|
Choanofila
Holozoa () is a clade of organisms that includes animals and their closest single-celled relatives, but excludes fungi and all other organisms. Together they amount to more than 1.5 million species of purely heterotrophic organisms, including around 300 unicellular species. It consists of various subgroups, namely Metazoa (or animals) and the protists Choanoflagellata, Filasterea, Pluriformea and Ichthyosporea. Along with fungi and some other groups, Holozoa is part of the Opisthokonta, a supergroup of eukaryotes. Choanofila was previously used as the name for a group similar in composition to Holozoa, but its usage is discouraged now because it excludes animals and is therefore paraphyletic. The holozoan protists play a crucial role in understanding the evolutionary steps leading to the emergence of multicellular animals from single-celled ancestors. Recent genomic studies have shed light on the evolutionary relationships between the various holozoan lineages, revealing ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choanozoa
Choanozoa is a clade of opisthokont eukaryotes consisting of the choanoflagellates (Choanoflagellatea) and the animals (Animalia, Metazoa). The sister-group relationship between the choanoflagellates and animals has important implications for the origin of the animals. The clade was identified in 2015 by Graham Budd and Sören Jensen, who used the name Apoikozoa. The 2018 revision of the classification first proposed by the International Society of Protistologists in 2012 recommends the use of the name Choanozoa. Introduction A close relationship between choanoflagellates and animals has long been recognised, dating back at least to the 1840s. A particularly striking and famous similarity between the single-celled choanoflagellates and multicellular animals is provided by the collar cells of sponges and the overall morphology of the choanoflagellate cell. The relationship has since been confirmed by multiple molecular analyses. This proposed homology was however thrown into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonian
The Tonian (from , meaning "stretch") is the first geologic period of the Neoproterozoic era (geology), Era. It lasted from to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, ICS based on radiometric dating, radiometric chronometry. The Tonian is preceded by the Stenian Period of the Mesoproterozoic Era and followed by the Cryogenian. Rifting leading to the breakup of supercontinent Rodinia, which had formed in the mid-Stenian, occurred during this period, starting from 900 to 850 Mya. Biology The first putative metazoan (animal) fossils are dated to the middle to late Tonian ( 890-800 Mya). The fossils of ''Otavia antiqua'', which has been described as a primitive sponge by its discoverers and numerous other scholars, date back to about 800 mya. Even earlier sponge-like fossils have been reported in reefs dating back to 890 million years before the present, but their identity is highly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
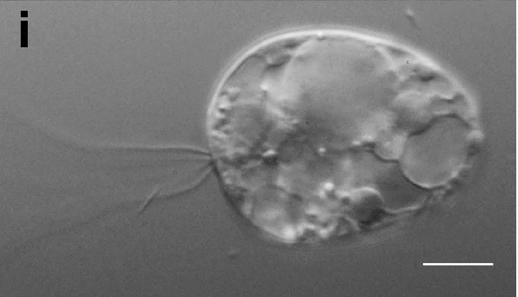
Filozoa
The Filozoa are a monophyletic grouping within the Opisthokonta. They include animals and their nearest unicellular relatives (organisms which are more closely related to animals than to fungi or Mesomycetozoa). Three groups are currently included within the clade Filozoa: * Group Filasterea - recently described to include the genera '' Ministeria'' and '' Capsaspora'' * Group Choanoflagellatea - collared flagellates * Kingdom Animalia - the group of which all extant animals belong to Etymology The name Filozoa originates from the Latin word ''filum'' meaning "thread" and the Greek word ''zōion'' meaning "animal". Phylogeny Below is a phylogenetic tree of Filozoa and the groups most closely related to the Filozoa : Characteristics The ancestral opisthokont cell is assumed to have possessed slender filose (thread-like) projections or 'tentacles'. In some opisthokonts (Mesomycetozoa and '' Corallochytrium'') these were lost. They are retained in Filozoa, where they are sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotes
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal kingdom Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as flagellated cells. The leading evolutionary theory is they were created by symbiogenesis between an anaerobic Promethearchaeati archaean and an aerobic proteobacterium, which form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supergroup (biology)
A supergroup or super-group, in systematics, is a large group of organisms that monophyletic, share one common ancestor and have important defining characteristics. It is an informal, mostly arbitrary rank in biology, biological Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy that is often greater than phylum or kingdom (biology), kingdom, although some supergroups are also treated as phylum, phyla. Eukaryotic supergroups Since the decade of the 2000s, the Eukaryote#Phylogeny, eukaryotic tree of life (abbreviated as eToL) has been divided into 5–8 major groupings called 'supergroups'. These groupings were established after the idea that only monophyletic groups should be accepted as ranks, as an alternative to the use of paraphyletic kingdom Protista. In the early days of the eToL six traditional supergroups were considered: Amoebozoa, Opisthokonta, "Excavata", Archaeplastida, "Chromalveolata" and Rhizaria. Since then, the eToL has been rearranged profoundly, and most of these groups were found as pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroups, such as Archaeplastida ( photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and " Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, including extreme habitats. Their diversity, larger than for all other eukaryotes, has only been discovered in rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoa
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology, and the study of animal behaviour is known as ethology. The animal kingdom is divided into five major clades, namely Porifera, Ctenophora, Placozoa, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicellular Organism
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular such as protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early organisms emerging 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Although some prokaryotes live in colonies, they are not specialised cells with differing functions. These organisms live together, and each cell must carry out all life processes to survive. In contrast, even the simplest multicellular organisms have cells that depend on each other to survive. Most multicellular organisms have a unicellular life-cycle stage. Gametes, for example, are reprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterotrophic
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but not producers. Living organisms that are heterotrophic include all animals and fungi, some bacteria and protists, and many parasitic plants. The term heterotroph arose in microbiology in 1946 as part of a classification of microorganisms based on their type of nutrition. The term is now used in many fields, such as ecology, in describing the food chain. Heterotrophs occupy the second and third trophic levels of the food chain while autotrophs occupy the first trophic level. Heterotrophs may be subdivided according to their energy source. If the heterotroph uses chemical energy, it is a chemoheterotroph (e.g., humans and mushrooms). If it uses light for energy, then it is a photoheterotroph (e.g., green non-sulfur bacteria). Heterotrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicellular
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular such as protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early organisms emerging 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Although some prokaryotes live in colonies, they are not specialised cells with differing functions. These organisms live together, and each cell must carry out all life processes to survive. In contrast, even the simplest multicellular organisms have cells that depend on each other to survive. Most multicellular organisms have a unicellular life-cycle stage. Gametes, for example, are reprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |