|
Chingis-Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongol tribes, he launched a series of military campaigns, conquering large parts of China and Central Asia. Born between 1155 and 1167 and given the name Temüjin, he was the eldest child of Yesugei, a Mongol chieftain of the Borjigin clan, and his wife Hö'elün. When Temüjin was eight, his father died and his family was abandoned by its tribe. Reduced to near-poverty, Temüjin killed his older half-brother to secure his familial position. His charismatic personality helped to attract his first followers and to form alliances with two prominent steppe leaders named Jamukha and Toghrul; they worked together to retrieve Temüjin's newlywed wife Börte, who had been kidnapped by raiders. As his reputation grew, his relationship with Jamukha deteriorated into open warfare. Temüjin was badly defeated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan-era
The Yuan dynasty (), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in the Battle of Yamen. His realm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hö'elün
Hö'elün ( Mongolian: , , ; ) was a noblewoman of the Mongol Empire and the mother of Temüjin, better known as Genghis Khan. She played a major role in his rise to power, as described in the ''Secret History of the Mongols''. Born into the Olkhonud clan of the Onggirat tribe, Hö'elün was originally married to Chiledu, a Merkit aristocrat; she was captured shortly after her wedding by Yesügei, an important member of the Mongols, who abducted her to be his primary wife. She and Yesügei had four sons and one daughter: Temüjin, Qasar, Hachiun, Temüge, and Temülen. After Yesügei was fatally poisoned and the Mongols abandoned her family, Hö'elün shepherded all her children through poverty to adulthood—her resilience and organisational skills have been remarked upon by historians. She continued to play an important role after Temüjin's marriage to Börte—together, the two women managed his camp and provided him with advice. Hö'elün married Münglig, an old retain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin Dynasty (1115–1234)
The Jin dynasty (, ; ) or Jin State (; Jurchen: Anchun Gurun), officially known as the Great Jin (), was an imperial dynasty of China that existed between 1115 and 1234. Its name is sometimes written as Kin, Jurchen Jin, Jinn, or Chin in English to differentiate it from an earlier Jìn dynasty whose name is rendered identically in Hanyu Pinyin without the tone marking. It is also sometimes called the "Jurchen dynasty" or the "Jurchen Jin", because members of the ruling Wanyan clan were of Jurchen descent. The Jin emerged from Wanyan Aguda's rebellion against the Liao dynasty (916–1125), which held sway over northern China until the nascent Jin drove the Liao to the Western Regions, where they became known in historiography as the Western Liao. After vanquishing the Liao, the Jin launched a century-long campaign against the Han-led Song dynasty (960–1279), which was based in southern China. Over the course of their rule, the ethnic Jurchen emperors of the Jin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dalan Balzhat and the shaman Kokochu proclaiming "... that the Eternal Blue Sky had set aside the world for Temüjin". In , Temüjin was elected Khan ...
The Battle of Dalan Baljut was fought in 1187 between Temüjin (later known as ''Genghis Khan'') and his blood brother Jamukha. Although Temüjin and Jamukha were close friends for many years, they began to drift apart as time went on. Central to this split was the political system each of them supported—Jamukha held up the traditional Mongol aristocracy, whereas Temüjin believed that a meritocracy would be best. Temüjin was able to find several successes, most notably in attracting a broad range of followers (including lower classes), a successful campaign against the Merkits The Merkit (literally ''"skillful/wise ones"''; mn, ᠮᠡᠷᠬᠢᠳ ; Мэргид, translit=, Mergid; ) was one of the five major tribal confederations (''khanlig'') of probably Mongol [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toghrul
Toghrul ( mn, Тоорил хан ''Tooril han''; ), also known as Wang Khan or Ong Khan ( ''Wan han''; ; died 1203) was a khan of the Keraites. He was the blood brother ( anda) of the Mongol chief Yesugei and served as an important early patron and ally to Yesugei's son Temüjin, later known as Genghis Khan. The main source on his life is ''The Secret History of Mongols''. Name "Wang Khan" was the name given to Toghrul by the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty of China; ''Wang'' means king or prince. During the 13th century, Toghrul was one of several Asian leaders who was identified with the legend of Prester John, but also King David, a brother to John. There's no credible proof that he was Christian. Early life He was born around 1130, to Nestorian family of Keraites. His father was Cyriacus Buyruk Khan, the leader of Keraites. Toghrul had a very difficult youth. The Merkits captured him during his childhood and he was reduced to slavery. It is possible that he left the Merkit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamukha
Jamukha ( mn, Жамуха; ) was a Mongol military and political leader and the chief rival to Temüjin (later Genghis Khan) in the unification of the Mongol tribes. Biography Jamukha was born in the Jadaran, a sub-tribe of the Khamag Mongol confederation, and was an ''anda'' (i.e. blood brother) to Temüjin. According to ''The Secret History of the Mongols'', when Börte, wife of Temüjin, was abducted by the Three Merkits; Wang Khan, Jamukha and Temüjin combined forces against the Merkits to recover her. In 1201, the leaders of the thirteen remaining tribes hostile to Temüjin (among them the Merkits, Tatar, and Naimans) and the Mongol tribes not allied with him (Jadaran, Taichuud, and others) assembled a kurultai and elected Jamukha as Gur-khan, ''universal ruler'', a title used by the rulers of the Kara-Khitan Khanate. Jamukha's assumption of this title was the final breach between Temüjin and Jamukha, leading Temüjin to form a coalition of tribes to oppose h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also simply called the Great Steppe or the steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova and Transnistria, Ukraine, Western Russia, Siberia, Kazakhstan, Xinjiang, Mongolia and Manchuria, with one major exclave, the Pannonian steppe or Puszta, located mostly in Hungary. Since the Paleolithic age, the Steppe Route has connected Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Western Asia, Central Asia, East Asia and South Asia economically, politically and culturally through overland trade routes. The Steppe route is a predecessor not only of the Silk Road which developed during antiquity and the Middle Ages, but also of the Eurasian Land Bridge in the modern era. It has been home to nomadic empires and many large tribal confederations and ancient states throughout history, such as the Xiongnu, Scythia, Cimmeria, Sarmatia, Hunni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behter
Behter or Bekter ( mn, Бэхтэр; died 1180) was the son of Yesugei, chief of the Kiyad clan, and a junior wife named Sochigel or Suchigu in some sources and Ko'agjin in others. He was also half-brother of Genghis Khan, then known as Temujin. On the death of Yesugei, Temujin, his mother Hoelun, his siblings and two half-brothers (including Behter, Belgutei and their mother Sochigel) were abandoned by their tribe and left to fend for themselves. Living off the land, they managed to survive. However, the older half-brothers deprived 14-year-old Temujin and his brother Qasar of their spoils. Temujin and Qasar stalked and killed Behter, for which they were scolded by their mother Hoelun Hoelun (also Hoelun Üjin; Mongolian: ; Cyrillic: Өэлүн үжин, Өэлүн эх, ''Mother Hoelun'', Öülen/Oulen; ), 1140-1221 was the mother of Genghis Khan and the wife of his father Yesügei, the chief of the Khamag Mongol confede ....The Secret History of the Mongols 75-76, p.22- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Invasion Of Central Asia
The Mongol invasion of Central Asia occurred after the unification of the Mongol and Turkic tribes on the Mongolian plateau in 1206. It was finally complete when Genghis Khan conquered the Khwarizmian Empire in 1221. Qara Khitai (1216-1218) The Qocho Uyghurs, Qarluqs and local Turkic peoples submitted to the Mongolians. The Uyghur state of Kara-Khoja was a vassal of the Qara Khitai, but in 1210, the Uyghur ruler of Kara-Khoja, Idiqut Barchuq appeared before the Khan to declare his allegiance to the Mongolians. He was rewarded with the daughter of Genghis in marriage, and the Uyghurs served under the Mongols as bureaucrats. A leader of the Qarluq and Buzar, the warlord of Chuy Valley, followed the Uyghur example. The Qara Khitai (Black Khitan) were Khitans of the Liao Dynasty (907–1125) who were driven out of China by the Jurchens of the Jin dynasty. In 1124 some Khitans moved westward under Yeh-lü Ta-shih’s leadership and created the Qara Khitai Khanate (Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Conquest Of China
The Mongol conquest of China was a series of major military efforts by the Mongol Empire to conquer various empires ruling over China. It spanned six decades in the 13th century and involved the defeat of the Jin dynasty, Western Liao, Western Xia, Tibet, the Dali Kingdom, the Southern Song, and the Eastern Xia. The Mongol Empire under Genghis Khan started the conquest with small-scale raids into Western Xia in 1205 and 1207. By 1279, the Mongol ruler Kublai Khan had established the Yuan dynasty in China and crushed the last Song resistance, which marked the onset of all of China under Yuan rule. This was the first time in history that the whole of China was unified by non-Han people, and it marked the first time in history when Tibet was unified with the rest of China. Conquest of Western Xia In the early 1200s, Temujin, soon to be Genghis Khan, began consolidating his power in Mongolia. Following the death of the Kerait leader Ong Khan to Temujin's emerging Mongol E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Invasions And Conquests
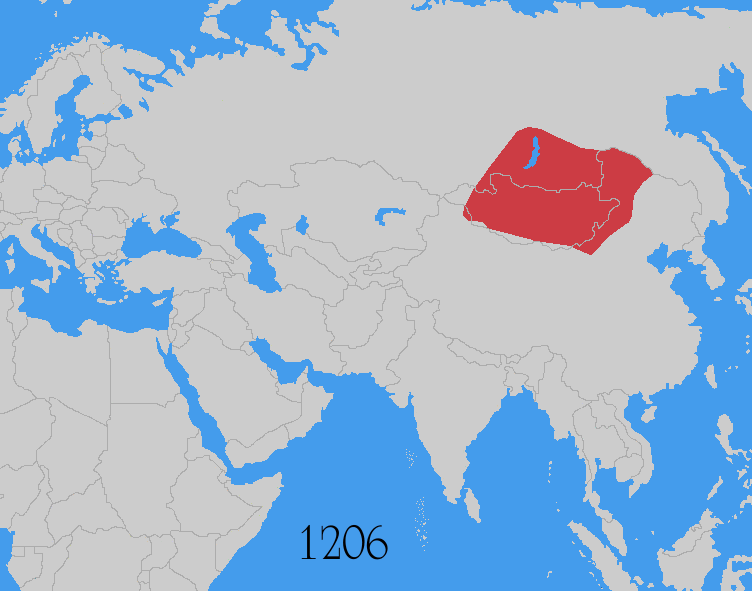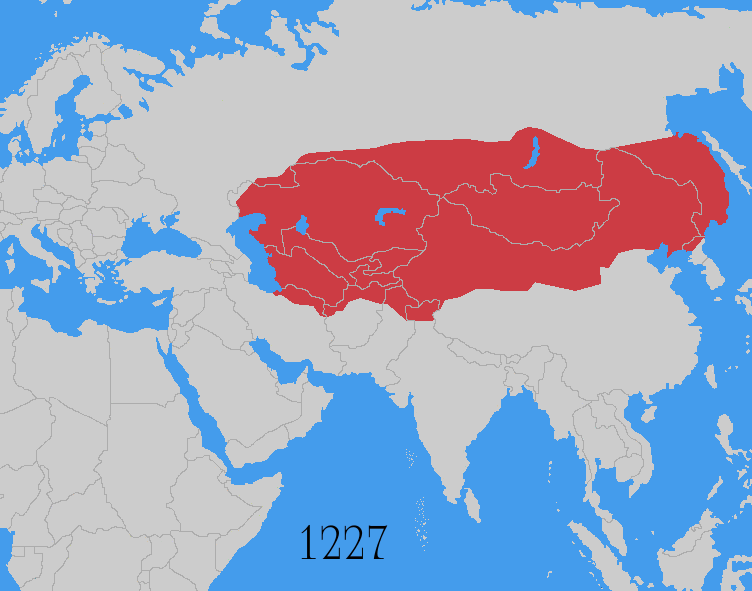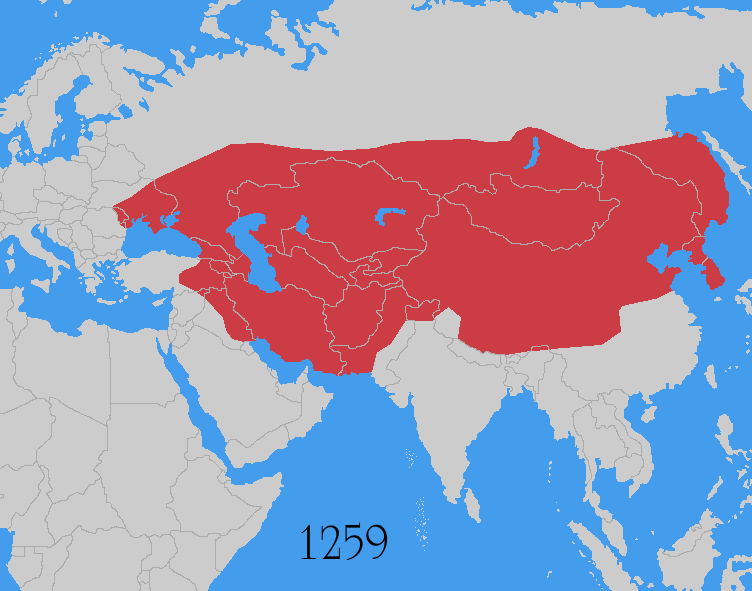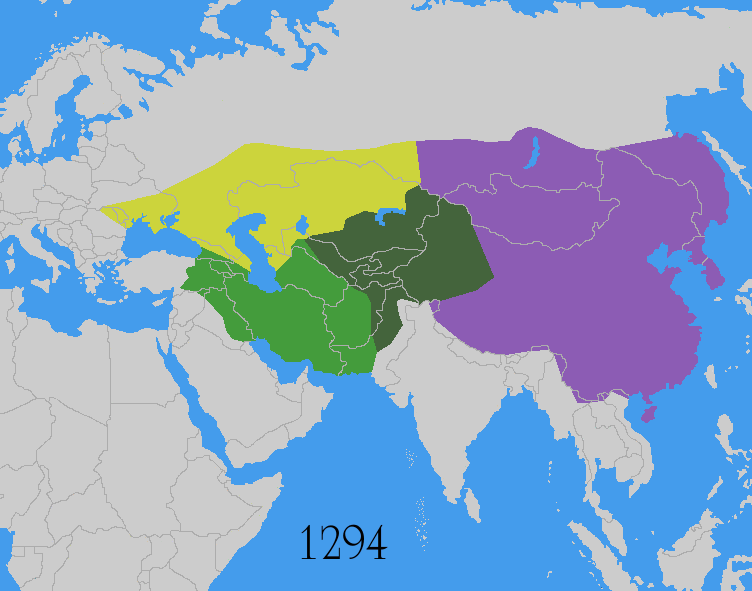
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire (1206-1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history. In addition, Mongol expeditions may have spread the bubonic plague across much of Eurasia, helping to spark the Black Death of the 14th century. The Mongol Empire developed in the course of the 13th century through a series of victorious campaigns throughout Asia, reaching Eastern Europe by the 1240s. In contrast with later "empires of the sea" such as European colonial powers, the Mongol Empire was a land power, fueled by the grass-foraging Mongol cavalry and cattle. Thus most Mongol conquest and plundering took place during the warmer seasons, when there was sufficient grazing for their herds. The rise of the Mongols was preceded by 15 years of wet and warm weather conditions from 1211 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishigten, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |