|
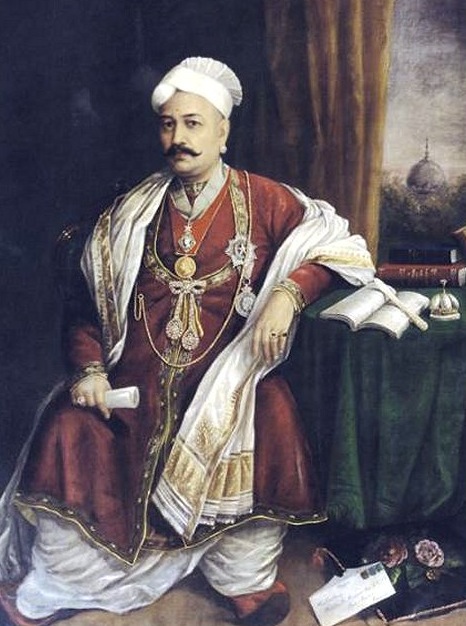
Christian Brahmin
Roman Catholic Brahmin (IAST ''Bamonns'' in Romi Konkani & '' Kupari'' in Bombay East Indian dialects) is a Christianised caste among the Goan, Bombay East Indian & Mangalorean Catholics; who are patrilineal descendants of Konkani Brahmin and Daivajna converts to the Latin Church. This occurred parts of the Konkan region that were annexed into the Portuguese East Indies, with the capital (metropole) at '' Velha Goa'' & Bombay ('' Bom Bahia'') was the largest territory (province) of Portuguese India. They retain some of the ethno-social values and customs of their ancestors, and most of them exhibit a noticeable hybrid Latino- Concanic culture. Origins In Goa, the Brahmins were engaged in the priestly occupation, but had also taken up various occupations like agriculture, trade, goldsmithing, etc. The origins of this particular caste can be traced back to the Christianisation of the Velhas Conquistas () that was undertaken by the Portuguese, during the 16th & 17th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Brahmic family, Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the 19th century from suggestions by Sir Charles Trevelyan, 1st Baronet, Charles Trevelyan, William Jones (philologist), William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva International Congress of Orientalists, Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars. Usage Scholars commonly use IAST in publications that cite textual material in Sanskrit, Pāḷi and other classical Indian languages. IAST is also used for major e-text repos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese India
The State of India, also known as the Portuguese State of India or Portuguese India, was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded seven years after the discovery of the sea route to the Indian subcontinent by Vasco da Gama, a subject of the Kingdom of Portugal. The capital of Portuguese India served as the governing centre of a string of military forts and maritime ports scattered along the coasts of the Indian Ocean. The first viceroy Francisco de Almeida established his base of operations at Fort Manuel in the Malabar region, after the Kingdom of Cochin negotiated to become a protectorate of Portugal in 1505. With the Portuguese conquest of Goa from the Bijapur Sultanate in 1510, Goa became the major anchorage for the Armadas arriving in India. The capital of the viceroyalty was transferred from Cochin to Goa in 1530. From 1535, Mumbai (Bombay) was a harbour of Portuguese India, known as '' Bom Bahia'', until it was handed over, through the Marriage Treaty, dowry o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deshastha Brahmin
Deshastha Brahmin is a Hinduism, Hindu Brahmin caste, subcaste mainly from the Indian state of Maharashtra and North Karnataka. Other than these states, according to authors K. S. Singh, Gregory Naik and Pran Nath Chopra, Deshastha Brahmins are also concentrated in the states of Telangana , Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh Historian Pran Nath Chopra and journalist Pritish Nandy say, "Most of the well-known saints from Maharashtra, Karnataka and Combined Andhra Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh were Deshastha Brahmins". The mother tongue of Deshastha Brahmins is either Marathi language, Marathi or Kannada language, Kannada. Over the millennia, the Deshastha community has produced Mathematicians such as Bhāskara II, Sanskrit scholars such as Bhavabhuti, Satyanatha Tirtha, Satyadharma Tirtha; Bhakti movement, Bhakti saints such as Dnyaneshwar, Eknath, Purandara Dasa, Samarth Ramdas and Vijaya Dasa; polemical logician such as Jayatirtha and non-polemical scholar such as Raghuttama Tirth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chitpavan Brahmin
The Chitpavan Brahmin or the Kokanastha Brahmin is a Hindu Maharashtrian Brahmin community inhabiting Konkan, the coastal region of the state of Maharashtra. Initially working as messengers and spies in the late seventeenth century, the community came into prominence during the 18th century when the heirs of Peshwa from the Bhat family of Balaji Vishwanath became the de facto rulers of the Maratha empire. Until the 18th century, the Chitpavans were held in low esteem by the Deshastha, the older established Brahmin community of Karnataka-Maharashtra region. As per Jayant Lele, the influence of the Chitpavans in the Peshwa era as well as the British era has been greatly exaggerated because even during the time of the most prominent Peshwas, their political legitimacy and their intentions were not trusted by all levels of the administration, not even by Shivaji's successors. He adds that after the defeat of Peshwas in the Anglo-Maratha wars, Chitpavans were one of the Hindu co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carambolim (Karmali)
Carambolim, also called Karmali, is a village in North Goa district, Goa, India. Geography It is located at an elevation of 5 m above MSL.http://www.fallingrain.com/world/IN/33/Carambolim.html Map and weather of Karmali Location The railway station at Carambolim (Karmali) falls under the jurisdiction of the Konkan Railway The Konkan Railway (abbreviated KR) is one of the 19 railway zones in India with its headquarters at CBD Belapur in Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. The Konkan Railway line from Roha to Thokur is operated and maintained by Konkan Railway co .... References External links Satellite map of Karmali Villages in North Goa district {{Goa-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kshatriya
Kshatriya () (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority"; also called Rajanya) is one of the four varnas (social orders) of Hindu society and is associated with the warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the context of later Vedic society wherein members were organised into four classes: ''brahmin'', kshatriya, '' vaishya,'' and '' shudra''. History Early Rigvedic tribal monarchy The administrative machinery in Vedic India was headed by a tribal king called a Rajan whose position may or may not have been hereditary. The king may have been elected in a tribal assembly (called a Samiti), which included women. The Rajan protected the tribe and cattle; was assisted by a priest; and did not maintain a standing army, though in the later period the rulership appears to have risen as a social class. The concept of the fourfold varna system is not yet recorded. Later Vedic period The hymn '' Purusha Sukta'' in the ''Rigveda'' describes the symbolic crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divar
The island of Divar (formerly ''Piedade'') (, pronounced ) (derived from the word ''Dipavati'' or 'small Island' in Konkani) lies in the Mandovi river in the Indian state of Goa. It is one of six major islands within the Mandovi, the others being: * Ilha de Goa, * Chorão, * Vanxim, * Cumbarjua, * St Estevam and * Several other small mangrove islands and sand banks. Location It is located approximately upriver from Panjim. The island is dis-connected from Old Goa on the south-east side, Ribandar, on the south-west side and Naroa on the north side, all by ferry. A launch also connects Divar to the city of Panjim from further north-west, in the island-village of Vanxim. The Konkan Railway passes through the village and the nearest stop to the village is the train station at Carambolim. The drive to the village is scenic, with paddy fields and wooded hills lacing the roadway, very typical of the Goan countryside. Villages Initially, there were three Communidades in D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers (, abbreviated OP), commonly known as the Dominican Order, is a Catholic Church, Catholic mendicant order of pontifical right that was founded in France by a Castilians, Castilian priest named Saint Dominic, Dominic de Guzmán. It was approved by Pope Honorius III via the papal bull on 22 December 1216. Members of the order, who are referred to as Dominicans, generally display the letters ''OP'' after their names, standing for , meaning 'of the Order of Preachers'. Membership in the order includes friars, nuns, Religious sister (Catholic), active sisters, and Laity, lay or secular Dominicans (formerly known as Third Order of Saint Dominic, tertiaries). More recently, there have been a growing number of associates of the religious sisters who are unrelated to the tertiaries. Founded to preach the The gospel, gospel and to oppose heresy, the teaching activity of the order and its scholastic organisation placed it at the forefront of the intellectual life of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
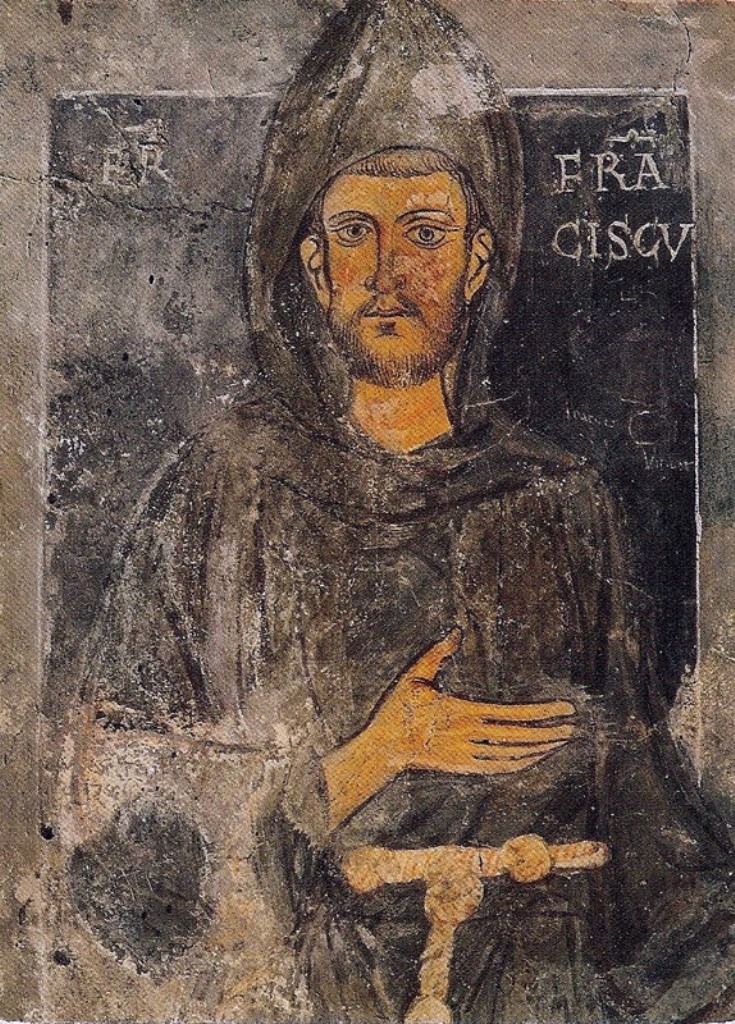
Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor being the largest contemporary male order), an order for nuns known as the Order of Saint Clare, and the Third Order of Saint Francis, a Third Order of Saint Francis#Third Order Regular, religious and Secular Franciscan Order, secular group open to male and female members. Franciscans adhere to the teachings and spiritual disciplines of the founder and of his main associates and followers, such as Clare of Assisi, Anthony of Padua, and Elizabeth of Hungary. Several smaller Franciscan spirituality in Protestantism, Protestant Franciscan orders have been established since the late 19th century as well, particularly in the Lutheranism, Lutheran and Anglicanism, Anglican traditions. Certain Franciscan communities are ecumenism, ecumenical in nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Jesus
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 by Ignatius of Loyola and six companions, with the approval of Pope Paul III. The Society of Jesus is the largest religious order in the Catholic Church and has played significant role in education, charity, humanitarian acts and global policies. The Society of Jesus is engaged in evangelization and apostolic ministry in 112 countries. Jesuits work in education, research, and cultural pursuits. They also conduct retreats, minister in hospitals and parishes, sponsor direct social and humanitarian works, and promote ecumenical dialogue. The Society of Jesus is consecrated under the patronage of Madonna della Strada, a title of the Blessed Virgin Mary, and it is led by a superior general. The headquarters of the society, its general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
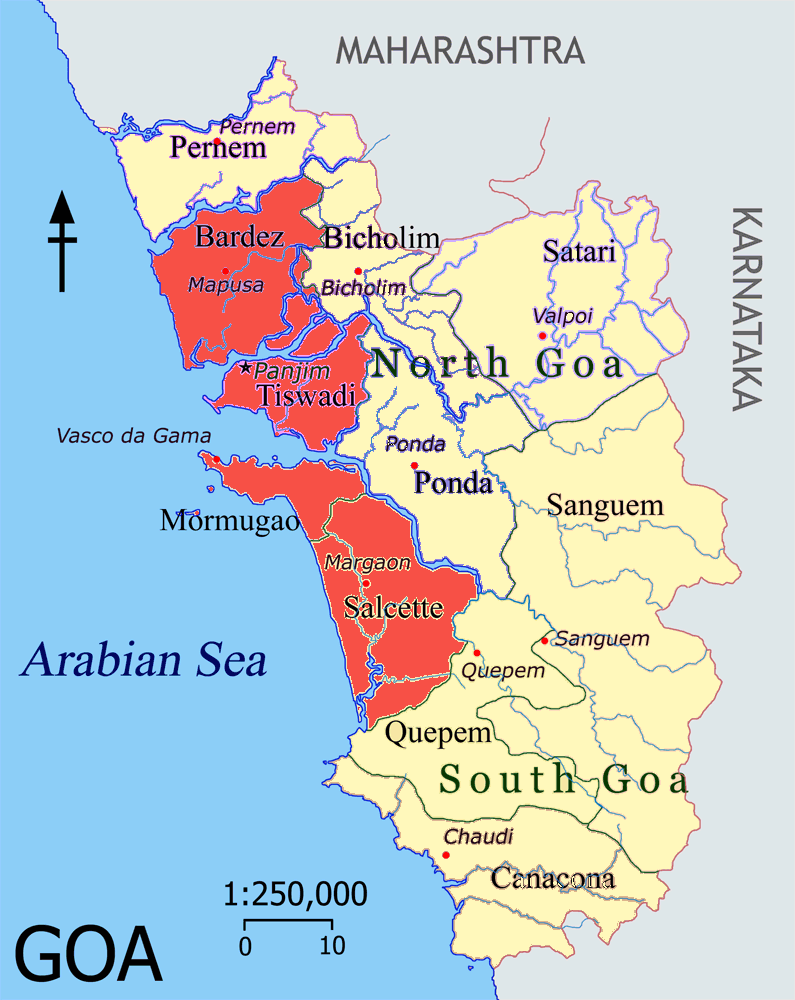
Velhas Conquistas
The ''Velhas Conquistas'' or "Old Conquests" are a grouping of the areas in Goa which were incorporated into Portuguese India in the early half of the sixteenth century AD. Goa, Daman and Diu comprised the last remaining Portuguese possessions in India. Portuguese Macao, Macao and Timor Leste were administratively separated. Over the course of nearly five centuries of European rule since the Portuguese conquest of Goa, these areas underwent urbanisation and they were elevated to ''concelhos'' (municipalities), with the administrative centre at Velha Goa. Having been acquired by 1510 AD or within the next few decades, they formed the oldest parts and the core of Portuguese Goa and remain the central theme in the history, geography, and culture of present-day Goa. The ''Novas Conquistas'' or New Conquests are the outer periphery of Goa, surrounding ''Velha Conquistas'' and bordering the erstwhile British India. ''Novas Conquistas'' of present-day Goa shares borders with the Konkan d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianisation
Christianization (or Christianisation) is a term for the specific type of change that occurs when someone or something has been or is being converted to Christianity. Christianization has, for the most part, spread through missions by individual conversions, but has also, in some instances, been the result of violence by individuals and groups such as governments and militaries. Christianization is also the term used to designate the conversion of previously non-Christian practices, spaces and places to Christian uses and names. In a third manner, the term has been used to describe the changes that naturally emerge in a nation when sufficient numbers of individuals convert, or when secular leaders require those changes. Christianization of a nation is an ongoing process. It began in the Roman Empire when the early individual followers of Jesus became itinerant preachers in response to the command recorded in Matthew 28:19 (sometimes called the Great Commission) to go to all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |