|
Chrislea Super Ace
The Chrislea Super Ace is a 1940s United Kingdom, British four-seat light aircraft built by Chrislea Aircraft, Chrislea Aircraft Limited. History The Super Ace was developed from the earlier Chrislea C.H.3 Series 1 Ace, a high-wing four seat cabin monoplane with a tricycle Landing gear, undercarriage and two fins. The Ace had an unusual 'steering wheel' control arrangement which eliminated the conventional rudder bar. The wheel was mounted on a universal joint; turning it applied aileron, moving it vertically applied elevator and sideways the rudder. It originally flew with a single vertical tail but was soon modified with twin fins. The lone C.H.3 Series 1 Ace first flew in September 1946. Soon after the company moved to Exeter, the first production aircraft, the C.H.3 Series 2 Super Ace flew in February 1948 in aviation, 1948. This model was powered by a de Havilland Gipsy Major, de Havilland Gipsy Major 10 inline piston engine. Wing and tailplane were n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrislea Aircraft
Chrislea Aircraft Limited was a British aircraft manufacturer, formed in 1936 and closed in 1952. History The company was formed on 2 October 1936 at Heston Aerodrome near London, England, to build the designs of Richard Christoforides. The company name was derived from the partners Christoforides and Bernard Victor Leak. The first product was the Airguard which first flew in 1938 in aviation, 1938. The Ace first flew in 1946 in aviation, 1946 and soon after in April 1947 in aviation, 1947 the company moved to Exeter International Airport (due to the closure of Heston). At Exeter the Super Ace and Skyjeep were produced, but the aircraft did not sell well due to resistance to the unusual control wheel used. The managing director and chief designer R.C. Christoforides left the company after internal problems, reduced demand and low production levels, with the assets of the company being bought by C.E.Harper Aircraft Limited in 1952, which scrapped all partly constructed and non-flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country#Countries, second-largest Muslim population as of 2023. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is List of cities in Pakistan by population, its largest city and financial centre. Pakistan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 33rd-largest country by area. Bounded by the Arabian Sea on the south, the Gulf of Oman on the southwest, and the Sir Creek on the southeast, it shares land borders with India to the east; Afghanistan to the west; Iran to the southwest; and China to the northeast. It shares a maritime border with Oman in the Gulf of Oman, and is separated from Tajikistan in the northwest by Afghanistan's narrow Wakhan Corridor. Pakistan is the site of History of Pakistan, several ancient cultures, including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia (historically known as Indochina and the Indochinese Peninsula) is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. It includes the countries of Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam as well as Peninsular Malaysia. The term ''Indochina'' (originally ''Indo-China'') was coined in the early nineteenth century, emphasizing the historical cultural influence of Indian and Chinese civilizations on the region. The term was later adopted as the name of the colony of French Indochina (present-day Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam). Today, the term "Mainland Southeast Asia" is more commonly used, in contrast to Maritime Southeast Asia for the island groups off the coast of the peninsula. Terminology In Indian sources, the earliest name connected with Southeast Asia is . Another possible early name of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast. It is part of the Southern Cone region of South America. Uruguay covers an area of approximately . It has a population of almost 3.5 million people, of whom nearly 2 million live in Montevideo metropolitan area, the metropolitan area of its capital and List of cities in Uruguay, largest city, Montevideo. The area that became Uruguay was first inhabited by groups of hunter gatherer, hunter gatherers 13,000 years ago. The first European explorer to reach the region was Juan Díaz de Solís in 1516, but the area was colonized later than its neighbors. At the time of Spanish colonization of the Americas, European arrival, the Charrúa were the predominant tribe, alongside other groups such as the Guaraní people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackburn Cirrus Major
The Blackburn Cirrus Major is a British, inline-four aircraft engine which was developed in the late 1930s, but continued development and production into the 1940s and post war. Design and development The Blackburn Cirrus Major started life as a clean-sheet replacement for the original 1920s Cirrus and Hermes series of upright inline four-cylinder air cooled aircraft engines originally designed by Frank Halford for the early DH60 de Havilland Cirrus Moth and which had been in production by the Aircraft Disposal Company (ADC) and later Cirrus Aero Engine Limited, which itself evolved into the Cirrus-Hermes Engineering Company. C. S. Napier, son of engine designer Montague Napier, was Technical Director and Chief Designer for Cirrus-Hermes Engineering when he began work on two new engines, the Cirrus minor and the larger Cirrus Major. The engines were still under development when the company was bought by the Blackburn Aeroplane & Motor Company, moved to a new factory at Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French language, French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds Aircrew, crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an Aircraft engine, engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft the single engine is mounted on a hardpoint, pylon attached to the fuselage, which in turn is used as a floating Hull (watercraft), hull. The fuselage also serves to position the Flight control surfaces, control and Stabilizer (aeronautics), stabilization surfaces in specific relationships to Wing, lifting surfaces, which is required for aircraft stability and maneuverability. Types of structures Truss structure This type of structure is still in use in many lightweight aircraft using welding, welded steel tube trusses. A box truss fuselage structure can also be built out of wood—often covered with plywood. Simple box structures may be rounded by the addition of supported lightweight strin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional Landing Gear
Conventional landing gear, or tailwheel-type landing gear, is an aircraft Landing gear, undercarriage consisting of two main wheels forward of the Center of gravity of an aircraft, center of gravity and a small wheel or skid to support the tail.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 133. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. From the Ground Up, 27th edition, page 11 The term taildragger is also used. The term "conventional" persists for historical reasons, but all modern jet aircraft and most modern propeller aircraft use tricycle gear. History In early aircraft, a tailskid made of metal or wood was used to support the tail on the ground. In most modern aircraft with conventional landing gear, a small articulated wheel assembly is attached to the rearmost part of the airframe in place of the skid. This wheel may be steered by the pilot through a connection to the rudder pedals, allowing the rudder and tailwheel to move together. Before aircraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1949 In Aviation
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1949: Events * Aerolíneas Argentinas is established. * Royal Jordanian Air Force is formed as the Arab League Air Force. * Republic of Korea Air Force is formed. * Lebanese Air Force is formed. * The de Havilland Sea Hornets of No. 801 Squadron, Fleet Air Arm, embark aboard the Royal Navy aircraft carrier , becoming the first British twin-engined single-seat aircraft to operate from an aircraft carrier. * Bahrain-based Gulf Aviation, the forerunner of Gulf Air, is founded. It will begin flight operations in July 1950. * The American Section of the International League of Aviators awards the National Trophy, a Harmon Trophy awarded from 1926 to 1938 to the outstanding aviator of the year in each of the 21 member countries of the now-defunct League and since 1945 by the American Section, for the last time. The trophies it presented from 1945 to 1949 stirred much controversy, with the awards going largely unrecognized. * The cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller islands. It has a total area of , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country in the world and the largest in Oceania. Australia is the world's flattest and driest inhabited continent. It is a megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and Climate of Australia, climates including deserts of Australia, deserts in the Outback, interior and forests of Australia, tropical rainforests along the Eastern states of Australia, coast. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south-east Asia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last glacial period. By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
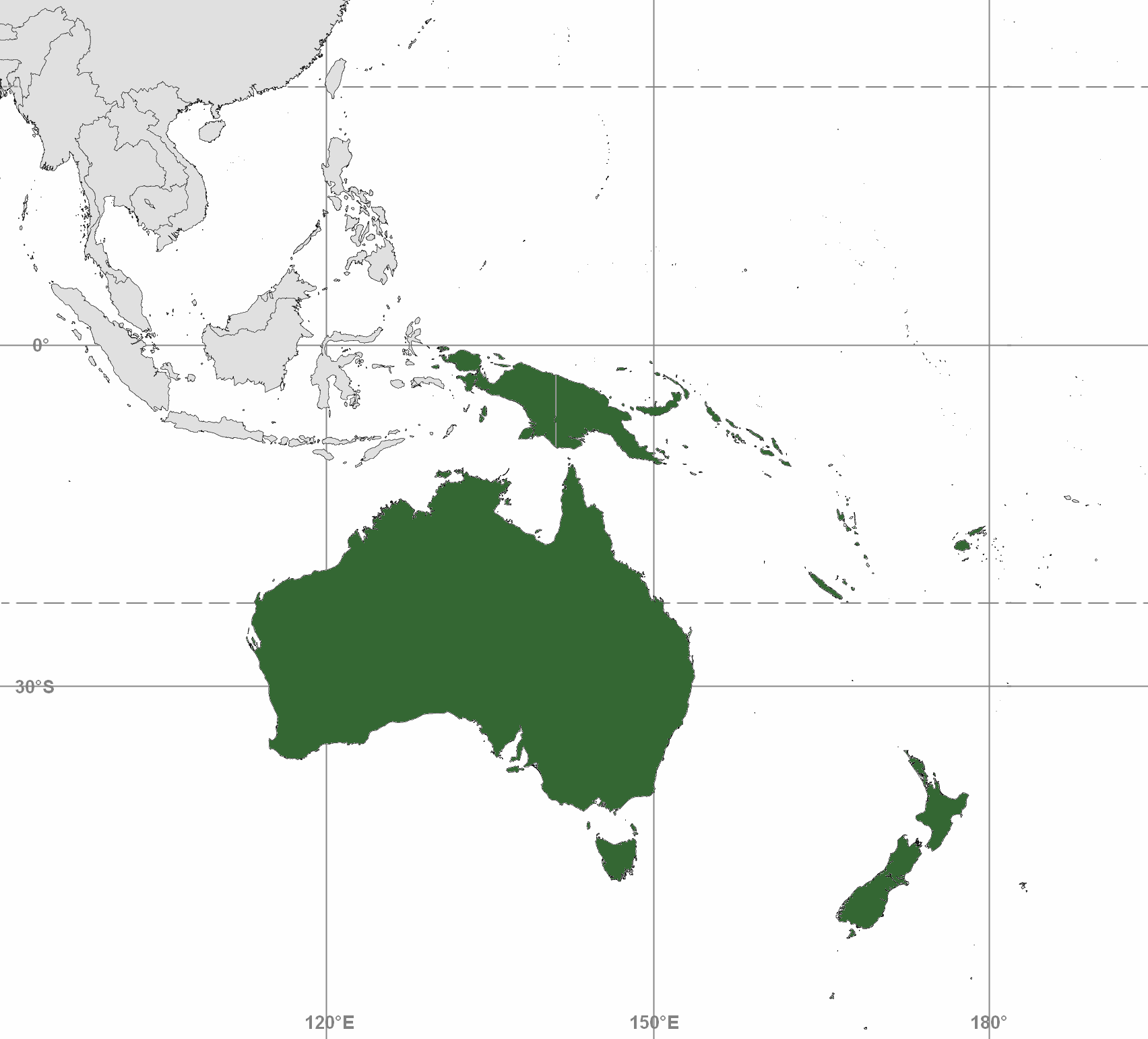
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |