|
Chlorophenylbiguanide
''meta''-Chlorophenylbiguanide (1-(3-Chlorophenylbiguanide, ''m''-CPBG) is an allosteric agonist and modulator of the 5-HT3 receptor and an antagonist of the α2A-adrenergic receptor. It has anxiogenic, emetic Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose. Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, preg ... and hypothermic effects in animal studies. See also * mCPP * Bufotenidine (5-HTQ) References External links * 5-HT3 receptor positive allosteric modulators Alpha-2 blockers Emetics Biguanides 3-Chlorophenyl compounds {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
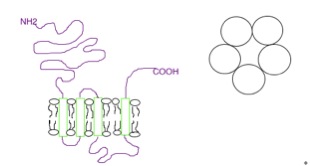
5-HT3 Receptor
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G-protein-coupled receptor, G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the Central nervous system, central and Peripheral nervous system, peripheral nervous systems. As with other ligand gated ion channels, the 5-HT3 receptor consists of five subunits arranged around a central ion conducting pore, which is permeable to sodium (Na), potassium (K), and calcium (Ca) ions. Binding of the neurotransmitter 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) to the 5-HT3 receptor opens the channel, which, in turn, leads to an excitatory response in neurons. The rapidly activating, desensitizing, inward current is predominantly carried by sodium and potassium ions. 5-HT3 receptors have a negligible perme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bufotenidine
Bufotenidine, also known as 5-hydroxy-''N'',''N'',''N''-trimethyltryptammonium (5-HTQ), is an indole toxin related to bufotenin, serotonin, and other tryptamines which is found in the venom of a variety of toads. It acts as a selective serotonin 5-HT3 receptor agonist, and has been used in scientific research to study the function of the serotonin 5-HT3 receptor, though this use has been limited by the fact that, as a quaternary amine, it is unable to readily cross the blood-brain-barrier and hence is peripherally selective. See also * 4-HO-TMT * Aeruginascin * 2-Methyl-5-HT * Chlorophenylbiguanide ''meta''-Chlorophenylbiguanide (1-(3-Chlorophenylbiguanide, ''m''-CPBG) is an allosteric agonist and modulator of the 5-HT3 receptor and an antagonist of the α2A-adrenergic receptor. It has anxiogenic, emetic Vomiting (also known as eme ... References 5-HT3 agonists Amphibian toxins Drugs with no legal status Emetics 5-Hydroxytryptamines Peripherally sele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT3 Receptor Positive Allosteric Modulators
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the central and peripheral nervous systems. As with other ligand gated ion channels, the 5-HT3 receptor consists of five subunits arranged around a central ion conducting pore, which is permeable to sodium (Na), potassium (K), and calcium (Ca) ions. Binding of the neurotransmitter 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) to the 5-HT3 receptor opens the channel, which, in turn, leads to an excitatory response in neurons. The rapidly activating, desensitizing, inward current is predominantly carried by sodium and potassium ions. 5-HT3 receptors have a negligible permeability to anions. They are most closely related by homology to the nicotinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an Receptor antagonist, antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists Receptor (biochemistry), Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or exogenous agonists (such as medication, drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonism an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosteric Modulator
In pharmacology and biochemistry, allosteric modulators are a group of substances that bind to a receptor to change that receptor's response to stimuli. Some of them, like benzodiazepines or alcohol, function as psychoactive drugs. The site that an allosteric modulator binds to (i.e., an ''allosteric site'') is not the same one to which an endogenous agonist of the receptor would bind (i.e., an ''orthosteric site''). Modulators and agonists can both be called receptor ligands. Allosteric modulators can be 1 of 3 types either: positive, negative or neutral. Positive types increase the response of the receptor by increasing the probability that an agonist will bind to a receptor (i.e. affinity), increasing its ability to activate the receptor (i.e. efficacy), or both. Negative types decrease the agonist affinity and/or efficacy. Neutral types don't affect agonist activity but can stop other modulators from binding to an allosteric site. Some modulators also work as allosteric agonist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves ." '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-2A Adrenergic Receptor
The alpha-2A adrenergic receptor (α2A adrenoceptor), also known as ADRA2A, is an α2-adrenergic receptor, and also denotes the human gene encoding it. Receptor α2-adrenergic receptors include 3 highly homologous subtypes: α2A, α2B, and α2C. These receptors have a critical role in regulating neurotransmitter release from sympathetic nerves and from adrenergic neurons in the central nervous system. Studies in mice revealed that both the α2A and α2C subtypes were required for normal presynaptic control of transmitter release from sympathetic nerves in the heart and from central noradrenergic neurons; the α2A subtype inhibited transmitter release at high stimulation frequencies, whereas the α2C subtype modulated neurotransmission at lower levels of nerve activity. Gene This gene encodes α2A subtype and it contains no introns in either its coding or untranslated sequences. Ligands Agonists * 4-NEMD * Brimonidine * Clonidine * Detomidine * Dexmedetomidine * Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiogenic
An anxiogenic or panicogenic substance is one that causes anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiolytic agents, which inhibits anxiety. Together these categories of psychoactive compounds may be referred to as anxiotropic compounds. Experimental Studies Anxiogenic effects can be measured by, for example, the hole-board test in rats and mice. A number of agents are used to provoke anxiety (anxiogens) or panic (panicogens) in experimental models. Mechanisms of Action Anxiogenic substances typically work through affecting levels of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, epinephrine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), norepinephrine (NE), and serotonin in the central nervous system (CNS). Some substances may alter functioning in the HPA axis, the neuroendocrine system that mediates responses to stress, where dysfunction has been linked to anxiety and panic disorders. Some substances, such as caffeine and sodium lactate, are largely reported to have anxiogenic effects only if they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emesis
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose. Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pregnancy, motion sickness, or hangover; or it can be an after effect of diseases such as brain tumors, elevated intracranial pressure, or overexposure to ionizing radiation. The feeling that one is about to vomit is called nausea; it often precedes, but does not always lead to vomiting. Impairment due to alcohol or anesthesia can cause inhalation of vomit. In severe cases, where dehydration develops, intravenous fluid may be required. Antiemetics are sometimes necessary to suppress nausea and vomiting. Self-induced vomiting can be a component of an eating disorder such as bulimia nervosa, and is itself now classified as an eating disorder on its own, purging disorder. Complications Aspiration Vomiting is dangerous if gastric content enters the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe hypothermia, there may be hallucinations and paradoxical undressing, in which a person removes their clothing, as well as an increased risk of the heart stopping. Hypothermia has two main types of causes. It classically occurs from exposure to cold weather and cold water immersion. It may also occur from any condition that decreases heat production or increases heat loss. Commonly, this includes alcohol intoxication but may also include low blood sugar, anorexia and advanced age. Body temperature is usually maintained near a constant level of through thermoregulation. Efforts to increase body temperature involve shivering, increased voluntary activity, and putting on warmer clothing. Hypothermia may be diagnosed based on either a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meta-Chlorophenylpiperazine
''meta''-Chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) is a psychoactive drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It was initially developed in the late-1970s and used in scientific research before being sold as a designer drug in the mid-2000s. It has been detected in pills touted as legal alternatives to illicit stimulants in New Zealand and pills sold as " ecstasy" in Europe and the United States. Despite its advertisement as a recreational substance, mCPP is actually generally considered to be an unpleasant experience and is not desired by drug users. It lacks any reinforcing effects, but has "psychostimulant, anxiety-provoking, and hallucinogenic effects." It is also known to produce dysphoric, depressive, and anxiogenic effects in rodents and humans, and can induce panic attacks in individuals susceptible to them. It also worsens obsessive–compulsive symptoms in people with the disorder. mCPP is known to induce headaches in humans and has been used for testing potential antimigraine m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |