|
Chinese Deep Space Network
The Chinese Deep Space Network (CDSN) is a network of large antennas and communication facilities that are used for radio astronomy, radar observations, and spacecraft missions of China. The CDSN is managed by the China Satellite Launch and Tracking Control Center General (CLTC) of the People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force Space Systems Department. The network was first needed for the lunar mission Chang'e 1, and since has been used to support subsequent missions to the Moon and Mars such as Chang'e 5, Tianwen-1, and Tianwen-2 missions. Similar deep space networks are run by the United States, Russia, European countries, Japan, and India. History In principle, a Chinese deep space network has existed since 1993 with the commissioning of the Nanshan 25-meter telescope in the mountains south of ÃrÞmqi. The 25-meter antenna of the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory was then not only able to participate in the Southern Hemisphere VLBI Experiment program, but also to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLASSF
The People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force was a service branch of the People's Liberation Army that existed from December 2015 to April 2024. With an aim to improve the army's ability to fight what China terms "informationized conflicts" and enhance the PLA's power projection capabilities in space and cyberspace, the PLASSF was a force purportedly designed to break stovepipes in the intelligence sharing and coordination departments of the different branches. On 19 April 2024, the Strategic Support Force was dissolved and split into three independent arms: the People's Liberation Army Aerospace Force, the People's Liberation Army Cyberspace Force and the People's Liberation Army Information Support Force. History At the 2015 China Victory Day Parade, the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) general secretary, President of China and Central Military Commission (CMC) chairman Xi Jinping announced sweeping reforms to the structure of the Chinese People's Liberation Army (PLA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usuda Deep Space Center
is a facility of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. It is a spacecraft tracking station in Saku, Nagano (formerly in Usuda, Nagano; Usuda merged into Saku in 2005), opened in October, 1984. The main features of the station are two large beam waveguide antennas, an older 64 meter antenna and a newer 54 meter dish. Usuda was the first deep-space antenna constructed with beam-waveguide technology. Although this construction dramatically simplifies installation and maintenance of electronics, it was previously thought to offer poor noise performance. However, after the U.S. Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) tested this antenna and found the noise performance was better than its conventional 64-meter antennas, it too switched to this method of construction for all subsequent antennas of their Deep Space Network (DSN). Because the 64 meter antenna is aging and is still in use over ten years after its designed service life, JAXA has built a new antenna nearby, the 54 meter dish of Misasa D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shandong
Shandong is a coastal Provinces of China, province in East China. Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilization along the lower reaches of the Yellow River. It has served as a pivotal cultural and religious center for Taoism, Chinese Buddhism and Confucianism. Shandong's Mount Tai is the most revered mountain of Taoism and a site with one of the longest histories of continuous religious worship in the world. The Buddhist temples in the mountains south of the provincial capital of Jinan were once among the foremost Buddhist sites in China. The city of Qufu was the birthplace of Confucius, and later became the center of Confucianism. Shandong's location at the intersection of ancient and modern northâsouth and eastâwest trading routes has helped establish it as an economic center. After a period of political instability and economic hardship beginning in the late 19th century, Shandong has experienced rapid growth in recent de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
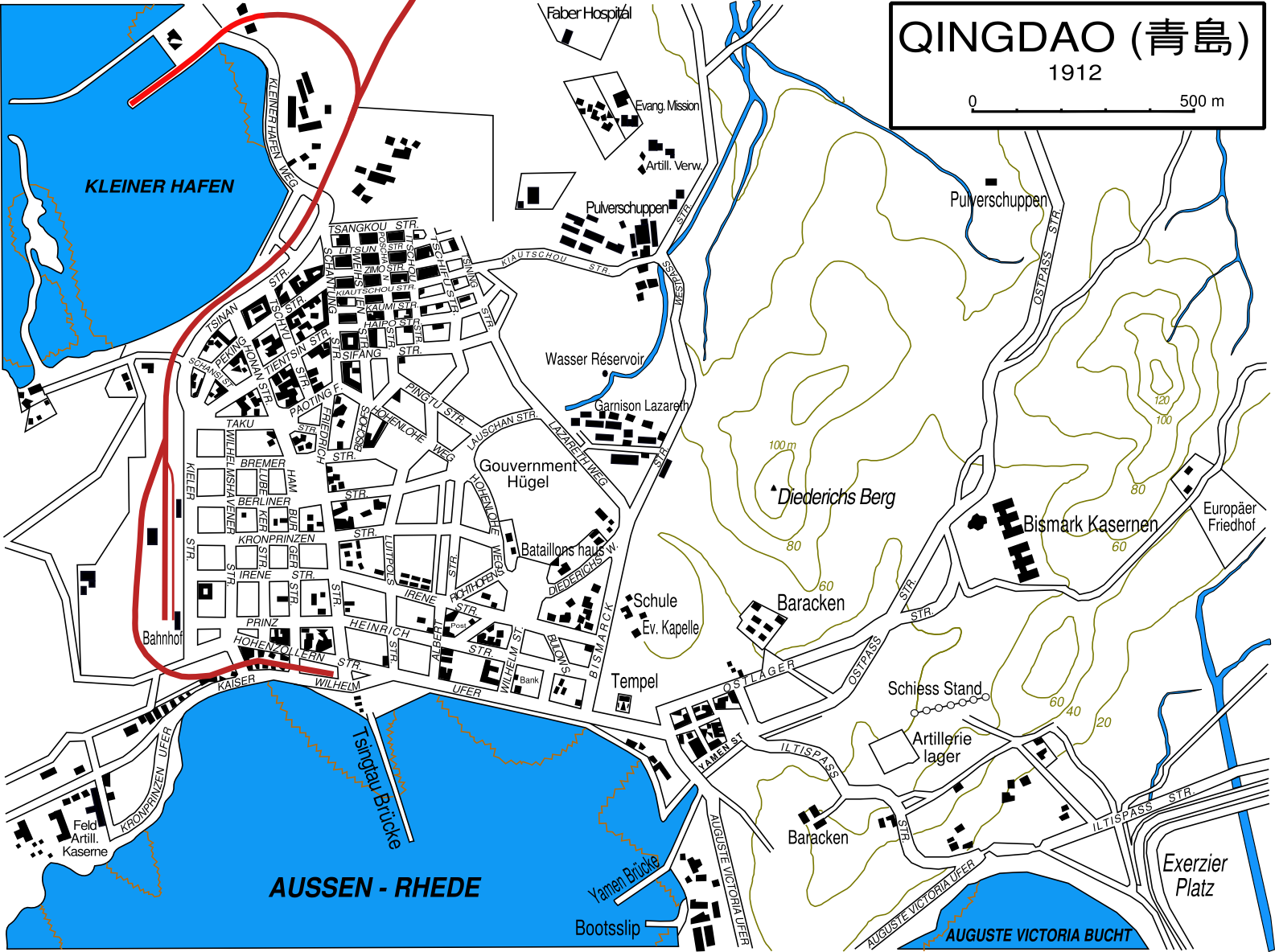
Qingdao
Qingdao, Mandarin: , (Qingdao Mandarin: tÍĄÉĘ°iÅ˧ËĐ tÉËĨ) is a prefecture-level city in the eastern Shandong Province of China. Located on China's Yellow Sea coast, Qingdao was long an important fortress. In 1897, the city was ceded to Germany. For the Germans Qingdao (Tsingtau) was a strategic trade center, port and base for its East Asia Squadron, allowing the German navy to project dominance in the Pacific. In 1914, following the outbreak of World War I, Japan occupied the city and the surrounding province during the Siege of Tsingtao. In 1915, China agreed to recognize Japan's special position in the territory through what became known as the Twenty-One Demands. In 1918, the Chinese government, under the control of the warlord Duan Qirui, secretly agreed to Japanese terms in exchange for a loan. Following the First World War, during the Paris Peace Conference, Japan secured agreements with the Allied powers to recognize its claim to the areas in Shandong, which in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
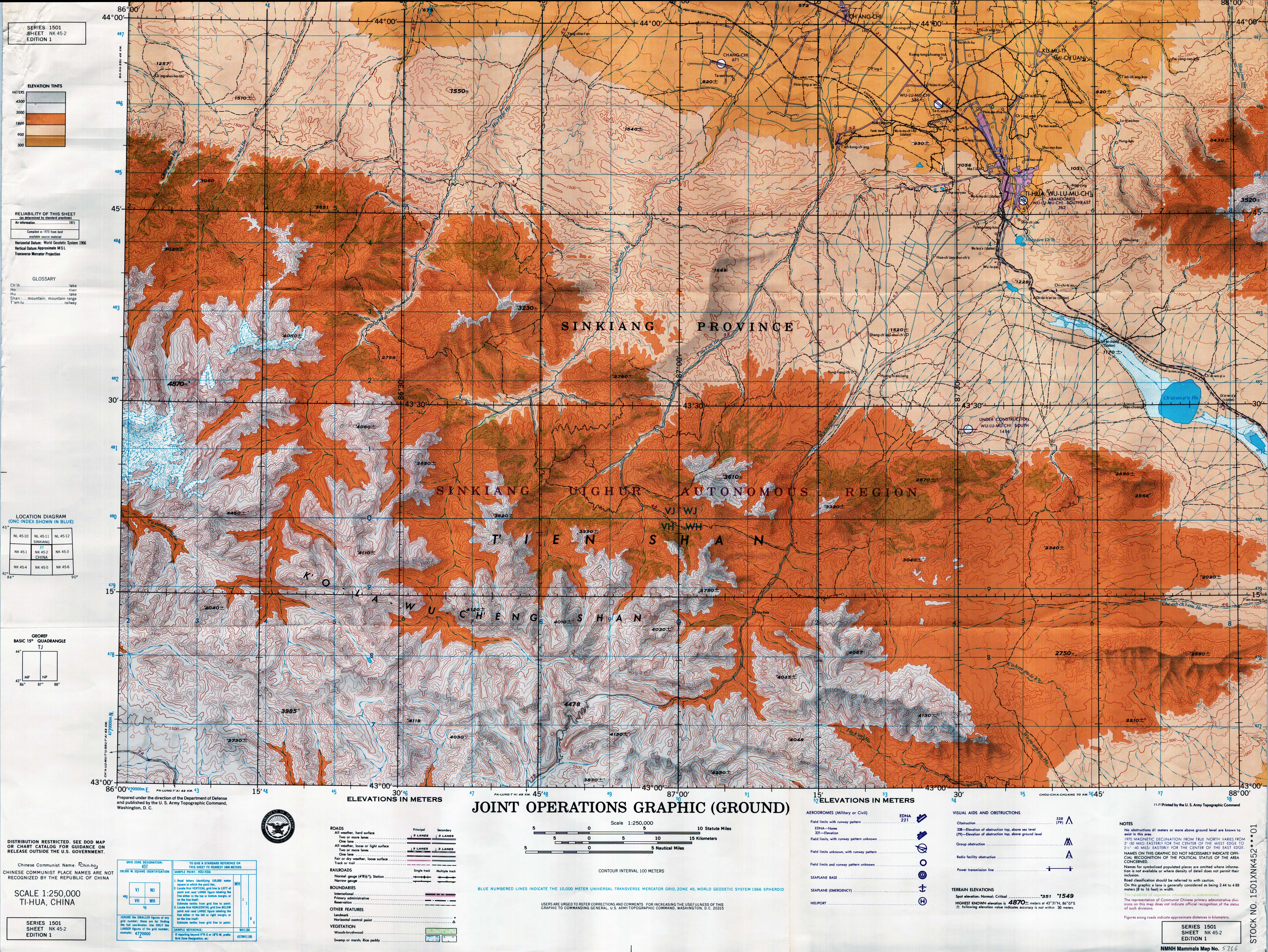
Kashgar
Kashgar () or Kashi ( zh, c=åäŧ) is a city in the Tarim Basin region of southern Xinjiang, China. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, located near the country's border with Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. For over 2,000 years, Kashgar was a strategically important oasis on the Silk Road between China, the Middle East, and Europe. It is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world and has a population of 711,300 people (). Kashgar's urban area covers , although its administrative area extends over . At the convergence point of widely varying cultures and empires, Kashgar has been under the rule of the Chinese, Turkic, Mongol and Tibetan empires. The city has also been the site of a number of battles between various groups of people on the steppes. Now administered as a county-level city, Kashgar is the administrative centre of Kashgar Prefecture, which has an area of and a population of approximately 4 million . Kashgar was declared a Special Economic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai 65-meter Tianma Radio Telescope
Shanghai, Shanghainese: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: is a direct-administered municipality and the most populous urban area in China. The city is located on the Chinese shoreline on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowing through it. The population of the city proper is the List of largest cities, second largest in the world after Chongqing, with around 24.87 million inhabitants in 2023, while the urban area is the List of cities in China by population, most populous in China, with 29.87 million residents. As of 2022, the Greater Shanghai metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product (GDP (nominal), nominal) of nearly 13 trillion Renminbi, RMB ($1.9 trillion). Shanghai is one of the world's major centers for finance, #Economy, business and economics, research, science and technology, manufacturing, transportation, List of tourist attractions in Shanghai, tourism, and Culture of Shanghai, culture. The Port of Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European VLBI Network
The European VLBI Network (EVN) is a network of radio telescopes located primarily in Europe and Asia, with additional antennas in South Africa and Puerto Rico, which performs very high angular resolution observations of cosmic radio sources using very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI). The EVN is the most sensitive VLBI array in the world, and the only one capable of real-time observations. The Joint Institute for VLBI ERIC (JIVE) acts as the central organisation in the EVN, providing both scientific user support and a correlator facility. Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) achieves ultra-high angular resolution and is a multi-disciplinary technique used in astronomy, geodesy and astrometry. The EVN operates an open-sky policy, allowing anyone to propose an observation using the network EVN Telescopes The EVN network comprises 22 telescope facilities: Additionally the EVN often links with the UK-based 7-element Jodrell Bank MERLIN interferometer. It can also be con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consultative Committee For Space Data Systems
Consultation or consultative may refer to: * Public consultation, a process by which the public's input on matters affecting them is sought * Consultation (Texas), the 1835 Texas meeting of colonists on a proposed rebellion against the Republic of Mexico * Consultation (doctor), a formal meeting with a medical doctor for discussion or the seeking of advice * Consultation in object-oriented programming, see Object aggregation * An event similar to a symposium * Consultative status The consultative status is a phrase that has been in use since the establishment of the United Nations and is used within the UN community to refer to "Non-governmental organizations (Non-governmental organisation, NGOs) in Consultative Status with ..., a standing granted by the United Nations to selected non-governmental organizations See also * Consultant (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Maser
A hydrogen maser, also known as hydrogen frequency standard, is a specific type of maser that uses the intrinsic properties of the hydrogen atom to serve as a precision frequency reference. Overview Both the proton and electron of a hydrogen atom have spins. The atom has a higher energy if both spins are aligned, and a lower energy if they are opposed. The amount of energy needed to reverse the spin of the electron is equivalent to a photon at the frequency of , which corresponds to the 21 cm line in the hydrogen spectrum. Hydrogen masers are very complex devices and sell for as much as . There are two types to be distinguished: active and passive. In both types, a small storage bottle of molecular hydrogen, , leaks a controlled amount of gas into a discharge bulb. The molecules are dissociated in the discharge bulb into individual hydrogen atoms by an electric arc. This atomic hydrogen passes through a collimator then a magnetic state selector and into a storage bulb. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very-long-baseline Interferometry
Very-long-baseline interferometry (VLBI) is a type of astronomical interferometry used in radio astronomy. In VLBI a signal from an astronomical radio source, such as a quasar, is collected at multiple radio telescopes on Earth or in space. The distance between the radio telescopes is then calculated using the time difference between the arrivals of the radio signal at different telescopes. This allows observations of an object that are made simultaneously by many radio telescopes to be combined, emulating a telescope with a size equal to the maximum separation between the telescopes. Data received at each antenna in the array include arrival times from a local atomic clock, such as a hydrogen maser. At a later time, the data are correlated with data from other antennas that recorded the same radio signal, to produce the resulting image. The resolution achievable using interferometry is proportional to the observing frequency. The VLBI technique enables the distance between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai Astronomical Observatory
Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO) is an astronomical observatory in Shanghai. It has a long history of astrometry and also operates the Sheshan radio telescope as part of the Chinese VLBI array and the European VLBI Network (EVN). History It was formed in 1962 from the merger of the Xujiahui (also romanized as "Ziikawei") and Sheshan (Zose) observatories in Shanghai. It was involved with the Chang'e 1 Moon mission as the VLBI array is used for position determinations. In October 2012 the Tian Ma radio telescope was completed for SHAO. It is part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS; ) is the national academy for natural sciences and the highest consultancy for science and technology of the People's Republic of China. It is the world's largest research organization, with 106 research i .... List of directors * Li Heng () (1962 â Cultural Revolution) * Ye Shuhua (1978â1979) * Li Heng (1979â1981) * Ye Shuhua (1981â19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ÃrÞmqi
ÃrÞmqi, , is the capital of the Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in Northwestern China. With a census population of 4 million in 2020, ÃrÞmqi is the second-largest city in China's northwestern interior after Xi'an, also the second-largest in Central Asia in terms of population, right after Kabul, Afghanistan. ÃrÞmqi has seen significant economic development since the 1990s and currently serves as a List of transport topics#Nodes, regional transport node and a cultural, political and commercial center. Etymology The name ÃrÞmqi comes from the Mongolic languages, Mongolic Oirat language and means "beautiful pasture" (, ). It was originally the name of a small town founded by the Mongolic peoples, Mongolic, Oirat-speaking Dzungar people, Dzungars. The Qing dynasty took ÃrÞmqi by force in 1755, during DzungarâQing Wars, its conquest of the Dzungar Khanate. Qing forces expanded the town into a walled city from 1763 to 1767, and upon completing the expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |