|
Chinese Ophthalmology
Chinese ophthalmology () is part of Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Diseases of the eyes are treated with Chinese herbs, acupuncture/moxibustion, tuina, Chinese dietary therapy as well as qigong and taijiquan. Inscriptions on oracle bones and tortoise shells from the Shang and Yin dynasties (16th century to 1066 BCE) already contain indications of eye diseases and of their treatment in China. The work ''Essential Subtleties on the Silver Sea'' (, yínhǎi jīngwēi) has had wide influence on the Chinese ophthalmology until today. It was likely written by Sun Simiao and published at the end of the Yuan Dynasty (1271−1368). A notable aspect of Chinese ophthalmology is the "five wheels" (, wǔlún) and "eight boundaries" (, bākuò). They characterise certain anatomical segments of the eyes and correspond to certain zang-fu organs. From changes of the five wheels and eight boundaries, diseases and the necessary therapy may be deduced. In modern Chinese ophthalmology, in C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Chinese Medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is an alternative medicine, alternative medical practice drawn from traditional medicine in China. A large share of its claims are pseudoscientific, with the majority of treatments having no robust evidence of effectiveness or logical mechanism of action. Some TCM ingredients Traditional Chinese medicine#Safety, are known to be toxic and cause disease, including cancer. Medicine in traditional China encompassed a range of sometimes competing health and healing practices, folk beliefs, Scholar-official, literati theory and Confucianism, Confucian philosophy, Chinese herbology, herbal remedies, Chinese food therapy, food, diet, exercise, medical specializations, and schools of thought. TCM as it exists today has been described as a largely 20th century invention. In the early twentieth century, Chinese cultural and political modernizers worked to eliminate traditional practices as backward and unscientific. Traditional practitioners then selec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Simiao
Sun Simiao (; 541-682)Chen, J. (2007). Philosopher, Practitioner, Politician: the Many Lives of Fazang (643-712). Netherlands: Brill. p. 242. was a Chinese physician and writer of the Sui and Tang dynasty, who was from Tongchuan, central Shaanxi. He was titled as China's King of Medicine (, ''Yaowang'') for his significant contributions to Chinese medicine and tremendous care to his patients. Books Sun wrote many books, of which two—'' Beiji qianjin yaofang'' ("Essential Formulas for Emergencies ortha Thousand Pieces/Catty of Gold") and ' ("Supplement to the Formulas of a Thousand Gold Worth")—were milestones in the history of Chinese medicine.Tan, S. Y. (2002). Sun Si Miao (581-682a. d.): China's pre-eminent physician. ''Singapore Medical Journal'', ''43''(5), 224-225. They summarized pre-Tang dynasty medicine. The former listed about 5300 recipes for medicines, and the latter 2000. He also put forth the “Thirteen measures to keep health”, which claimed that actions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortsightedness
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. Other symptoms may include headaches and eye strain. Severe myopia is associated with an increased risk of macular degeneration, retinal detachment, cataracts, and glaucoma. Myopia results from the length of the eyeball growing too long or less commonly the lens being too strong. It is a type of refractive error. Diagnosis is by the use of cycloplegics during eye examination. Tentative evidence indicates that the risk of myopia can be decreased by having young children spend more time outside. This decrease in risk may be related to natural light exposure. Myopia can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or by refractive surgery. Eyeglasses are the simplest and safest method of correction. Contact lenses can provide a relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysanthemum
Chrysanthemums ( ), sometimes called mums or chrysanths, are flowering plants in the Asteraceae family. They are native to East Asia and northeastern Europe. Most species originate from East Asia, and the center of diversity is in China. Countless horticultural varieties and cultivars exist. Description The genus ''Chrysanthemum'' are perennial herbaceous flowering plants, sometimes subshrubs. The leaves are alternate, divided into leaflets and may be pinnatisect, lobed, or serrate (toothed) but rarely entire; they are connected to stalks with hairy bases. The compound inflorescence is an array of several flower heads, or sometimes a solitary head. The head has a base covered in layers of phyllaries. The simple row of ray florets is white, yellow, or red. The disc florets are yellow. Pollen grains are approximately 34 microns. The fruit is a ribbed achene. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
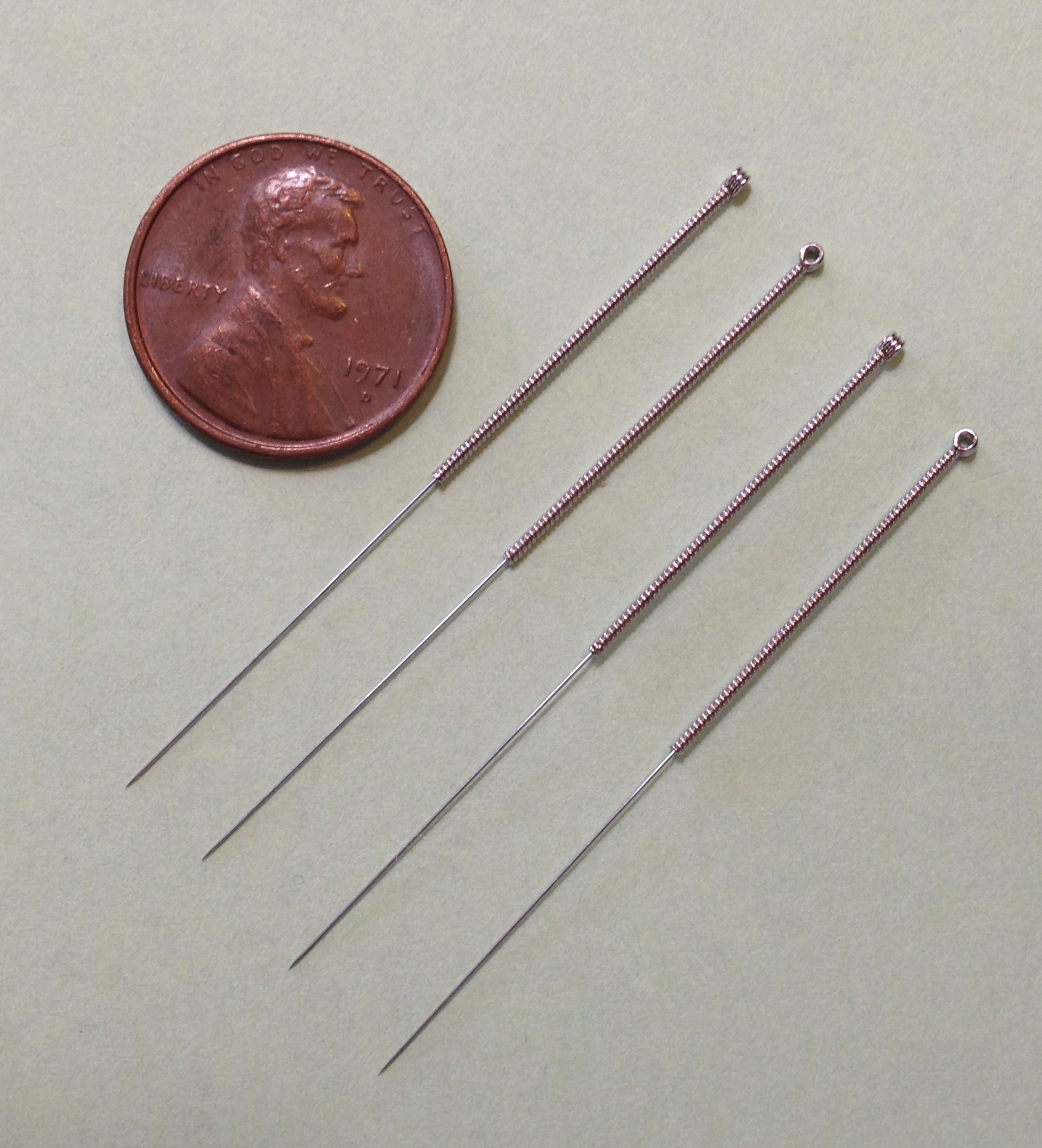
Acupuncture Point
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body. Acupuncture is a pseudoscience; the theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge, and it has been characterized as quackery. There is a range of acupuncture technological variants that originated in different philosophies, and techniques vary depending on the country in which it is performed. However, it can be divided into two main foundational philosophical applications and approaches; the first being the modern standardized form called eight principles TCM and the second being an older system that is based on the ancient Daoist '' wuxing'', better known as the five elements or phases in the West. Acupuncture is most often used to attempt pain relief, though acupuncturists say that it can also be used for a wide range of other conditions. Acupuncture is typically used in combination with other forms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue Diagnosis
Tongue diagnosis in Chinese Medicine is a method of diagnosing disease and disease patterns by visual inspection of the tongue and its various features. It is one of the major diagnostic methods in Chinese Medicine since the time of the Yellow Emperor's Inner Classic. It is considered a part of the “Inspection” method within the four methods of diagnosis. Practitioners claim that the tongue provides important clues reflecting the conditions of the internal organs. Like other diagnostic methods in Traditional Chinese Medicine, tongue diagnosis is based on the “outer reflects the inner” principle, which is that external structures often reflect the conditions of the internal structures and can give us important indications of internal disharmony. Topography of the Tongue The tongue is divided into topographic regions corresponding to the Triple Burner and Zang Fu organs. By observing the various regions of the tongue, one can determine where the disease is located within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Diagnosis
Pulse diagnosis is a diagnostic technique used in Ayurveda, traditional Chinese medicine, traditional Mongolian medicine, Siddha medicine, traditional Tibetan medicine, and Unani. Pulse diagnosis is ill-defined and subjective. Traditional Indian medicine (Ayurveda and Siddha-Veda) In Ayurveda, advocates claim that by taking a pulse examination, imbalances in the three Doshas ( Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) can be diagnosed. The ayurvedic pulse also claims to determine the balance of prana, tejas, and ojas.Peter Koch, December 1, 2012Ayurvedische Pulsdiagnose/ref> Ayurvedic pulse measurement is done by placing index, middle and ring finger on the wrist. The index finger is placed below the wrist bone on the thumb side of the hand (radial styloid). This index finger represents the Vata dosha. The middle finger and ring finger are placed next to the index finger and represents consequently the Pitta and Kapha doshas of the patient. Pulse can be measured in the superficial, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slit Lamp
In ophthalmology and optometry, a slit lamp is an instrument consisting of a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine a thin sheet of light into the eye. It is used in conjunction with a biomicroscope. The lamp facilitates an examination of the anterior segment and posterior segment of the human eye, which includes the eyelid, sclera, conjunctiva, iris (anatomy), iris, natural crystalline lens, and cornea. The binocular slit-lamp examination provides a stereoscopic magnified view of the eye structures in detail, enabling anatomical diagnoses to be made for a variety of eye conditions. A second, hand-held lens is used to examine the retina. History Two conflicting trends emerged in the development of the slit lamp. One trend originated from clinical research and aimed to apply the increasingly complex and advanced technology of the time. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zang-fu
The ''zangfu'' () organs are functional entities stipulated by traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). These classifications are based on east Asian cosmological observations rather than bio medical definitions that are used in Western evidence based medical models. In TCM theory they represent the energetic representation of the internal organs rather than the anatomical viscera that is referred to in Western medicine. Each ''zang'' is paired with a ''fu'', and each pair is assigned to one of the '' wuxing''. The ''zangfu'' are also connected to the twelve standard meridians – each yang meridian is attached to a ''fu'' organ and each yin meridian is attached to a ''zang''. They are five systems of Heart, Liver, Spleen, Lung, Kidney. To highlight the fact that the ''zangfu'' are not equivalent to the anatomical organs, their names are often capitalized. Anatomical organs To understand the ''zangfu'' it is important to realize that their concept did not primarily develop out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Division of the Mongol Empire, its division. It was established by Kublai (Emperor Shizu or Setsen Khan), the fifth khagan-emperor of the Mongol Empire from the Borjigin clan, and lasted from 1271 to 1368. In Chinese history, the Yuan dynasty followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although Genghis Khan's enthronement as Khagan in 1206 was described in Chinese language, Chinese as the Han Chinese, Han-style title of Emperor of China, Emperor and the Mongol Empire had ruled territories including modern-day northern China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Han style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279 when the Southern Song dynasty was defeated in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yin Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dynasty. The classic account of the Shang comes from texts such as the ''Book of Documents'', ''Bamboo Annals'' and ''Shiji''. Modern scholarship dates the dynasty between the 16th and 11th centuries BC, with more agreement surrounding the end date than beginning date. The Shang dynasty is the earliest dynasty within traditional Chinese history that is firmly supported by archaeological evidence. The archaeological site of Yinxu, near modern-day Anyang, corresponds to the final Shang capital of Yin. Excavations at Yinxu have revealed eleven major royal tombs, the foundations of former palace buildings, and the remains of both animals and humans that were sacrificed in official state rituals. Tens of thousands of bronze, jade, stone, bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyes
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system. In higher organisms, the eye is a complex optical system that collects light from the surrounding environment, regulates its intensity through a diaphragm, focuses it through an adjustable assembly of lenses to form an image, converts this image into a set of electrical signals, and transmits these signals to the brain through neural pathways that connect the eye via the optic nerve to the visual cortex and other areas of the brain. Eyes with resolving power have come in ten fundamentally different forms, classified into compound eyes and non-compound eyes. Compound eyes are made up of multiple small visual units, and are common on insects and crustaceans. Non-compound eyes have a single lens and focus light onto the retina to form a single image. This type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |