|
Château De Fallais
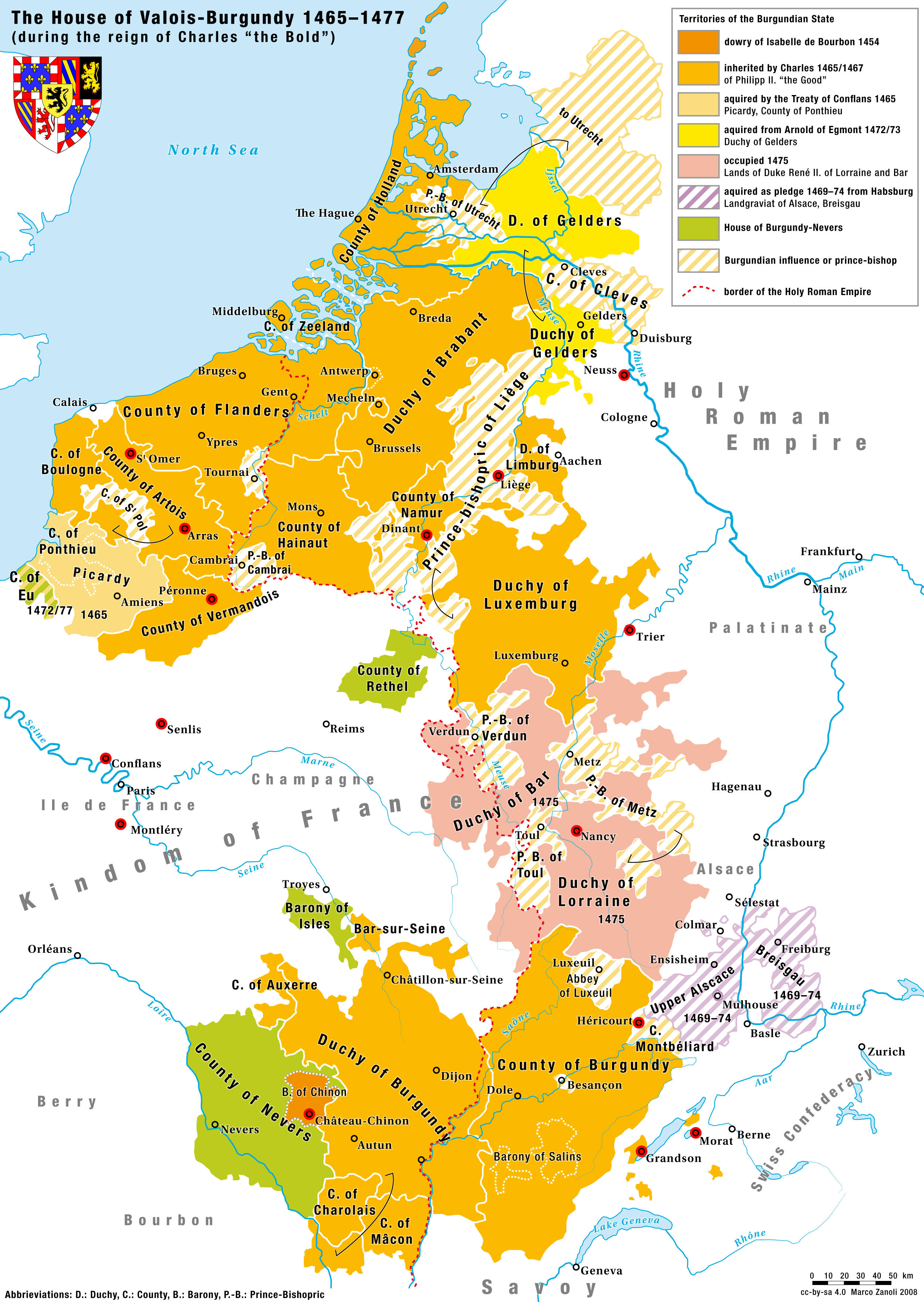
Château de Fallais (, "Fallais Castle") is a castle originating in the 11th century in the '' ancienne commune'' of Fallais, municipality of Braives, Liège Province, Wallonia, Belgium. The castle was built in the 13th Century by the Beaufort family. Twice the lords were involved in armed conflicts with the Prince-Bishopric of Liège. The first conflict was the so-called war of cows in the period of 1275–1278, fought between Guy I, Count of Namur, and John of Enghien, Prince-Bishop of Liege. In 1458 Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, made his 18-year-old nephew, Louis de Bourbon, the Prince-Bishop of Liege. When Louis finished his studies and took on his duties in 1465, the First Liège War broke out when Louis was deposed by the citizens of the city of Liège. In October 1465, Louis met with his cousin, Charles the Bold (future Duke of Burgundy) at Château de Fallais. Charles then led the Burgundians to the Battle of Montenaken, where they routed the Liégeoise, suppress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liège Province
Liège ( ; ; ; ; ) is the easternmost province of the Wallonia region of Belgium. Liège Province is the only Belgian province that has borders with three countries. It borders (clockwise from the north) the Dutch province of Limburg, the German states of North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate, the Luxembourgish canton of Clervaux, the Belgian Walloon (French-speaking) provinces of Luxembourg, Namur and Walloon Brabant and the Belgian Flemish (Dutch-speaking) provinces of Flemish Brabant and Limburg. Part of the eastern-most area of the province, bordering Germany, is the German-speaking region of Eupen-Malmedy, which became part of Belgium in the aftermath of World War I. The capital and the largest city of the province is the city of the same name, Liège. The province has an area of , and a population of 1.12 million as of January 2024. History The modern borders of the province of Liège date from 1795, which saw the unification of the Principali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bishops And Prince-bishops Of Liège
This is a list of the bishops and prince-bishops of Liège. It includes the bishops of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Liège and its predecessor see of Tongeren and Maastricht. From 972 to 1795, the bishops of Liège also ruled a lordship (not co-extensive with their diocese) known as the Prince-Bishopric of Liège. Bishops of Tongeren-Maastricht-Liège, 315–971 See in Tongeren (4th-century) * St. Maternus of Tongeren (?) (c. 315) * Saint Servatius (342–384) See in Maastricht (380s? to 718) * Falco (c. 498–c. 512) *Domitian (?–560) * Saint Monulphus (549–588) * Saint Gondulphus (589–614) * Saint Ebregise ? (614–627) * Saint John I Agnus (627–647) * Saint Amand (647–650) * Saint Remaclus (652–662) * Saint Theodard (662–669) * Saint Lambert, patron saint of the diocese (669–705 or later) *Saint Hubert of Liège, patron saint of the city (705 or before – 727) See in Maastricht and/or Liège (718 to 810) * Floribert of Liège (727–736 or 738) * (736 o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Castles In Belgium
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole". Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of '' The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, and lists help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Montenaken
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles The Bold
Charles Martin (10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), called the Bold, was the last duke of Burgundy from the House of Valois-Burgundy, ruling from 1467 to 1477. He was the only surviving legitimate son of Philip the Good and his third wife, Isabella of Portugal. As heir and as ruler, Charles vied for power and influence with rivals such as his overlord, King Louis XI of France. In 1465 Charles led a successful revolt of Louis's vassals in the War of the Public Weal. After becoming the Duke of Burgundy in 1467, Charles pursued his ambitions for a kingdom, independent from France, that would stretch contiguously from the North Sea in the north to the borders of Savoy in the south. For this purpose, he acquired Guelders and Upper Alsace; sought the title King of the Romans; and gradually became an enemy of the Germans. Charles married Margaret of York for an English alliance. He arranged the betrothal between his sole child, Mary, with Maximilian of Austria. A passiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liège
Liège ( ; ; ; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the Liège Province, province of Liège, Belgium. The city is situated in the valley of the Meuse, in the east of Belgium, not far from borders with the Netherlands (Maastricht is about to the north) and with Germany (Aachen is about north-east). In Liège, the Meuse meets the river Ourthe. The city is part of the ''sillon industriel'', the former industrial backbone of Wallonia. It still is the principal economic and cultural centre of the region. The municipality consists of the following Deelgemeente, sub-municipalities: Angleur, Bressoux, Chênée, Glain, Grivegnée, Jupille-sur-Meuse, Liège proper, Rocourt, Liège, Rocourt, and Wandre. In November 2012, Liège had 198,280 inhabitants. The metropolitan area, including the outer commuter zone, covers an area of 1,879 km2 (725 sq mi) and had a total population of 749,110 on 1 January 2008. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wars Of Liège
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organized groups. It is generally characterized by widespread violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular or irregular military forces. ''Warfare'' refers to the common activities and characteristics of types of war, or of wars in general. Total war is warfare that is not restricted to purely legitimate military targets, and can result in massive civilian or other non-combatant suffering and casualties. Etymology The English word ''war'' derives from the 11th-century Old English words and , from Old French ( as in modern French), in turn from the Frankish , ultimately deriving from the Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic . The word is related to the Old Saxon , Old High German , and the modern German , meaning . History An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis De Bourbon, Bishop Of Liège
Louis de Bourbon (1438 – 30 August 1482 in Liège) was Prince-Bishop of Liège from 1456 until his death. Family He was the son of Charles I, Duke of Bourbon, and Agnes of Burgundy. His own sister Isabella was the second wife of Charles the Bold. He was brought up and educated by his uncle Philip, Duke of Burgundy, who let him study for ten years at the University of Leuven. It has been said that Louis married, in secret in 1464, Catherine, daughter of Arnold, Duke of Gelderland; these claims date only from the seventeenth century and are now believed to be false. Louis' three children (all likely to have been born from a mistress) were: *Pierre de Bourbon, bâtard de Liège (1464–1529) *Louis de Bourbon, bâtard de Liège (1465–1500) *Jacques de Bourbon, bâtard de Liège (1466–1537) Louis' eldest son, Pierre, founded the Bourbon-Busset family. Conflict over the bishopric In 1456, Louis was given, through the efforts of Philip, Duke of Burgundy, the Prince-Bishopr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy () was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by the Crown lands of France, French crown in 1477, and later by members of the House of Habsburg, including Holy Roman Emperors and kings of Spain, who claimed Burgundy proper and ruled the Burgundian Netherlands. The Duchy of Burgundy was a small portion of the traditional lands of the Burgundians west of the river Saône which, in 843, was allotted to Charles the Bald's kingdom of the West Franks. Under the Ancien Régime, the duke of Burgundy was the premier lay Peerage of France, peer of the Kingdom of France. Beginning with Robert II of France (), the title was held by the Capetians, the French royal family. In 1032 King Henry I of France granted the duchy to his younger brother, Robert I, Duke of Burgundy, Robert, who founded the House of Burgundy. When the senior line of the House of Burgundy became extinct in 1361, the title was inherited by King Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip The Good
Philip III the Good (; ; 31 July 1396 – 15 June 1467) ruled as Duke of Burgundy from 1419 until his death in 1467. He was a member of a cadet line of the Valois dynasty, to which all 15th-century kings of France belonged. During his reign, the Burgundian State reached the apex of its prosperity and prestige, and became a leading centre of the arts. Duke Philip has a reputation for his administrative reforms, for his patronage of Flemish artists (such as Jan van Eyck) and of Franco-Flemish composers (such as Gilles Binchois), and for the 1430 seizure of Joan of Arc, whom Philip ransomed to the English after his soldiers captured her, resulting in her trial and eventual execution. In political affairs, he alternated between alliances with the English and with the French in an attempt to improve his dynasty's powerbase. Additionally, as ruler of Flanders, Brabant, Limburg, Artois, Hainaut, Holland, Luxembourg, Zeeland, Friesland and Namur, he played an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Enghien
John of Enghien (died 1281) was the 54th bishop of Tournai and the 69th bishop of Liège in the Low Countries. Life John of Enghien was born to a noble family in the County of Hainaut, son of Siger of Enghien and Alix of Sotteghem. Alphonse Le Roy, "Jean d'Enghien", ''Biographie Nationale de Belgique''vol. 10(Brussels, 1889), 340-344. He was appointed to a canonry of Tournai Cathedral, where he established a reputation as a theologian and in 1266 was elected bishop. He was enthroned as bishop on 8 January 1267. In 1274, when Henry of Guelders resigned as bishop of Liège, John was designated as his successor by Pope Gregory X during the Second Council of Lyon. His predecessor, Henry of Guelders, claimed he was still owed money by the cathedral chapter of Liège and John of Enghien agreed to a meeting with him in Hoegaarden. Henry had him seized and carried off, but during the abduction he was mortally wounded. He died of his wounds at Heylissem, near Tienen Tienen (; ) is a ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallonia
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—along with Flemish Region, Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the country, Wallonia is primarily Geographical distribution of French speakers, French-speaking. It accounts for 55% of Belgium's territory, but only a third of its population. The Walloon Region and the French Community of Belgium, which is the political entity responsible for matters related mainly to culture and education, are independent concepts, because the French Community of Belgium encompasses both Wallonia and the bilingual Brussels-Capital Region but not the German-speaking Community of Belgium, which administers nine municipalities in Eastern Wallonia. During the Industrial Revolution, Wallonia was second only to the United Kingdom in industrialization, capitalizing on its extensive deposits of coal and iron. This brought the regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |