
Nicolas Bachelier (1485–1557) was a French surveyor, architect, and sculptor who particularly worked in Toulouse. Bachelier is famous in Toulouse for having been the architect, proven or presumed, of several '' hôtels particuliers'' of the Renaissance, as well as for his religious sculptures. He was particularly renowned for his great scholarly culture. In 1539, Bachelier and his colleague Arnaud Casanove, who described themselves as ''expert levelers'', proposed a survey for a canal from Toulouse to Carcassonne to Francis I. Francis I had previously discussed the possibility of such a canal with Leonardo da Vinci. They also proposed that barges could either float down the Garonne River to Bordeaux or could traverse a canal parallel to the river. Francis I approved their plans which included a lock-free canal of variable depth. These plans proved to be inaccurate and could not be executed. In 1598, Henri IV re-examined the plans, but nothing was done until Pierre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Du Faur, Seigneur De Pibrac
Guy Du Faur, Seigneur de Pibrac (1529–1584) was a French jurist and poet. Life Guy Du Faur, Seigneur de Pibrac was born at Toulouse to an old family of the magistracy. He studied law there with Jacques Cujas, and afterwards at Padua. In 1548 Pibrac was admitted to the bar at Toulouse, at once took high rank, and in 1557 rose to be ''juge-mage'', an office in Languedocian cities about equal to that of ''privat''. He was selected in 1562 as one of the three representatives of the king of France at the Council of Trent. There he gave a speech arguing for gallicanism. In 1565 Pibrac became general advocate to the Parlement of Paris, and extended the renaissance in jurisprudence which was transforming French justice. In 1573 he was sent by Charles IX of France to accompany as chancellor his brother Henry (afterwards Henry III) to Poland, of which country Henry had been elected king. Pibrac's fluent Latin won much applause from the Poles, but his second visit to Poland in 1575, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monument Historique
() is a designation given to some national heritage sites in France. It may also refer to the state procedure in France by which national heritage protection is extended to a building, a specific part of a building, a collection of buildings, a garden, a bridge, or other structure, because of their importance to France's architectural and historical cultural heritage. Both public and privately owned structures may be listed in this way, as well as movable objects. there were 44,236 monuments listed. The term "classification" is reserved for designation performed by the French Ministry of Culture for a monument of national-level significance. Monuments of lesser significance may be "inscribed" by various regional entities. Buildings may be given the classification (or inscription) for either their exteriors or interiors. A monument's designation could be for a building's décor, its furniture, a single room, or even a staircase. An example is the classification of the déco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ministry Of Culture
The Ministry of Culture () is the ministry (government department), ministry of the Government of France in charge of List of museums in France, national museums and the . Its goal is to maintain the French identity through the promotion and protection of the arts (visual, plastic, theatrical, musical, dance, architectural, literary, televisual and cinematographic) on national soil and abroad. Its budget is mainly dedicated to the management of the (six national sites and hundred decentralised storage facilities) and the regional (culture centres). Its main office is in the in the 1st arrondissement of Paris on the . It is headed by the Minister of Culture, a cabinet member. The current officeholder has been Rachida Dati since 11 January 2024. History Deriving from the Italian Renaissance, Italian and Duchy of Burgundy, Burgundian courts of the Renaissance, the notion that the state had a key role to play in the sponsoring of artistic production and that the arts were linke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry IV Of France
Henry IV (; 13 December 1553 – 14 May 1610), also known by the epithets Good King Henry (''le Bon Roi Henri'') or Henry the Great (''Henri le Grand''), was King of Navarre (as Henry III) from 1572 and King of France from 1589 to 1610. He was the first monarch of France from the House of Bourbon, a cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. He pragmatically balanced the interests of the Catholic and Protestant parties in France, as well as among the European states. He was assassinated in Paris in 1610 by a Catholic zealot, and was succeeded by his son Louis XIII. Henry was baptised a Catholic but raised as a Huguenot in the Protestant faith by his mother, Queen Jeanne III of Navarre. He inherited the throne of Navarre in 1572 on his mother's death. As a Huguenot, Henry was involved in the French Wars of Religion, barely escaping assassination in the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre. He later led Protestant forces against the French royal army. Henry inherited the thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |