|
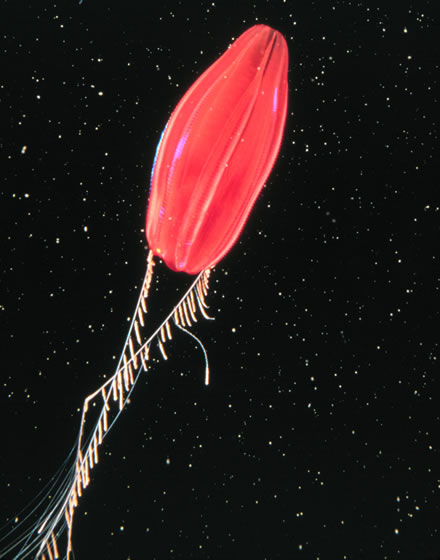
Chtenopteryx Sicula
''Chtenopteryx sicula'', also known as the comb-finned squid or toothed-fin squid, is a species of squid native to at least the Mediterranean Sea. It is characterised by several distinct morphological features: ocular photophores are present but visceral photophores are absent, cephalopod arm, arm suckers are arranged in at least 4 series distally, and club suckers are borne in more than 8 series. The type specimen was collected off Messina, Italy; the specific name ''sicula'' means "of Sicily". It is deposited at the Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle (Musée Barla) in Nice. Gallery [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of Naples, province-level municipality is the third most populous Metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city in Italy with a population of 2,958,410 residents, and the List of urban areas in the European Union, eighth most populous in the European Union. Naples metropolitan area, Its metropolitan area stretches beyond the boundaries of the city wall for approximately . Naples also plays a key role in international diplomacy, since it is home to NATO's Allied Joint Force Command Naples and the Parliamentary Assembly of the Mediterranean. Founded by Greeks in the 1st millennium BC, first millennium BC, Naples is one of the oldest continuously inhabited urban areas in the world. In the eighth century BC, a colony known as Parthenope () was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nidamental Gland
Nidamental glands are internal organs found in some elasmobranchs and certain molluscs, including cephalopods (specifically Decapodiformes and nautiluses) and gastropod Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and fro ...s.Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold (1999)Cephalopoda Glossary Tree of Life Web Project. In cephalopods, nidamental glands are large, paired glandular structures found in the mantle cavity. Accessory nidamental glands may also be present. Nidamental glands are composed of lamellae and are involved in the secretion of egg cases or the gelatinous substance comprising egg masses. They are also found in phoronids. Culinary uses Nidamental glands of cuttlefish are eaten as food in various parts of the world, included either in dishes in which the whole ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopods Of Europe
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symmetry, bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of cephalopod arm, arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt Cephalopod ink, ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, Extant taxon, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus (genus), Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Molluscs Of Europe
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean. Marine or marines may refer to: Ocean * Maritime (other) * Marine art * Marine biology * Marine current power * Marine debris * Marine energy * Marine habitats * Marine life * Marine pollution Military * Marines, a naval-based infantry force ** United States Marine Corps ** Royal Marines of the UK ** Brazilian Marine Corps ** Spanish Marine Infantry ** Fusiliers marins (France) ** Indonesian Marine Corps ** Republic of China Marine Corps ** Republic of Korea Marine Corps ** Royal Thai Marine Corps *"Marine" also means "navy" in several languages: ** Austro-Hungarian Navy () ** Belgian Navy (, , ) ** Royal Canadian Navy () *** Provincial Marine (1796–1910), a predecessor to the Royal Canadian Navy ** Navy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo () ** Royal Danish Navy () ** Finnish Navy (, ) ** French Navy () ** Gabonese Navy () ** German Navy () ** Royal Moroccan Navy () ** Royal Netherlands Navy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopods Described In 1851
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head, and a set of arms or tentacles (muscular hydrostats) modified from the primitive molluscan foot. Fishers sometimes call cephalopods "inkfish", referring to their common ability to squirt ink. The study of cephalopods is a branch of malacology known as teuthology. Cephalopods became dominant during the Ordovician period, represented by primitive nautiloids. The class now contains two, only distantly related, extant subclasses: Coleoidea, which includes octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish; and Nautiloidea, represented by ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. In the Coleoidea, the molluscan shell has been internalized or is absent, whereas in the Nautiloidea, the external shell remains. About 800 living species of cephalopods have been identified. Tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathyteuthida
Bathyteuthida is an order of cephalopods, consisting of small, mesopelagic to bathypelagic squid that in some ways resemble myopsid squid, such as ''Loligo'' and in others the pelagic oegopsid squid. Its two families, the Bathyteuthidae and Chtenopterygidae, each containing a single genus, have previously been included with the oegopsids. As with the oegopsids, the Bathyteuthida lack corneal membranes covering their eyes, something common to myopsid squid, and have paired oviducts, lacking in myopsids. As with the myopsids, bathyteuthids have tentacle pockets in the head and small suckers on the buccal supports, found only in this group, Loliginidae, and Sepiidae; neither is found in true oegopsids. The Bathyteuthida do share the open ocean pelagic habitat with the oegopsid squid, uniting them in that way with that diverse group. The Bathyteuthidae and Chtenopterygidae differ in body conformation, the internal shell, and in the manner in which buccal supports attach to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladius (cephalopod)
The gladius (: ''gladii''), or pen, is a hard internal bodypart found in many cephalopods of the superorder Decapodiformes (particularly squids) and in a single extant taxon, extant member of the Octopodiformes, the vampire squid (''Vampyroteuthis infernalis''). It is so named for its superficial resemblance to the Roman Empire, Roman Gladius, short sword of the same name, and is a Vestigiality, vestige of the ancestral mollusc shell, which was external. The gladius is located Dorsal (anatomy), dorsally within the mantle (mollusc), mantle and usually extends for its entire length. Composed primarily of chitin, it lies within the shell sac, which is responsible for its secretion. Some species, like the bigfin reef squid, still has a gladius with some degree of mineralization. Gladii are known from a number of extinct cephalopod groups, including Teudopseina, teudopseids (''e.g.'' ''Actinosepia'', ''Glyphiteuthis'', ''Muensterella'', ''Palaeololigo'', ''Teudopsinia'', ''Teudopsis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (mollusc)
The mantle (also known by the Latin language, Latin word pallium meaning mantle, robe or cloak, adjective pallial) is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsum (biology), dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself. In many species of molluscs the Epidermis (skin), epidermis of the mantle secretes calcium carbonate and conchiolin, and creates a mollusc shell, shell. In sea slugs there is a progressive loss of the shell and the mantle becomes the dorsal surface of the animal. The words mantle and pallium both originally meant ‘cloak’ or ‘cape’; see mantle (vesture). This anatomical structure in molluscs often resembles a cloak because in many groups the edges of the mantle, usually referred to as the ''mantle margin'', extend far beyond the main part of the body, forming flaps, double-layered structures which have been adapted for many different uses, including for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatophore
Chromatophores are cells that produce color, of which many types are pigment-containing cells, or groups of cells, found in a wide range of animals including amphibians, fish, reptiles, crustaceans and cephalopod A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...s. Mammals and birds, in contrast, have a class of cells called melanocytes for animal coloration, coloration. Chromatophores are largely responsible for generating skin and eye color, eye colour in ectothermic animals and are generated in the neural crest during embryonic development. Mature chromatophores are grouped into subclasses based on their colour under white light: xanthophores (yellow), erythrophores (red), iridophores (reflective / iridescence, iridescent), leucophores (white), melanophores (black/brown), and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentacular
In zoology, a tentacle is a flexible, mobile, and elongated organ present in some species of animals, most of them invertebrates. In animal anatomy, tentacles usually occur in one or more pairs. Anatomically, the tentacles of animals work mainly like muscular hydrostats. Most forms of tentacles are used for grasping and feeding. Many are sensory organs, variously receptive to touch, vision, or to the smell or taste of particular foods or threats. Examples of such tentacles are the eyestalks of various kinds of snails. Some kinds of tentacles have both sensory and manipulatory functions. A tentacle is similar to a cirrus, but a cirrus is an organ that usually lacks the tentacle's strength, size, flexibility, or sensitivity. A nautilus has cirri, but a squid has tentacles. Invertebrates Molluscs Many molluscs have tentacles of one form or another. The most familiar are those of the pulmonate land snails, which usually have two sets of tentacles on the head: when extende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionDemographia: World Urban Areas , Demographia.com, April 2016 on an area of . Located on the French Riviera, the southeastern coast of France on the , at the foot of the French Alps, Nice is the second-largest French city on the Mediterranean coast an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baptiste Vérany
Chevalier Jean Baptiste Vérany (1800, in Nice – 1865) was a French pharmacist and naturalist who specialised in the study of cephalopods. In 1846, with Jean-Baptiste Barla (1817–1896), he founded the Muséum d'histoire naturelle de Nice. Vérany discovered and described many species. André Étienne d'Audebert de Férussac named ''Chiroteuthis veranyi'' for him. File:Chiroteuthis veranyi Haeckel.jpg, ''Chiroteuthis veranii'' File:Chromolithographie de Poulpe (Octopus Macropus) en Méditerranée.jpg, ''Callistoctopus macropus'' See also *:Taxa named by Jean Baptiste Vérany Works Partial list: * 1842 – Illustrations. ''Isis von Oken'', pp. 252–253. * 1844 – Description de deux genres nouveaux de mollusques nudibranches. ''Revue Zoologique par la Societe Cuvierienne'', pp. 302–303. * 1845 – Janus spinolae. ''Guerin Magazin de Zoologie'', series 2, 7:121-122, pl. 136. * 1846 – Descrizione di Genova e del Genovesato 1(2): ''Regno Animale Molluschi'', pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |