|
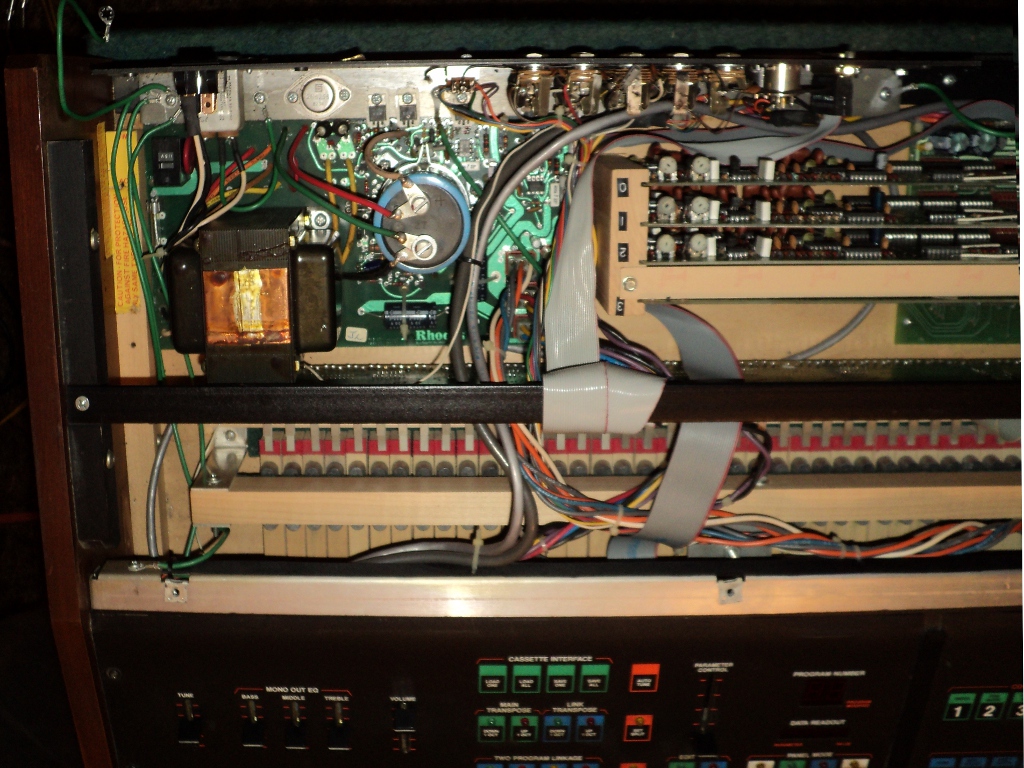
Chroma Expander
The Rhodes Chroma, initially the ARP Chroma, is a polyphonic, multitimbral, microprocessor controlled, subtractive synthesis analog synthesizer developed in 1979-1980 by ARP Instruments, Inc. just before the company's bankruptcy and collapse in 1981. The design was purchased by CBS Musical Instruments and put into production by their Rhodes Division in 1982 as the Rhodes Chroma, at a list price of US $5295. Rhodes also released a keyboard-less version of the Chroma called the Chroma Expander at a list price of US $3150. The Chroma was one of the early microprocessor-controlled analog synthesizers. It was designed before MIDI and featured a 25-pin D-sub connector computer interface used to slave the Expander to the Chroma. Also, an Apple IIe interface card and sequencing software was available. The Rhodes Chroma and Expander were discontinued in 1984. Somewhere between 1400 and 3000 Chromas and Expanders were built. Keyboard velocity and pressure The Chroma has a velocity- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fender Rhodes
The Rhodes piano (also known as the Fender Rhodes piano) is an electric piano invented by Harold Rhodes, which became popular in the 1970s. Like a conventional piano, the Rhodes generates sound with keys and hammers, but instead of strings, the hammers strike thin metal tines, which vibrate next to an electromagnetic pickup. The signal is then sent through a cable to an external keyboard amplifier and speaker. The instrument evolved from Rhodes's attempt to manufacture pianos while teaching recovering soldiers during World War II. Development continued after the war and into the following decade. In 1959, Fender began marketing the Piano Bass, a cut-down version; the full-size instrument did not appear until after Fender's sale to CBS in 1965. CBS oversaw mass production of the Rhodes piano in the 1970s, and it was used extensively through the decade, particularly in jazz, pop, and soul music, as well by many rock artists. It was less used in the 1980s because of compet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtractive Synthesis
Subtractive synthesis is a method of sound synthesis in which Harmonic_series_(music)#Partial.2C_harmonic.2C_fundamental.2C_inharmonicity.2C_and_overtone, overtones of an audio signal are attenuated by a audio filter, filter to alter the timbre of the sound. Overview Subtractive synthesis relies on source sounds that have overtones, such as Sine wave, non-sinusoidal waveforms like Square wave (waveform), square and triangle wave, triangle waves, or white noise, white and pink noise. These overtones are then Modulation, modulated to alter the source sound. This modulation can happen in a wide variety of ways, such as Voltage-controlled filter, voltage-controlled or low-pass filter, low-pass filters. The technology developed in experimental electronic studios which were primarily focused on telecommunications and military applications. Early examples include Bell Labs' Voder (1937–8). Composers began applying the concept of subtractive synthesis beyond the recording studio in conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARP 2600
The ARP 2600 is a subtractive synthesizer first produced by ARP Instruments in 1971. History Developed by a design team headed by ARP namesake Alan R. Pearlman and engineer Dennis Colin, the ARP 2600 was introduced in 1971 as the successor to ARP's first instrument, the ARP 2500, at a retail price of US$2600. Unlike fully modular synthesizers, which often required modules to be purchased individually and wired by the user, the 2600 is semi-modular with a fixed selection of basic synthesizer components internally pre-wired. It sports clear text labels and front panel screen printed graphics indicating the function of different sections of controls, and the signal flow between them. The 2600 is thus ideal for musicians new to synthesis, due to its ability to be operated without patch cords, while still offering greater flexibility to sound designers who are comfortable using them. On its initial release it was heavily marketed to high schools and universities. Features and arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patch Cord
A patch cable, patch cord or patch lead is an electrical or fiber-optic cable used to connect ("patch in") one electronic or optical device to another for signal routing. Devices of different types (e.g., a switch connected to a computer, or a switch to a router) are connected with patch cords. Patch cords are usually produced in many different colors so as to be easily distinguishable from each other. Types of patch cords include microphone cables, fiber optic spectroscopy cables, headphone extension cables, XLR connector, Tiny Telephone (TT) connector, RCA connector and ¼" TRS phone connector cables (as well as modular Ethernet cables), and thicker, hose-like cords ( snake cable) used to carry video or amplified signals. However, patch cords typically refer only to short cords used with patch panels. The term "patch" came from early use in telephony and radio studios, where extra equipment kept on standby could be temporarily substituted for failed devices. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Synthesizer
Modular synthesizers are synthesizers composed of separate modules for different functions. The modules can be connected together by the user to create a patch. The outputs from the modules may include audio signals, analog control voltages, or digital signals for logic or timing conditions. Typical modules are voltage-controlled oscillators, voltage-controlled filters, voltage-controlled amplifiers and envelope generators. History The first modular synthesizer was developed by German engineer Harald Bode in the late 1950s. The 1960s saw the introduction of the Moog synthesizer and the Buchla Modular Electronic Music System, created around the same period. The Moog was composed of separate modules which created and shaped sounds, such as envelopes, noise generators, filters, and sequencers, connected by patch cords. The Japanese company Roland released the Roland System 100 in 1975, followed by the System 700 in 1976 and the System 100m in 1979. In the late 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-frequency Oscillation
Low-frequency oscillation (LFO) is an electronic frequency that is usually below 20 Hz and creates a rhythmic pulse or sweep. This is used to modulate musical equipment such as synthesizers to create audio effects such as vibrato, tremolo and phasing. History Low-frequency oscillation was introduced with modular synthesizers of the 1960s, such as the Moog synthesizer. Often the LFO effect was accidental, as there were myriad configurations that could be "patched" by the synth operator. LFOs have since appeared in some form on almost every synthesizer. More recently other electronic musical instruments, such as samplers and software synthesizers, have included LFOs to increase their sound alteration capabilities. Overview The primary oscillator circuits of a synthesizer are used to create the audio signals. An LFO is a secondary oscillator that operates at a significantly lower frequency than other oscillators, typically below 20 Hz — that is, below the range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveshaper
In electronic music, waveshaping is a type of distortion synthesis in which complex spectra are produced from simple tones by altering the shape of the waveforms. Uses Waveshapers are used mainly by electronic musicians to achieve an extra-abrasive sound. This effect is most used to enhance the sound of a music synthesizer by altering the waveform or vowel. Rock musicians may also use a waveshaper for heavy distortion of a guitar or bass. Some synthesizers or virtual software instruments have built-in waveshapers. The effect can make instruments sound noisy or overdriven. In digital modeling of analog audio equipment such as tube amplifiers, waveshaping is used to introduce a static, or memoryless, nonlinearity to approximate the transfer characteristic of a vacuum tube or diode limiter. How it works A waveshaper is an audio effect that changes an audio signal by mapping an input signal to the output signal by applying a fixed or variable mathematical function, call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Keyboard
A musical keyboard is the set of adjacent depressible levers or keys on a musical instrument. Keyboards typically contain keys for playing the twelve notes of the Western musical scale, with a combination of larger, longer keys and smaller, shorter keys that repeats at the interval of an octave. Pressing a key on the keyboard makes the instrument produce sounds—either by mechanically striking a string or tine ( acoustic and electric piano, clavichord), plucking a string (harpsichord), causing air to flow through a pipe organ, striking a bell (carillon), or activating an electronic circuit (synthesizer, digital piano, electronic keyboard). Since the most commonly encountered keyboard instrument is the piano, the keyboard layout is often referred to as the piano keyboard or simply piano keys. Description The twelve notes of the Western musical scale are laid out with the lowest note on the left. The longer keys (for the seven "natural" notes of the C major scale: C, D, E, F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple IIe
The Apple IIe (styled as Apple //e) is the third model in the Apple II series of personal computers produced by Apple Inc., Apple Computer. It was released in January 1983 as the successor to the Apple II Plus. The ''e'' in the name stands for ''enhanced''. It is the first Apple II with built-in lowercase, 80-column text support and 64K RAM standard, while reducing the total chip count from previous models by approximately 75%. Improved expandability combined with the new features made for an attractive general-purpose machine to first-time computer shoppers. As the last surviving model of the Apple II computer line before discontinuation, and having been manufactured and sold for nearly 11 years with relatively few changes, the IIe was the longest-lived computer in Apple's history. History Apple Inc., Apple Computer planned to discontinue the Apple II series after the introduction of the Apple III in 1980; the company intended to clearly establish market segmentation by desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-subminiature
The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems. Description, nomenclature, and variants A D-sub contains two or more parallel rows of pins or sockets usually surrounded by a D-shaped metal shield, or shell, that provides mechanical support, ensures correct orientation, and may screen against electromagnetic interference. Calling that shield a shell (or D-shell) can be ambiguous, as the term shell is also short for the cable shell, or backshell. D-sub connectors have gender: parts with pin contacts are called ''male connectors'' or ''plugs'', while those with socket contacts are called ''female connectors'' or ''sockets''. The socket's shield fits tightly inside the plug's shield. Panel-mounted connectors usually have #4-40 UNC (as designated with the Unified Thread Standard) jackscrews that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |