|
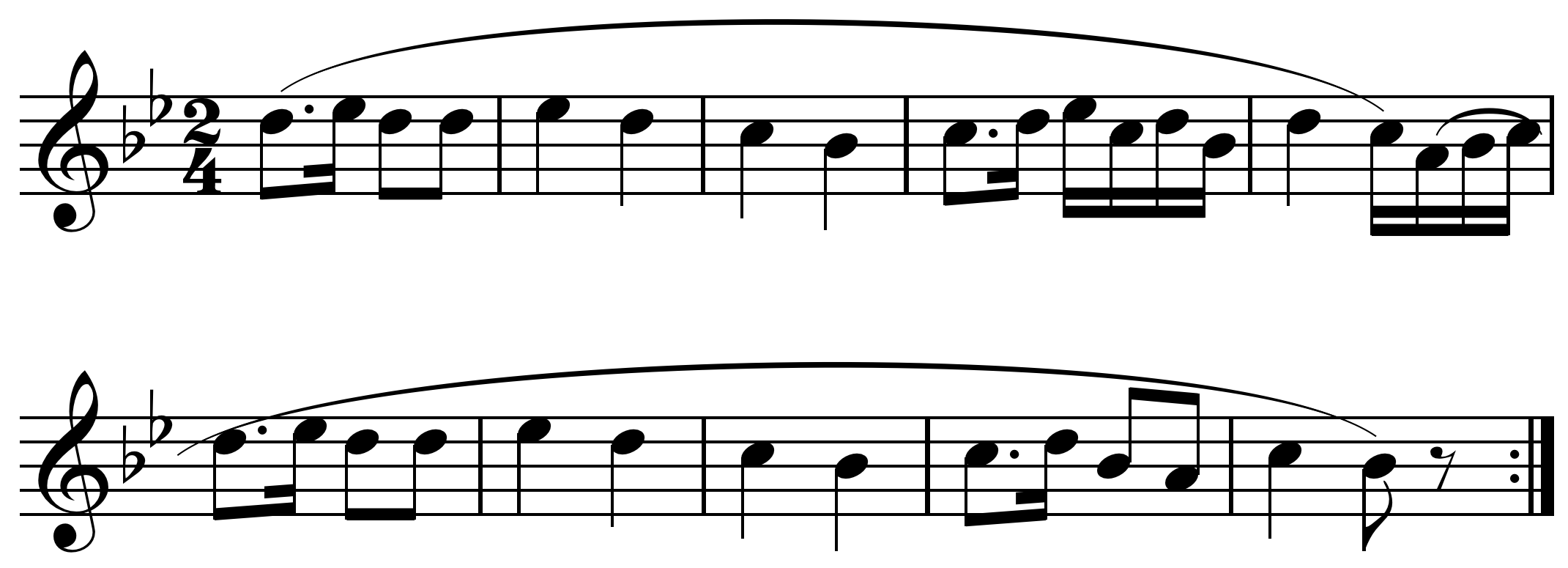
Chitta Swara
In Indian classical music, chitte swara (, ) are a set of solfa passages (phrases of swaras). These are sung after the anupallavi and charanam, in the krithis which enriches the beauty of the composition. Chitte in Kannada means butterfly. The swaras enhance the beauty of the song like butterflies. Accessed January 17, 2015. This is usually done by the performers and not by the composers and in is an important '''' aspect ('' |
Indian Classical Music
Indian classical music is the art music, classical music of the Indian subcontinent. It is generally described using terms like ''Shastriya Sangeet'' and ''Marg Sangeet''. It has two major traditions: the North Indian classical music known as ''Hindustani classical music, Hindustani'' and the South Indian expression known as ''Carnatic classical music, Carnatic''. These traditions were not distinct until about the 15th century. During the period of Mughal Empire, Mughal rule of the Indian subcontinent, the traditions separated and evolved into distinct forms. Hindustani music emphasizes improvisation and exploration of all aspects of a raga, while Carnatic performances tend to be short composition-based. However, the two systems continue to have more common features than differences. Another unique classical music tradition from the eastern part of India is ''Odissi music'', which has evolved over the last two thousand years. The roots of the classical music of India are found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
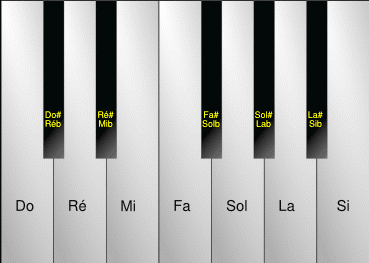
Solfège
In music, solfège (British English or American English , ) or solfeggio (; ), also called sol-fa, solfa, solfeo, among many names, is a mnemonic used in teaching aural skills, Pitch (music), pitch and sight-reading of Western classical music, Western music. Solfège is a form of solmization, though the two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Syllables are assigned to the notes of the Scale (music), scale and assist the musician in Gordon music learning theory#Audiation, audiating, or mentally hearing, the pitches of a piece of music, often for the purpose of singing them aloud. Through the Renaissance music, Renaissance (and much later in some shapenote publications) various interlocking four-, five- and six-note systems were employed to cover the octave. The tonic sol-fa method popularized the seven syllables commonly used in English-speaking countries: ''do'' (spelled ''doh'' in tonic sol-fa),''Oxford English Dictionary'' 2nd Ed. (1998) ''re'', ''mi'', ''fa'', ''so(l)'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passage (music)
In music, a section is a complete, but not independent, musical idea. Types of sections include the Introduction (music), introduction or intro, Exposition (music), exposition, Musical development, development, recapitulation (music), recapitulation, Verse-chorus form, verse, Verse-chorus form, chorus or refrain, Conclusion (music), conclusion, coda (music), coda or outro, fade (audio engineering)#Origins and early examples, fadeout, bridge (music), bridge or wikt:interlude, interlude. In sectional forms such as binary form, binary, the larger unit (form (music), form) is built from various smaller clear-cut units (sections) in combination, analogous to stanzas in poetry or somewhat like stacking Lego. Some well known songs consist of only one or two sections, for example "Jingle Bells" commonly contains verses ("Dashing through the snow...") and choruses ("Oh, jingle bells..."). It may contain "auxiliary members" such as an introduction and/or outro, especially when accompanied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase (music)
In music theory, a phrase () is a unit of Meter (music), musical meter that has a complete musical sense of its own, built from figure (music), figures, motif (music), motifs, and Cell (music), cells, and combining to form Melody, melodies, period (music), periods and larger Section (music), sections. Terms such as ''sentence'' and ''verse'' have been adopted into the vocabulary of music from linguistic syntax. Though the analogy between the musical and the phrase, linguistic phrase is often made, still the term "is one of the most ambiguous in music....there is no consistency in applying these terms nor can there be...only with melodies of a very simple type, especially those of some dances, can the terms be used with some consistency." John D. White defines a phrase as "the smallest musical unit that conveys a more or less complete musical thought. Phrases vary in length and are terminated at a point of full or partial repose, which is called a ''cadence''." Edward T. Cone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swara
Swara () or svara is an Indian classical music term that connotes simultaneously a breath, a vowel, a note, the sound of a musical note corresponding to its name, and the successive steps of the octave, or ''saptanka''. More comprehensively, it is the ancient Indian concept of the complete dimension of musical pitch. At its most basic comparison to western music, a ''swara'' is, essentially, a "note" of a given scale. However, that is but a loose interpretation of the word, as a ''swara'' is identified as both a musical note and tone; a "tone" is a precise substitute for sur, relating to "tunefulness". Traditionally, Indian musicians have just seven ''swara''s/notes with short names: sa, re, ga, ma, pa, dha, ni, which they collectively refer to as ''saptank'' or ''saptaka''. This is one of the reasons why ''swara'' is considered a symbolic expression for the number seven. In another loose comparison to western music, ''saptak'' (as an octave or scale) may be interpreted as s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anupallavi (music)
In Carnatic music, the anupallavi comes after the pallavi and is usually the second section of any composition. It is then followed by one or more charanam Charanam (meaning ''foot'') in Carnatic music (South Indian classical music) is usually the end section of a composition which is sung after the anupallavi. There may be multiple ''charanams'' in a composition which make up different stanzas, ...s. The anupallavi is optional. In compositions that do not have an anupallavi, there often exists a Samrashti Charanam that combines both the anupallavi and charanam of the composition which directly follows the pallavi. It is usually sung at a higher pitch and adds more beauty to the music. Usually the Anupallavi is shorter than the Charanam . In Sanskrit 'anu' means 'next'. It literally means 'next to pallavi'. References Carnatic music terminology {{India-music-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charanam
Charanam (meaning ''foot'') in Carnatic music (South Indian classical music) is usually the end section of a composition which is sung after the anupallavi. There may be multiple ''charanams'' in a composition which make up different stanzas, but in compositions that do not have an anupallavi, there often exists a ''samrashti charanam'' that combines both the anupallavi and charanam of the composition which directly follows the ''pallavi''. The charana swara Swara () or svara is an Indian classical music term that connotes simultaneously a breath, a vowel, a note, the sound of a musical note corresponding to its name, and the successive steps of the octave, or ''saptanka''. More comprehensively ...s are grouped in four different ways: *1st - one tala cycle. *2nd - one tala cycle. *3rd - two long tala cycles *4th - four long tala cycles References Carnatic music terminology {{Carnatic-music-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krithi
A ''kriti'' () is a form of musical composition in the Carnatic music literature. The Sanskrit common noun ''Kriti'' means 'creation' or 'work'. A kriti forms the mental backbone of any typical Carnatic music concert and is the longer format of a Carnatic song. Structure A conventional ''kriti'' typically contain three parts: #''Pallavi'', the equivalent of a refrain in Western music #'' Anupallavi'', the second verse, which is sometimes optional #''Charanam'', the final (and longest) verse that wraps up the song The ''charanam'' usually borrows patterns from the ''anupallavi''. The ''charanam's'' last line usually contains the composer's signature, or ''mudra'', with which the composer leaves their mark. Variations Some Kritis have a verse between the ''anupallavi'' and the ', called the '' ''. This verse consists only of notes, and has no words. Other ''krithis'', particularly some of Oothukkadu Venkata Kavi and Muthuswami Dikshitar's compositions, are intentionally compose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a second or third language for 15 million speakers in Karnataka. It is the official and administrative language of Karnataka. It also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton University Press, 2012, Kannada was the court language of a number of dynasties and empires of South India, Central India and the Deccan Plateau, namely the Kadamba dynasty, Western Ganga dynasty, Nolamba dynasty, Chalukya dynasty, Rashtrakutas, Western Chalukya Empire, Seuna dynasty, kingdom of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi, Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnatic Music
Carnatic music (known as or in the Dravidian languages) is a system of music commonly associated with South India, including the modern Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Telangana and southern Odisha. It is one of three main subgenres of Indian classical music that evolved from ancient Hindu texts and traditions, particularly the Samaveda. (The other two are Hindustani music and Odissi music.) The main emphasis in Carnatic music is on vocal music; most compositions are written to be sung, and even when played on instruments, they are meant to be performed in ''gāyaki'' (singing) style. Although there are stylistic differences, the basic elements of (the relative musical pitch), (the musical sound of a single note), (the mode or melodic formulae), and (the rhythmic cycles) form the foundation of improvisation and composition in both Carnatic and Hindustani music. Although improvisation plays an important role, Carnatic music is mainly sung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Improvisation
Improvisation, often shortened to improv, is the activity of making or doing something not planned beforehand, using whatever can be found. The origin of the word itself is in the Latin "improvisus", which literally means un-foreseen. Improvisation in the performing arts is a very spontaneous performance without specific or scripted preparation. The skills of improvisation can apply to many different faculties across all artistic, scientific, physical, cognitive, academic, and non-academic disciplines; see Applied improvisation. Skills and techniques The skills of improvisation can apply to many different abilities or forms of communication and expression across all artistic, scientific, physical, cognitive, academic, and non-academic disciplines. For example, improvisation can make a significant contribution in music, dance, cooking, presenting a speech, sales, personal or romantic relationships, sports, flower arranging, martial arts, psychotherapy, and much more. Technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manodharma
Manodharma is a form of improvised South Indian classical Carnatic music. It is created on the spot during the performance, while remaining within the confines of musical grammar, as codified in the raga and/or the tala. Every Carnatic concert has one or many music pieces that showcases the singer's prowess and intellect in the form of Manodharma sangeetham. Often the centerpiece of a Carnatic concert will explore all the five types of manodharma. It serves as an important and integral aspect of Carnatic music. Types of Manodharma Based out of manodharma, individual styles are developed. Manodharma has many aspects and performers develop distinct styles based on their musical values, interpretation and understanding. There is ample scope for manodharma when rendering raga alapana, tanam, neraval, pallavi, swaram and also kritis. There are five improvisational forms that fall under the practice of manodharma in Carnatic Music. They include: Alapana: A free flowing explor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |