|
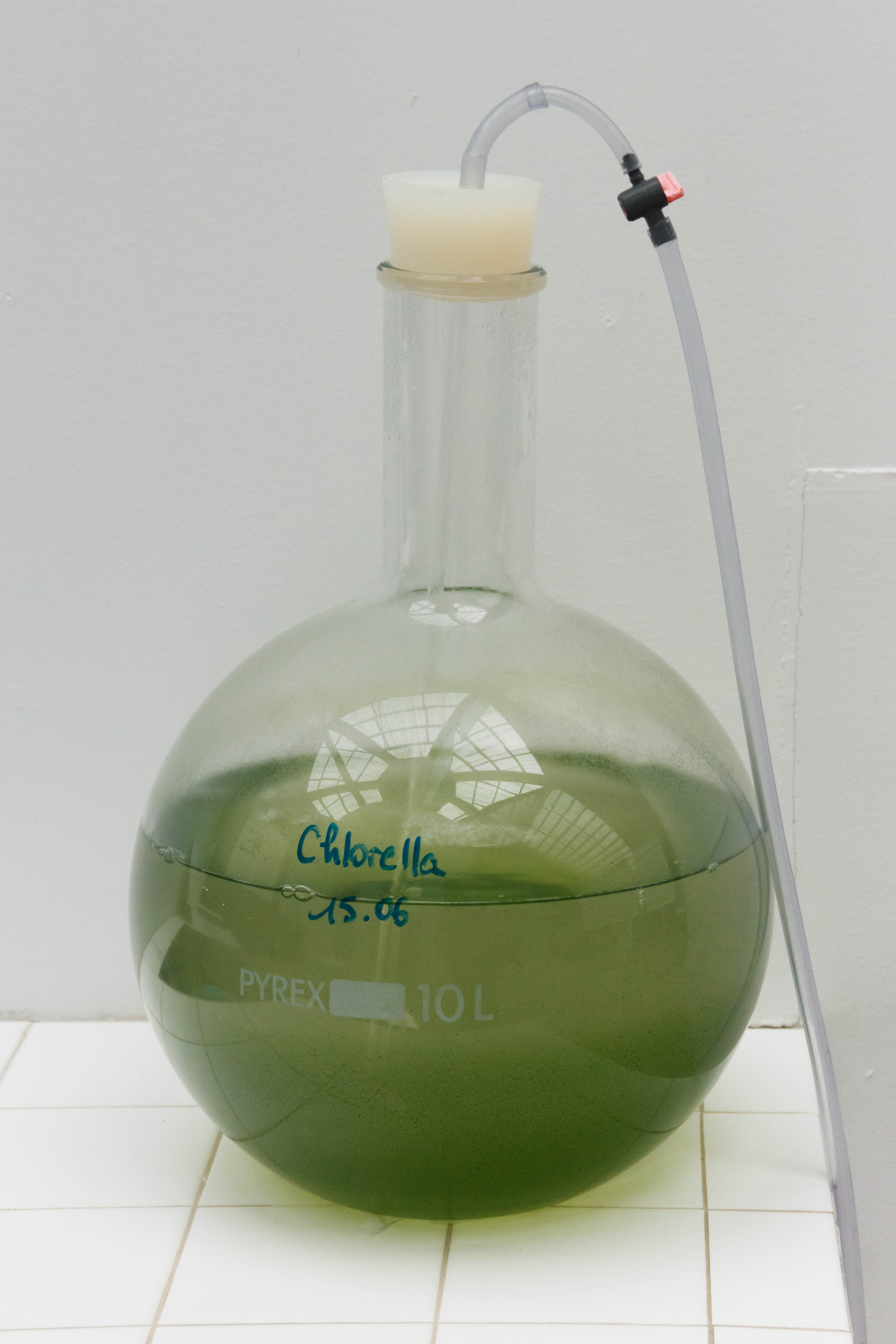
Chlorellosis
Chlorellosis is a disease caused by the infection of ''Chlorella'', a type of microalgae containing large amount of chloroplasts. It is mainly found in sheep and cattle, while cases in humans, dogs, antelopes, beavers, camels and fish, were also reported. Symptoms of Chlorellosis including focal cutaneous lesions, lymphadenitis, and peritonitis. See also *Protothecosis Protothecosis, otherwise known as Algaemia, is a disease found in dogs, cats, cattle, and humans caused by a type of green alga known as ''Prototheca'' that lacks chlorophyll and enters the human or animal bloodstream. It and its close relative ' ... References Chlorella {{Veterinary-med-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorella
''Chlorella'' is a genus of about thirteen species of single- celled green algae belonging to the division Chlorophyta. The cells are spherical in shape, about 2 to 10 μm in diameter, and are without flagella. Their chloroplasts contain the green photosynthetic pigments chlorophyll-a and -b. In ideal conditions cells of ''Chlorella'' multiply rapidly, requiring only carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and a small amount of minerals to reproduce. The name ''Chlorella'' is taken from the Greek χλώρος, ''chlōros/ khlōros'', meaning green, and the Latin diminutive suffix ''ella'', meaning small. German biochemist and cell physiologist Otto Heinrich Warburg, awarded with the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1931 for his research on cell respiration, also studied photosynthesis in ''Chlorella''. In 1961, Melvin Calvin of the University of California received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his research on the pathways of carbon dioxide assimilation in plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protothecosis
Protothecosis, otherwise known as Algaemia, is a disease found in dogs, cats, cattle, and humans caused by a type of green alga known as ''Prototheca'' that lacks chlorophyll and enters the human or animal bloodstream. It and its close relative '' Helicosporidium'' are unusual in that they are actually green algae that have become parasites. The two most common species are '' Prototheca wickerhamii'' and '' Prototheca zopfii''. Both are known to cause disease in dogs, while most human cases are caused by ''P. wickerhami''. ''Prototheca'' is found worldwide in sewage and soil. Infection is rare despite high exposure, and can be related to a defective immune system. In dogs, females and Collies are most commonly affected. The first human case was identified in 1964 in Sierra Leone. Cause ''Prototheca'' has been thought to be a mutant of ''Chlorella'', a type of single-celled green alga. However, while ''Chlorella'' contains galactose and galactosamine in the cell wall, ''Proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist individually, or in chains or groups. Depending on the species, their sizes can range from a few micrometers (μm) to a few hundred micrometers. Unlike higher plants, microalgae do not have roots, stems, or leaves. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces. Microalgae, capable of performing photosynthesis, are important for life on earth; they produce approximately half of the atmospheric oxygen and use the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide to grow photoautotrophically. "Marine photosynthesis is dominated by microalgae, which together with cyanobacteria, are collectively called phytoplankton." Microalgae, together with bacteria, form the base of the food web and provide energy for all the trophic levels above them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like '' Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order (biology), order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and sheep milk, milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult males are referred to as bulls. Cattle are commonly raised as livestock for meat (beef or veal, see beef cattle), for milk (see dairy cattle), and for hides, which are used to make leather. They are used as riding animals and draft animals ( oxen or bullocks, which pull carts, plows and other implements). Another product of cattle is their dung, which can be used to create manure or fuel. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle have significant religious significance. Cattle, mostly small breeds such as the Miniature Zebu, are also kept as pets. Different types of cattle are common to different geographic areas. Taurine cattle are found primarily in Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zeb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only Extant taxon, extant member. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
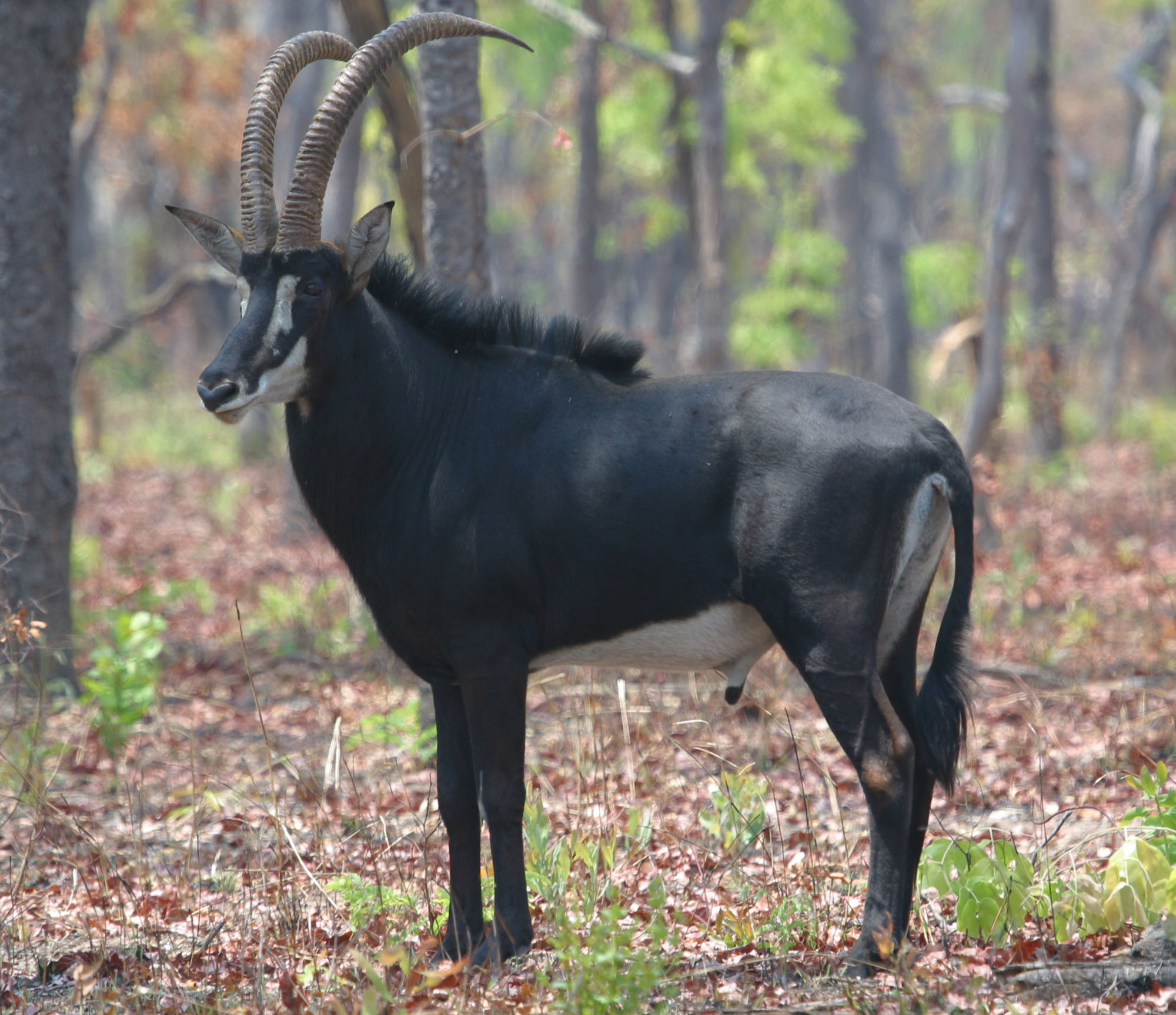
Antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia. Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mammals belonging to the family Bovidae of the order Artiodactyla. A stricter definition, also known as the "true antelopes," includes only the genera '' Gazella'', '' Nanger'', '' Eudorcas'' and '' Antilope''. One North American species, the pronghorn, is colloquially referred to as the "American antelope," but it belongs to a different family from the African and Eurasian antelopes. A group of antelope is called a herd. Unlike deer antlers, which are shed and grown annually, antelope horns grow continuously. Etymology The English word "antelope" first appeared in 1417 and is derived from the Old French ''antelop'', itself derived from Medieval Latin ''ant(h)alopus'', which in turn comes from the Byzantine Greek word ἀνθόλοψ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers are the second-largest living rodents after the capybaras. They have stout bodies with large heads, long chisel-like incisors, brown or gray fur, hand-like front feet, webbed back feet and flat, scaly tails. The two species differ in the shape of the skull and tail and fur color. Beavers can be found in a number of freshwater habitats, such as rivers, streams, lakes and ponds. They are herbivorous, consuming tree bark, aquatic plants, grasses and sedges. Beavers build dams and lodges using tree branches, vegetation, rocks and mud; they chew down trees for building material. Dams impound water and lodges serve as shelters. Their infrastructure creates wetlands used by many other species, and because of their effect on other organism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provide food ( milk and meat) and textiles (fiber and felt from hair). Camels are working animals especially suited to their desert habitat and are a vital means of transport for passengers and cargo. There are three surviving species of camel. The one-humped dromedary makes up 94% of the world's camel population, and the two-humped Bactrian camel makes up 6%. The Wild Bactrian camel is a separate species and is now critically endangered. The word ''camel'' is also used informally in a wider sense, where the more correct term is "camelid", to include all seven species of the family Camelidae: the true camels (the above three species), along with the "New World" camelids: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Cutaneous Lesion
*
{{disambiguation ...
Focal or FOCAL may refer to: *Focal (lexicographical website), an Irish lexicographical website *FOCAL (programming language), a programming language for the PDP-8 and similar machines *Focal (HP-41), for programming HP calculators *FOCAL (spacecraft), a proposed space telescope *FOCAL International, a trade body representing the film archive industry *Focal-JMLab, a French manufacturer of audio equipment *Focal Radio, a radio station based in Stoke-on-Trent, England *Focal neurologic signs See also *Focal point (other) *Focus (other) Focus, or its plural form foci may refer to: Arts * Focus or Focus Festival, former name of the Adelaide Fringe arts festival in South Australia Film *''Focus'', a 1962 TV film starring James Whitmore * ''Focus'' (2001 film), a 2001 film based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_b_068_white_background.jpg)
