|
Chlamydophila Psittaci
''Chlamydia psittaci'' is a lethal intracellular bacterial species that may cause endemic avian chlamydiosis, epizootic outbreaks in other mammals, and respiratory psittacosis in humans. Potential hosts include feral birds and domesticated poultry, as well as cattle, pigs, sheep, and horses. ''C. psittaci'' is transmitted by inhalation, contact, or ingestion among birds and to mammals. Psittacosis in birds and in humans often starts with flu-like symptoms and becomes a life-threatening pneumonia. Many strains remain quiescent in birds until activated by stress. Birds are excellent, highly mobile vectors for the distribution of chlamydia infection, because they feed on, and have access to, the detritus of infected animals of all sorts. ''Chlamydia psittaci'' in birds is often systemic, and infections can be inapparent, severe, acute, or chronic with intermittent shedding. ''C. psittaci'' strains in birds infect mucosal epithelial cells and macrophages of the respiratory tract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Fluorescent Antibody
A direct fluorescent antibody (DFA or dFA), also known as "direct immunofluorescence", is an antibody that has been tagged in a direct fluorescent antibody test. Its name derives from the fact that it directly tests the presence of an antigen with the tagged antibody, unlike western blotting, which uses an indirect method of detection, where the primary antibody binds the target antigen, with a secondary antibody directed against the primary, and a tag attached to the secondary antibody. Commercial DFA testing kits are available, which contain fluorescently labelled antibodies, designed to specifically target unique antigens present in the bacteria or virus, but not present in mammals (Eukaryotes). This technique can be used to quickly determine if a subject has a specific viral or bacterial infection. In the case of respiratory viruses, many of which have similar broad symptoms, detection can be carried out using nasal wash samples from the subject with the suspected infection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia Infection
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear, they may occur only several weeks after infection; the incubation period between exposure and being able to infect others is thought to be on the order of two to six weeks. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination. Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Chlamydia infections can occur in other areas besides the genitals, including the anus, eyes, throat, and lymph nodes. Repeated chlamydia infections of the eyes that go without treatment can result in trachoma, a common cause of blindness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16S Ribosomal RNA
16S ribosomal RNA (or 16 S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome ( SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure. The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S rRNA genes and are used in reconstructing phylogenies, due to the slow rates of evolution of this region of the gene. Carl Woese and George E. Fox were two of the people who pioneered the use of 16S rRNA in phylogenetics in 1977. Multiple sequences of the 16S rRNA gene can exist within a single bacterium. Terminology The descriptor ''16S'' refers to the size of these ribosomal subunits as reflected indirectly by the speed at which they sediment when samples are centrifuged. Thus ''16S'' means 16 Svedburg units. Functions * Like the large (23S) ribosomal RNA, it has a structural role, acting as a scaffold defining the positions of the ribosomal proteins. * The 3-end contains the anti- Shine-Dalgarno sequence, which binds upstream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cell (biology), cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. After cells of interest have been Cell isolation, isolated from living tissue, they can subsequently be maintained under carefully controlled conditions. They need to be kept at body temperature (37 °C) in an incubator. These conditions vary for each cell type, but generally consist of a suitable vessel with a substrate or rich growth medium, medium that supplies the essential nutrients (amino acids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals), growth factors, hormones, and gases (Carbon dioxide, CO2, Oxygen, O2), and regulates the physio-chemical environment (Buffer solution, pH buffer, osmotic pressure, temperature). Most cells require a surface or an artificial substrate to form an adherent culture as a monolayer (one single-cell thick), whereas others can be grown free floating in a medium as a suspension culture. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctiva
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva (: conjunctivae) is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly Angiogenesis, vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies. Structure The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts: Blood supply Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents. Nerve supply Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (anatomy)
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type Cell (biology), cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma (tissue), stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerve t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
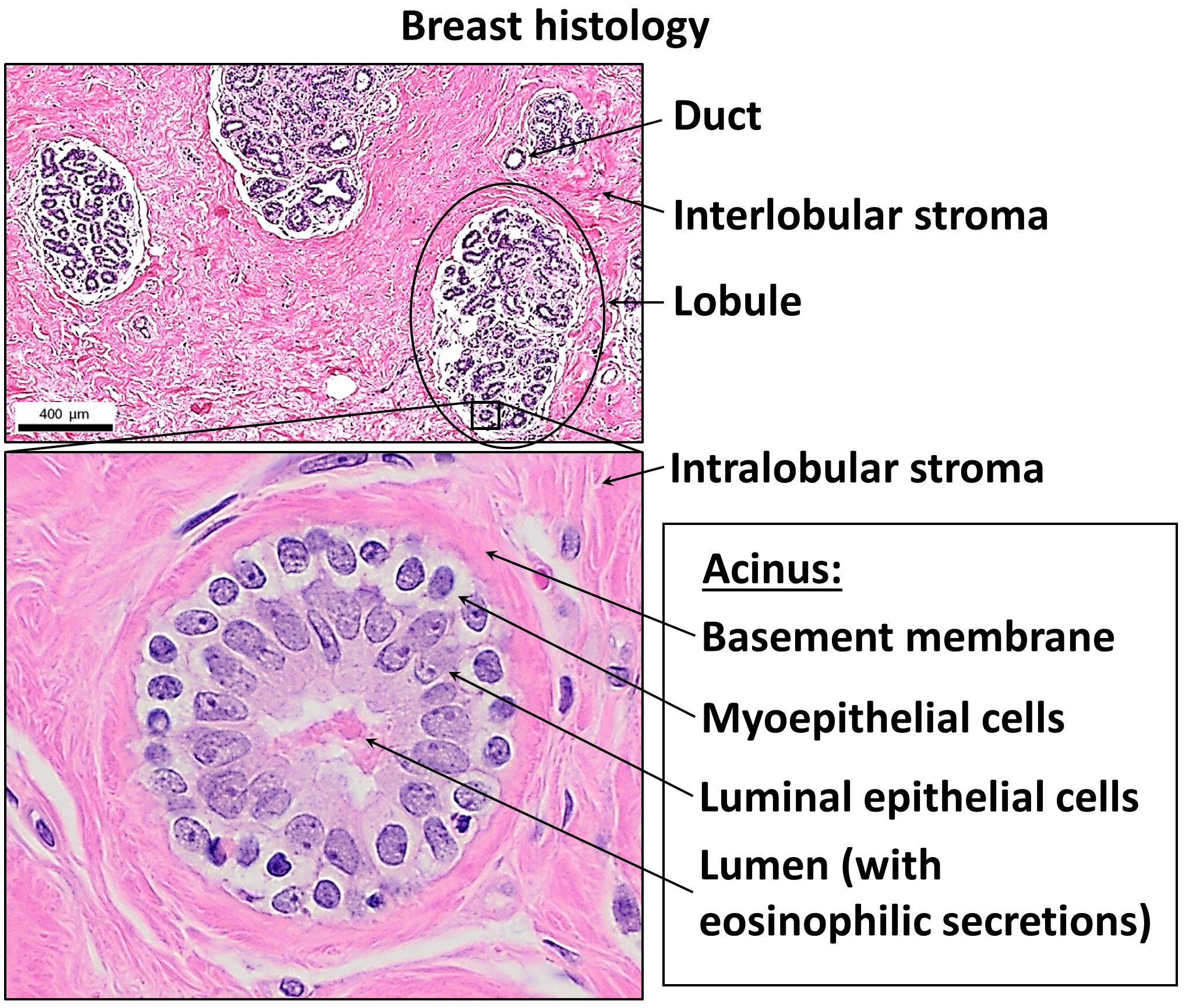
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and symptoms include fever, tachycardia, increased heart rate, hyperventilation, increased breathing rate, and mental confusion, confusion. There may also be symptoms related to a specific infection, such as a cough with pneumonia, or dysuria, painful urination with a pyelonephritis, kidney infection. The very young, old, and people with a immunodeficiency, weakened immune system may not have any symptoms specific to their infection, and their hypothermia, body temperature may be low or normal instead of constituting a fever. Severe sepsis may cause organ dysfunction and significantly reduced blood flow. The presence of Hypotension, low blood pressure, high blood Lactic acid, lactate, or Oliguria, low urine output may suggest poor blood flow. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa. Air is breathed in through the nose to the nasal cavity, where a layer of nasal mucosa acts as a filter and traps pollutants and other harmful substances found in the air. Next, air moves into the pharynx, a passage that contains the intersection between the oesophagus and the larynx. The opening of the larynx has a special flap of cartilage, the epiglottis, that opens to allow air to pass through but closes to prevent food from moving into the airway. From the larynx, air moves into the trachea and down to the intersection known as the carina that branches to form the right and left primary (main) bronchi. Each of these bronchi branches into a secondary (lobar) bronchus that branches into tertiary (segmental) bronchi, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. This self-protection method can be contrasted with that employed by Natural killer cell, Natural Killer cells. This process of engulfment and digestion is called phagocytosis; it acts to defend the host against infection and injury. Macrophages are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |