|
Christopher Roy Monroe
Christopher Roy Monroe (born October 19, 1965) is an American physicist and engineer in the areas of atomic, molecular, and optical physics and quantum information science, especially quantum computing. He directs one of the leading research and development efforts in ion trap quantum computing. Monroe is the Gilhuly Family Presidential Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Physics at Duke University and was College Park Professor of Physics at the University of Maryland and Fellow of the Joint Quantum Institute and Joint Center for Quantum Computer Science until 2020 when he moved to Duke. He is also co-founder of IonQ, Inc. Career After receiving his undergraduate degree from MIT in 1987, Monroe joined Carl Wieman's research group at the University of Colorado in the early days of laser cooling and trapping of atoms. With Wieman and postdoctoral researcher Eric Cornell, Monroe contributed to the path for cooling a gas of atoms to the Bose-Eins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southfield, Michigan
Southfield is a city in Oakland County, Michigan, Oakland County in the U.S. state of Michigan. An inner-ring suburb of Detroit, Southfield borders Detroit to the north, roughly northwest of downtown Downtown Detroit, Detroit. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city had a population of 76,618. Southfield is notable as the home of multiple business districts, including the Southfield City Centre (an edge city which contains the tallest building in Detroit's suburbs) and the area surrounding the former Northland Center shopping mall. It is also home to Lawrence Technological University. The city was originally part of Southfield Township, Michigan, Southfield Township before incorporating in 1958. The autonomous city of Lathrup Village, Michigan, Lathrup Village is an enclave within Southfield. History Southfield was surveyed in 1817 according to the plan by Michigan territorial governor Lewis Cass. The first settlers came from nearby Birmingham, Michigan, Birm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the limitations imposed by practicality, regulation, safety and cost. "Science is knowledge based on our observed facts and tested truths arranged in an orderly system that can be validated and communicated to other people. Engineering is the creative application of scientific principles used to plan, build, direct, guide, manage, or work on systems to maintain and improve our daily lives." The word ''engineer'' (Latin , the origin of the Ir. in the title of engineer in countries like Belgium, The Netherlands, and Indonesia) is derived from the Latin words ("to contrive, devise") and ("cleverness"). The foundational qualifications of a licensed professional engineer typically include a four-year Bachelor of Engineering, bache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Simulator
Quantum simulators permit the study of a quantum system in a programmable fashion. In this instance, simulators are special purpose devices designed to provide insight about specific physics problems. Note: This manuscript is a contribution of the US National Institute of Standards and Technology and is not subject to US copyright. Quantum simulators may be contrasted with generally programmable "digital" quantum computers, which would be capable of solving a wider class of quantum problems. A universal quantum simulator is a quantum computer proposed by Yuri Manin in 1980 and Richard Feynman in 1982. A quantum system may be simulated by either a Turing machine or a quantum Turing machine, as a classical Turing machine is able to simulate a universal quantum computer (and therefore any simpler quantum simulator), meaning they are equivalent from the point of view of computability theory. The simulation of quantum physics by a classical computer has been shown to be ineffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor Chip
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components are etched onto a small, flat piece ("chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Integrated circuits are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and televisions, to perform various functions such as processing and storing information. They have greatly impacted the field of electronics by enabling device miniaturization and enhanced functionality. Integrated circuits are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete components, allowing a large transistor count. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design have ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Michigan, Ann Arbor
The University of Michigan (U-M, U of M, or Michigan) is a public research university in Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest institution of higher education in the state. The University of Michigan is one of the earliest American research universities and is a founding member of the Association of American Universities. In the fall of 2023, the university employed 8,189 faculty members and enrolled 52,065 students in its programs. The university is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". It consists of nineteen colleges and offers 250 degree programs at the undergraduate and graduate levels. The university is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission. In 2021, it ranked third among American universities in research expenditures according to the National Science Foundation. The University of Michigan's athletic teams are collectively known as the Wolverines. They compete in NCAA Division I ( FBS) as a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qubits
In quantum computing, a qubit () or quantum bit is a basic unit of quantum information—the quantum version of the classic binary bit physically realized with a two-state device. A qubit is a two-state (or two-level) quantum-mechanical system, one of the simplest quantum systems displaying the peculiarity of quantum mechanics. Examples include the spin of the electron in which the two levels can be taken as spin up and spin down; or the polarization of a single photon in which the two spin states (left-handed and the right-handed circular polarization) can also be measured as horizontal and vertical linear polarization. In a classical system, a bit would have to be in one state or the other. However, quantum mechanics allows the qubit to be in a coherent superposition of multiple states simultaneously, a property that is fundamental to quantum mechanics and quantum computing. Etymology The coining of the term ''qubit'' is attributed to Benjamin Schumacher. In the acknowledgmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States National Research Council
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), also known as the National Academies, is a congressionally chartered organization that serves as the collective scientific national academy of the United States. The name is used interchangeably in two senses: (1) as an umbrella term or parent organization for its three sub-divisions that operate as quasi-independent honorific learned society member organizations known as the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), the National Academy of Engineering (NAE), and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM); and (2) as the brand for studies and reports issued by the unified operating arm of the three academies originally known as the National Research Council (NRC). The National Academies also serve as public policy advisors, research institutes, think tanks, and public administration consultants on issues of public importance or on request by the government. The National Research Council, National Academy of Engineer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Wineland
David Jeffery Wineland (born February 24, 1944) is an American physicist at the Physical Measurement Laboratory of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). His most notable contributions include the laser cooling of trapped ions and the use of ions for quantum-computing operations. He received the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Serge Haroche, for "ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems." Early life and career Wineland was born in Wauwatosa, Wisconsin. He lived in Denver until he was three years old, at which time his family moved to Sacramento, California. Wineland graduated from Encina High School in Sacramento in 1961.Class of 1961 Graduation List encinahighschool.com In Sept. 1961–Dec. 1963, he studied at |
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred Nobel, Alfred Nobel's death. The original Nobel Prizes covered five fields: Nobel Prize in Physics, physics, Nobel Prize in Chemistry, chemistry, Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, physiology or medicine, Nobel Prize in Literature, literature, and Nobel Peace Prize, peace, specified in Nobel's will. A sixth prize, the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, Prize in Economic Sciences, was established in 1968 by Sveriges Riksbank (Sweden's central bank) in memory of Alfred Nobel. The Nobel Prizes are widely regarded as the most prestigious awards available in their respective fields.Nobel Prize#Shalev69, Shalev, p. 8. Except in extraordinary circumstances, such as war, all six prizes are given annually. Each recipient, known as a laur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
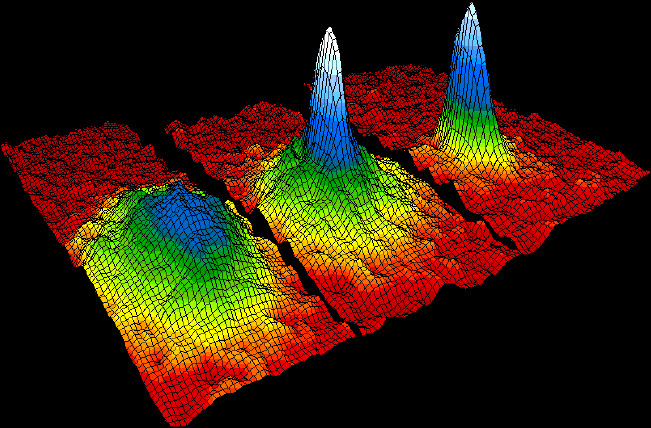
Bose–Einstein Condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low Density, densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero#Relation with Bose–Einstein condensate, absolute zero, i.e. . Under such conditions, a large fraction of bosons occupy the lowest quantum state, at which microscopic Quantum mechanics, quantum-mechanical phenomena, particularly wave interference#Quantum interference, wavefunction interference, become apparent Macroscopic quantum phenomena, macroscopically. More generally, condensation refers to the appearance of macroscopic occupation of one or several states: for example, in BCS theory, a superconductor is a condensate of Cooper pairs. As such, condensation can be associated with phase transition, and the macroscopic occupation of the state is the order parameter. Bose–Einstein condensate was first predicted, generally, in 1924–1925 by Albert Einstein, credit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Cornell
Eric Allin Cornell (born December 19, 1961) is an American physicist who, along with Carl E. Wieman, was able to synthesize the first Bose–Einstein condensate in 1995. For their efforts, Cornell, Wieman, and Wolfgang Ketterle shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2001. Biography Cornell was born in Palo Alto, California, where his parents were completing graduate degrees at nearby Stanford University. Two years later he moved to Cambridge, Massachusetts, where his father was a professor of civil engineering at MIT. Here he grew up with his younger brother and sister, with year-long stints in Berkeley, California, and Lisbon, Portugal, accompanying his father whilst on sabbatical. In Cambridge he attended Cambridge Rindge and Latin School. The year before his graduation he moved back to California with his mother and finished high school at San Francisco's Lowell High School, a local magnet school for academically talented students. After high school he enrolled at Stanford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IonQ
IonQ, Inc. is an American quantum computing hardware and software company headquartered in College Park, Maryland. The company develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and accompanying software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits. History IonQ was co-founded by Christopher Monroe and Jungsang Kim, professors at Duke University, in 2015, with the help of Harry Weller and Andrew Schoen, partners at venture firm New Enterprise Associates. The company is an offshoot of the co-founders’ 25 years of academic research in quantum information science. Monroe's quantum computing research began as a Staff Researcher at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) with Nobel-laureate physicist David Wineland where he led a team using trapped ions to produce the first controllable qubits and the first controllable quantum logic gate, culminating in a proposed architecture for a large-scale trapped ion computer. Kim and Monroe began collabora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |