|
Chukot
Chukchi , also known as Chukot, is a Chukotko–Kamchatkan language spoken by the Chukchi people in the easternmost extremity of Siberia, mainly in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The language is closely related to Koryak. Chukchi, Koryak, Kerek, Alutor, and Itelmen form the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. There are many cultural similarities between the Chukchis and Koryaks, including economies based on reindeer herding. Both peoples refer to themselves by the endonym ''Luorawetlat'' (ԓыгъоравэтԓьат ; singular ''Luorawetlan'' ԓыгъоравэтԓьан ), meaning "the real people". All of these peoples and other unrelated minorities in and around Kamchatka are known collectively as Kamchadals. ''Chukchi'' and ''Chukchee'' are anglicized versions of the Russian exonym ''Chukcha'' (plural ''Chukchi''). This came into Russian from ''Čävča'', the term used by the Chukchis' Tungusic-speaking neighbors, itself a rendering of the Chukchi word чавчыв , which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
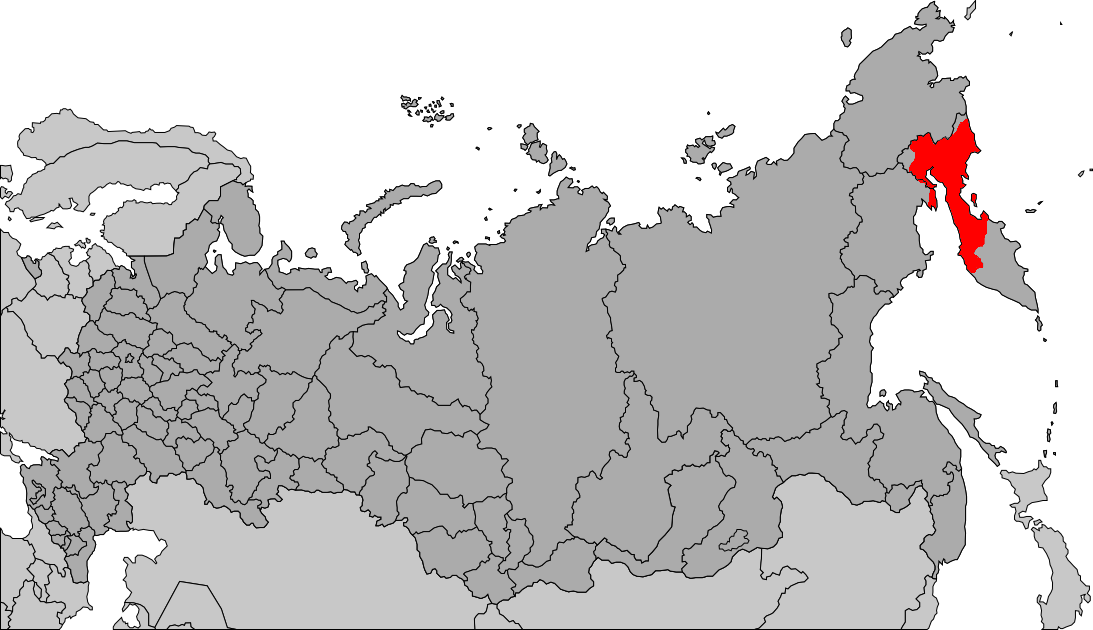
Chukotka Autonomous Okrug
Chukotka (russian: Чуко́тка), officially the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug,, ''Čukotkakèn avtonomnykèn okrug'', is the easternmost federal subject of Russia. It is an autonomous okrug situated in the Russian Far East, and shares a border with the Sakha Republic to the west, Magadan Oblast to the south-west, and Kamchatka Krai to the south. Anadyr is the largest town and the capital, and the easternmost settlement to have town status in Russia. Chukotka is primarily populated by ethnic Russians, Chukchi, and other indigenous peoples. It is the only autonomous okrug in Russia that is not included in, or subordinate to, another federal subject, having separated from Magadan Oblast in 1992. It is home to Lake Elgygytgyn, an impact crater lake, and Anyuyskiy, an extinct volcano. The village of Uelen is the easternmost settlement in Russia and the closest substantial settlement to the United States (Alaska). The autonomous okrug covers an area of over , and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukotko-Kamchatkan Languages
The Chukotko-Kamchatkan or Chukchi–Kamchatkan languages are a language family of extreme northeastern Siberia. Its speakers traditionally were indigenous hunter-gatherers and reindeer-herders. Chukotko-Kamchatkan is endangered. The Kamchatkan branch is moribund, represented only by Western Itelmen, with only 4 or 5 elderly speakers left. The Chukotkan branch had close to 7,000 speakers left (as of 2010, the majority being speakers of Chukchi), with a reported total ethnic population of 25,000. While the family is sometimes grouped typologically and geographically as Paleosiberian, no external genetic relationship has been widely accepted as proven. The most popular such proposals have been for links with Eskimo–Aleut, either alone or in the context of a wider grouping. Alternative names Less commonly encountered names for the family are Chukchian, Chukotian, Chukotan, Kamchukchee and Kamchukotic. Of these, ''Chukchian'' and ''Chukotian'' are ambiguous, since both terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itelmen Language
Itelmen ( itl, script=latn, Itənmən) or Western Itelmen, formerly known as Western Kamchadal, is a language of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan family spoken on the western coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula. Fewer than a hundred native speakers, mostly elderly, in a few settlements in the southwest of Koryak Autonomous Okrug, remained in 1993. The 2002 Census counted 3,180 ethnic Itelmens, virtually all of whom are now monolingual in Russian. However, there are attempts to revive the language, and it is being taught in a number of schools in the region. (Western) Itelmen is the only surviving Kamchatkan language. It has two dialects, Sedanka and Xajrjuzovo (Ukä). History Originally the Kamchatkan languages were spoken throughout Kamchatka and possibly also in the northern Kuril Islands. Vladimir Atlasov, who annexed Kamchatka and established military bases in the region, estimated in 1697 that there were about 20,000 ethnic Itelmens. The explorer Stepan Krasheninnikov, who ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukotkan Languages
Chukotkan (Chukotian, Chukotic) is a dialect cluster that forms one branch of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. It is spoken in two autonomous regions at the extreme northeast of Russia, bounded on the east by the Pacific and on the north by the Arctic. The term Luorawetlan (Luoravetlan), used for Chukchi in the 1930s, is actually the ethnonym of both the Chukchi and Koryak. Varieties * Chukchi, spoken mostly within Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. * Koryak, also called Nymylan, spoken in Koryak Okrug of Kamchatka Krai. The main dialect is known as Chavchuven Koryak. * Alyutor (Alutor, Aliutor), also spoken in Koryakia. According to Michael Fortescue Michael David Fortescue (born 8 August 1946) is a British-born linguist specializing in Arctic and native North American languages, including Kalaallisut, Inuktun, Chukchi and Nitinaht. He gained his PhD in Linguistics from the University of ... (2005), Palana Koryak and Alutor should be considered dialects of a single l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerek Language
Kerek (russian: link=no, Керекский язык) is an extinct language of Russia of the northern branch of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages. On historical linguistic grounds it is most closely related to Koryak (both languages have a merger of the proto-Chuktotian phonemes /*ð/ and /*r/ with /*j/). The next closest relative is Chukchi (/*ð/ and /*r/ are merged, but not /*j/). In 1997 there were still two speakers remaining, but by 2005 the language was considered extinct. According to the 2010 census, there were 10 people claiming Kerek as their native language, a number which may include partial speakers and non-speakers who claim the language as part of their ethnic heritage. Over the 20th century many members of the Kerek ethnic group shifted to Chukchi, the language of the majority ethnic group in the area, but now most Chukchis The Chukchi, or Chukchee ( ckt, Ԓыгъоравэтԓьэт, О'равэтԓьэт, ''Ḷygʺoravètḷʹèt, O'ravètḷʹèt'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koryak Language
Koryak () is a Chukotko-Kamchatkan language spoken by about 1,700 people as of 2010 in the easternmost extremity of Siberia, mainly in Koryak Okrug. It is mostly spoken by Koryaks. Its close relative, the Chukchi language, is spoken by about three times that number. The language together with Chukchi, Kerek, Alutor and Itelmen forms the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. Its native name in Koryak is нымылан ''nymylan'', but variants of the Russian "Koryak" name are most commonly used in English and other languages. The Chukchi and Koryaks form a cultural unit with an economy based on reindeer herding and both have autonomy within the Russian Federation. Phonology may be an allophone In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is a set of multiple possible spoken soundsor ''phones''or signs used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, (as in '' ... of .Zhukova, 1972 Koryak a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alutor Language
Alyutor or Alutor is a language of Russia that belongs to the Chukotkan branch of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan languages. Sociolinguistic situation The Alutor are the indigenous inhabitants of the northern part of the Kamchatka Peninsula. The language is unwritten and moribund; in the 1970s residents of the chief Alutor village of Vyvenka under the age of 25 did not know the language. In recent years the Vyvenka village school has started teaching the language. Until 1958 the language was considered the "village" (settled) dialect of the Koryak language, but it is not intelligible with traditionally nomadic varieties of Koryak. The autonym means "villager". Orthography Typology Alutor is a polysynthetic language. The morphology is agglutinative, with extensive prefixes and suffixes. The argument structure is ergative. The word order is variable, and it is difficult to say which typology is basic. The verb-absolutive orders AVO and VAO are perhaps most common. Phon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukchi People
The Chukchi, or Chukchee ( ckt, Ԓыгъоравэтԓьэт, О'равэтԓьэт, ''Ḷygʺoravètḷʹèt, O'ravètḷʹèt''), are a Indigenous peoples of Siberia, Siberian indigenous people native to the Chukchi Peninsula, the shores of the Chukchi Sea and the Bering Sea region of the Arctic Ocean all within modern Russia. They speak the Chukchi language. The Chukchi originated from the people living around the Okhotsk Sea. According to several studies on genomic research conduct from 2014 to 2018, the Chukchi are one of the Indigenous peoples of Siberia, they are also the closest Asiatic relatives of the indigenous peoples of the Americas as well as of the Ainu people and other East Asian people, being the descendants of settlers who did not cross the Bering Strait or settled the Japanese archipelago. Cultural history The majority of Chukchi reside within Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, but some also reside in the neighboring Sakha Republic to the west, Magadan Oblast to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuri Rytkheu
Yuri Sergeyevich Rytkheu ( rus, Ю́рий Серге́евич Рытхэ́у, , ˈjʉrʲɪj sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ rɨtˈxɛʊ; ckt, Ю́рий Серге́евич Рытгэ́в; 8 March 1930 – 14 May 2008) was a Chukchi writer, who wrote in both his native Chukchi and in Russian. He is considered to be the father of Chukchi literature. Early life Yuri Rytkheu was born 8 March 1930 to a family of trappers and hunters. His birthplace, the village of Uelen, was then in the Chukotka District, Far Eastern Territory, RSFSR, USSR; it is now part of the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. His grandfather was a shaman. At birth, he was given the name "Rytgėv", which means "forgotten" in the Chukchi language (from the Chukchi word ''"рытгэватъё" (rytgėvatʺjo'') – "unremembered" or "forgotten"). Since Soviet institutions did not recognize Chukchi names and the Chukchi do not commonly use surnames, in order to obtain his passport he used his first name as his surnam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koryaks
Koryaks () are an indigenous people of the Russian Far East, who live immediately north of the Kamchatka Peninsula in Kamchatka Krai and inhabit the coastlands of the Bering Sea. The cultural borders of the Koryaks include Tigilsk in the south and the Anadyr basin in the north. The Koryaks are culturally similar to the Chukchis of extreme northeast Siberia. The Koryak language and Alutor (which is often regarded as a dialect of Koryak), are linguistically close to the Chukchi language. All of these languages are members of the Chukotko-Kamchatkan language family. They are more distantly related to the Itelmens on the Kamchatka Peninsula. All of these peoples and other, unrelated minorities in and around Kamchatka are known collectively as Kamchadals. Neighbors of the Koryaks include the Evens to the west, the Alutor to the south (on the isthmus of Kamchatka Peninsula), the Kerek to the east, and the Chukchi to the northeast. The Koryak are typically split into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungusic Languages
The Tungusic languages (also known as Manchu-Tungus and Tungus) form a language family spoken in Eastern Siberia and Manchuria by Tungusic peoples. Many Tungusic languages are endangered. There are approximately 75,000 native speakers of the dozen living languages of the Tungusic language family. Some linguists consider Tungusic to be part of the controversial Altaic language family, along with Turkic, Mongolic, and sometimes Koreanic and Japonic. The term "Tungusic" is from an exonym for the Evenk people (Ewenki) used by the Yakuts ("tongus"). It was borrowed into Russian as "тунгус", and ultimately transliterated into English as "Tungus". Classification Linguists working on Tungusic have proposed a number of different classifications based on different criteria, including morphological, lexical, and phonological characteristics. Some scholars have criticized the tree-based model of Tungusic classification, arguing the long history of contact among the Tungusic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukchi Textbook Cover
Chukchi may refer to: *Chukchi people *Chukchi language *Chukchi Peninsula *Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea ( rus, Чуко́тское мо́ре, r=Chukotskoye more, p=tɕʊˈkotskəjə ˈmorʲɪ), sometimes referred to as the Chuuk Sea, Chukotsk Sea or the Sea of Chukotsk, is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west ... See also * Chukotka (other) * Chukotsky (other) {{Disambig, geo Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |