|
Chojnik
Chojnik Castle (pronounced , , 1945–1948 ) is a castle located above the town of Sobieszów, today part of Jelenia Góra in southwestern Poland. Its remains stand on top of the Chojnik hill () within the Karkonosze National Park, overlooking the Jelenia Góra valley. The building of the fortress dates back to the times of the Silesian Piasts and for most of its time was in the possession of the Schaffgotsch noble family. Today the semi-ruined stronghold is a major tourist attraction and houses a hotel and a restaurant. History The castle of Chojnik was originally raised by the order of Duke Bolko I the Strict in 1292 at the site of a former hunting lodge built by his father Bolesław II the Bald. The fortress was meant to protect the borders of Bolko's Duchy of Jawor against the menacing Wenceslaus II of Bohemia. Bolko's grandson Bolko II the Small, the last independent Piast duke, had the castle reconstructed starting from 1355. After Bolko II had died without issue i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
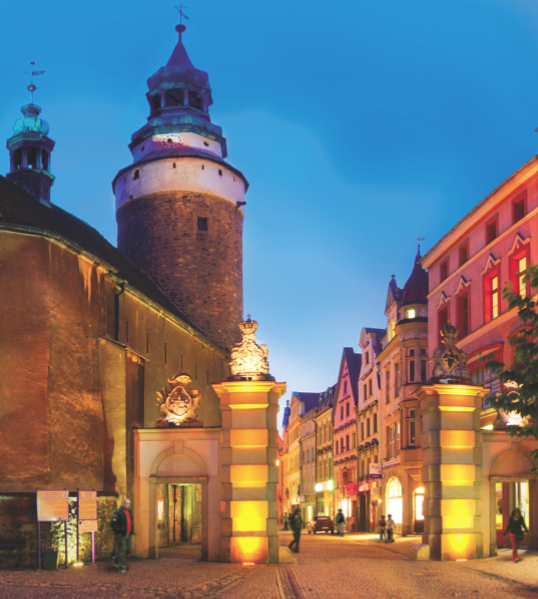
Jelenia Góra
Jelenia Góra (; ; ) is a historic city in southwestern Poland, within the historical region of Lower Silesia. Jelenia Góra is situated in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, close to the Karkonosze mountain range running along the Polish-Czech border – ski resorts such as Karpacz and Szklarska Poręba are situated from the city. Jelenia Góra constitutes a separate urban gmina as well as being the seat of surrounding Karkonosze County (formerly Jelenia Góra County). In 2021 the population of Jelenia Góra was 77,366. The area, including the oldest spa district of Cieplice Śląskie-Zdrój, is one of the most valued recreational and leisure spots in Poland. The city's history dates back to as early as the 10th century, but the settlement was granted town rights under Polish rule in 1288. Jelenia Góra was founded on important trade routes linking the Holy Roman Empire and Bohemia with Eastern Europe. The region flourished as a result of trade privileges that became the ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Schaffgotsch
The Schaffgotsch family is an old and influential Silesian nobility which dates back to the thirteenth century. Some of its members played important roles in the public life of Bohemia, then Habsburg monarchy and later Prussia. History Around 1240, the first Schaffgotsch appears in a Silesian document as ''Sibotho de nobili Familia Ovium'' (''ovium'' is the Latin word for "sheep", the translation of the German word ''Schaf(f)''). According to tradition, Sibotho came in the entourage of Duke Henry I the Bearded and his wife Hedwig of Andechs. One of Sibotho's successors, the knight Gotsche II Schoff (†1420), bought extensive possessions in the foreland of the Giant Mountains (''Riesengebirge'') and Jizera Mountains (''Isergebirge'') at the end of the fourteenth century: the Kynast and Greiffenstein dominions. The Schaffgotsch family thus became the most important noble family in the Jelenia Góra Valley (''Hirschberger Tal''). In 1403, Gotsche II donated the church at Warmb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jelenia Góra Valley
Jelenia Góra Valley (; ; ; Literally ''"Deer Mountain Valley"'') in Poland is a big valley at the Silesian northern side of the Western Sudetes and next to Kłodzko Valley the largest intermontane basin of the Sudetes. It is situated at an altitude of 250–400 meters above sea level and covers an area of 273 km2. In the 19th century, the lovely landscape attracted the Prussian high nobility, which built magnificent palaces, manors and parks. The enormous number of stately homes turned the valley into one of the most important garden landscapes in Middle Europe. The palaces and landscape parks of the Jelenia Góra valley represent one of Poland's official national Historic Monuments (''Pomnik historii''), as designated on 20 September 2011. Its listing is maintained by the National Heritage Board of Poland. Geography Jelenia Góra valley is surrounded by parts of the Sudetes mountains. It lies at the foot of the Karkonosze, which are also its southern limit. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sobieszów
Sobieszów is a part of Jelenia Góra in Poland, located in the south-western part of the city. It is located near Karkonosze National Park Giant Mountains National Park () is a National Park in the Giant Mountains in the Sudetes in southwestern Poland, along the border with the Czech Republic. The national park is located in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in the highest part of the Sud .... The ruined castle Chojnik is located in Sobieszów. References Jelenia Góra Neighbourhoods in Poland {{LowerSilesian-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
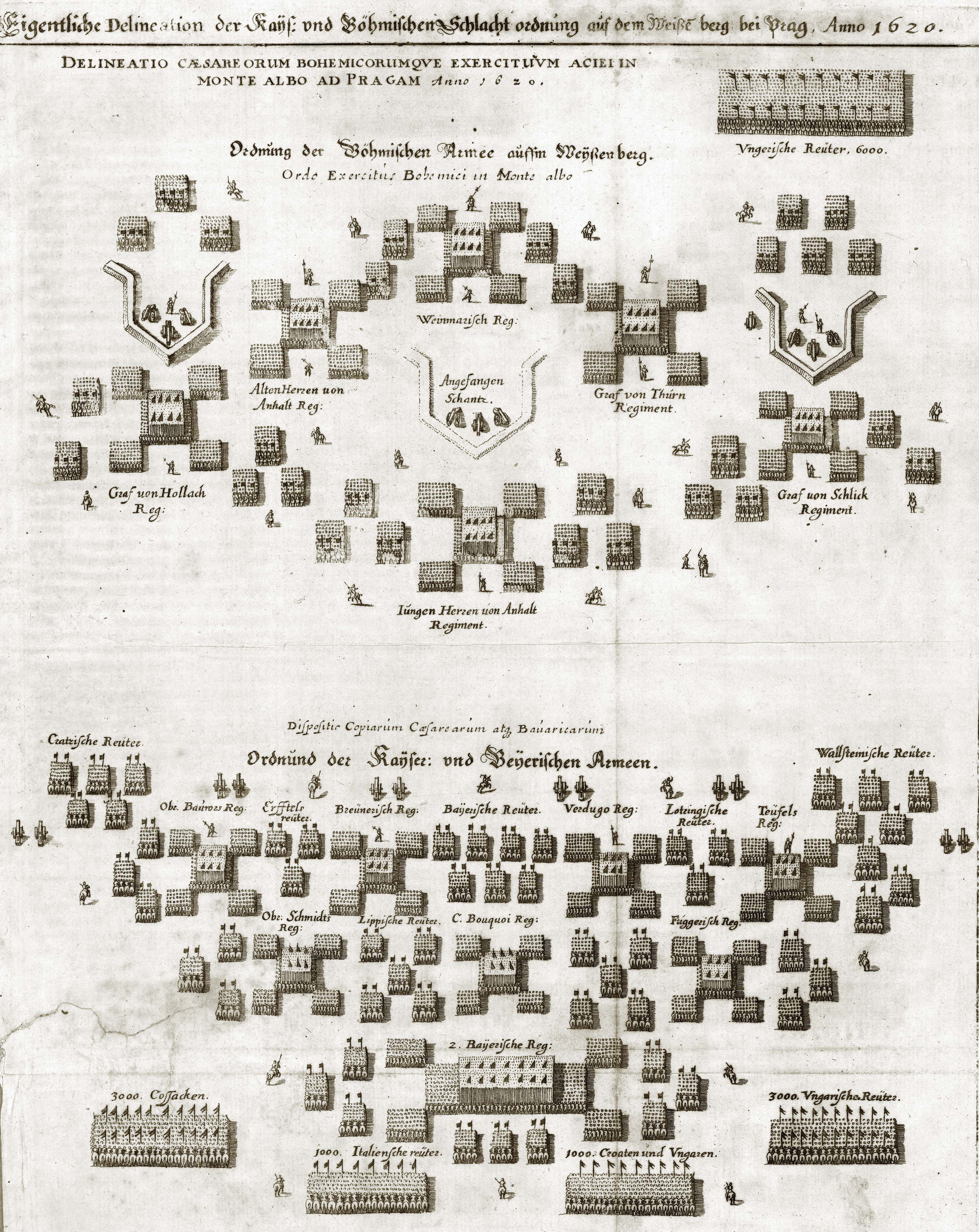
Battle Of White Mountain
The Battle of White Mountain (; ) was an important battle in the early stages of the Thirty Years' War. It led to the defeat of the Bohemian Revolt and ensured Habsburg control for the next three hundred years. It was fought on 8 November 1620. An army of 21,000 Bohemians and mercenaries under Christian of Anhalt was defeated by 23,000 men of the combined armies of Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor, led by Charles Bonaventure de Longueval, Count of Bucquoy, and the German Catholic League led by Johann Tserclaes, later Count of Tilly, at Bílá Hora ("White Mountain") near Prague. Bohemian casualties were not severe but their morale collapsed and Imperial forces occupied Prague the next day. Prelude In the early 17th century most of the Bohemian estates, although under the dominion of the predominantly Catholic Holy Roman Empire, had large Protestant populations, and had been granted rights and protections allowing them varying degrees of religious and political freedom. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, while parts of Germany reported population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, the Torstenson War, the Dutch-Portuguese War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. The war had its origins in the 16th-century Reformation, which led to religious conflict within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Catholic and Lutheran states, but the settlement was destabilised by the subsequent expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries. Combined with differences over the limits of imperial authority, religion was thus an important factor in star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Ulrich Von Schaffgotsch
Hans Ulrich von Schaffgotsch (28 August 1595 – 24 July 1635) was a Silesian nobleman and Generalfeldwachtmeister who fought in the Silesian front of the Thirty Years' War. He was falsely convicted of treason and executed following a purge within the army of the Holy Roman Empire that targeted officers associated with former Generalissimo Albrecht von Wallenstein. Early life Hans Ulrich was born on 28 August 1595 in Greiffenstein castle, as the son of Christoph, Freiherr von Schaffgotsch zu Trachenberg, Kynast and Greifenstein (1552-1601) by his second wife, Baroness Eleonore von German nobility, Promnitz (1576-1611). The Schaffgotsch family belonged to an old Silesian nobility. Upon the death of his father and his relative Adam von Schaffgotsch (1542-1601), he inherited vast estates including Gryfów Śląski, Greiffenberg, Greiffenstein, Kynast, Gierałtowiec, Giersdorf, Trachenberg-Prausnitz, Kowary, Schmiedeberg as well as territories between the Riesengebirge mountain and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Union
The Protestant Union (), also known as the Evangelical Union, Union of Auhausen, German Union or the Protestant Action Party, was a coalition of Protestant German states. It was formed on 14 May 1608 by Frederick IV, Elector Palatine in order to defend the rights, land and safety of each member. It included both Calvinism, Calvinist and Lutheran states, and dissolved in 1621. Formation The union was formed following two events. Firstly, the Holy Roman Emperor Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, Rudolf II and Duchy of Bavaria, Bavarian Duke Maximilian I, Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian I reestablished Catholic Church, Catholicism in Donauwörth in 1607. Secondly, by 1608, a majority of the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet had decided that the renewal of the 1555 Peace of Augsburg should be conditional upon the restoration of all church land appropriated since 1552. The Protestant princes met in Auhausen, and formed a coalition of Protestant states under the leadership of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High Middle Ages, High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as ''opus Francigenum'' (); the term ''Gothic'' was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the Classical architecture, architecture of classical antiquity. The defining design element of Gothic architecture is the Pointed arch (architecture), pointed arch. The use of the pointed arch in turn led to the development of the pointed rib vault and flying buttresses, combined with elaborate tracery and stained glass windows. At the Abbey of Basilica of Saint-Denis, Saint-Denis, near Paris, the choir was rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand II (9 July 1578 – 15 February 1637) was Holy Roman Emperor, King of Bohemia, King of Hungary, Hungary, and List of Croatian monarchs, Croatia from 1619 until his death in 1637. He was the son of Archduke Charles II, Archduke of Austria, Charles II of Inner Austria and Maria Anna of Bavaria (born 1551), Maria of Bavaria, who were devout Catholic Church, Catholics. In 1590, when Ferdinand was 11 years old, they sent him to study at the University of Ingolstadt, Jesuits' college in Ingolstadt because they wanted to isolate him from the Lutheranism, Lutheran nobles. A few months later, his father died, and he inherited Inner Austria–Duchy of Styria, Styria, Duchy of Carinthia, Carinthia, Duchy of Carniola, Carniola and smaller provinces. His cousin, Rudolf II, Holy Roman Emperor, who was the head of the Habsburg family, appointed regents to administer these lands. Ferdinand was installed as the actual ruler of the Inner Austrian provinces in 1596 and 1597. Rudolf II al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrecht Von Wallenstein
Albrecht Wenzel Eusebius von Wallenstein, Duke of Friedland (; 24 September 1583 – 25 February 1634), also von Waldstein (), was a Bohemian military leader and statesman who fought on the Catholic side during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). His successful martial career made him one of the richest and most influential men in the Holy Roman Empire by the time of his death. Wallenstein became the supreme commander of the armies of Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II and was a major figure of the Thirty Years' War. Wallenstein was born in the Kingdom of Bohemia into a poor Czech Protestant noble family, affiliated with the Utraquist Hussites, a group of notable anti-German sentiment in some of its circles, and following the teachings of the early reformer Jan Hus. He acquired a multilingual university education across Europe and converted to Catholicism in 1606. A marriage in 1609 to the wealthy widow of a Bohemian landowner gave him access to considerable estates and wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |