|
Chimalapas Montane Forests
The Chimalapas montane forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in southern Mexico. It includes the montane tropical forests of the Chimalapas region on the boundary of Chiapas and Oaxaca. Geography The Chimalapas region is in the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, and the region's mountains form part of the divide between Mexico's Pacific watersheds to the south and Gulf of Mexico watersheds to the north. The montane forests are bounded by the lowland Petén–Veracruz moist forests on the north. The Chiapas Depression dry forests lie to the northeast. The montane forests adjoin the Sierra Madre de Oaxaca pine–oak forests on the west, and the Central American pine–oak forests to the east. The Southern Pacific dry forests lie to the south between the mountains and the Pacific Ocean. Climate The climate of the ecoregion is tropical and humid. The forests have a cooler climate than the surrounding lowlands, and average annual temperatures decrease with elevation. Flora The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solitary Eagle
The solitary eagle or montane solitary eagle (''Buteogallus solitarius'') is a large Neotropical eagle. It is also known as the black solitary eagle. Range and habitat The solitary eagle is native to Mexico and Central and South America. It is found in mountainous or hilly forests, at elevations between 600 m and 2,200 m. The frequent reports from lowlands are usually misidentifications of another species, usually the common black hawk or great black hawk; no reports from lowlands have been confirmed. It is rare that in all areas of its range and poorly known. Very little is known about its diet, other than that it appears to have often been predating large snakes and one adult pair was seen hunting deer fawns. The remains of a chachalaca were noted in one nest. Description The adult solitary eagle is uniformly dark gray, often appearing black, with white markings on the tail. It is and has a wingspan. With a body mass of approximately , it appears to rival its simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montane Forests
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial factor in shaping plant community, biodiversity, metabolic processes and ecosystem dynamics for montane ecosystems. Dense montane forests are common at moderate elevations, due to moderate temperatures and high rainfall. At higher elevations, the climate is harsher, with lower temperatures and higher winds, preventing the growth of trees and causing the plant community to transition to montane grasslands and shrublands or alpine tundra. Due to the unique climate conditions of montane ecosystems, they contain increased numbers of endemic species. Montane ecosystems also exhibit variation in ecosystem services, which include carbon storage and water supply. Life zones As elevation increases, the climate becomes cooler, due to a decrease in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregions Of Mexico
The following is a list of ecoregions in Mexico as identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). A different system of ecoregional analysis is used by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation, a trilateral body linking Mexican, Canadian and United States environmental regime. Terrestrial ecoregions The terrestrial ecoregions of Mexico span two biogeographic realms - the Nearctic and Neotropic - which together constitute the entire biogeography of the Americas. Veracruz is the most biodiverse state with 10 ecoregions across 5 biomes and 2 realms. Chiapas comes in a close second with 10 ecoregions across 4 biomes in the same realm. By contrast, Morelos is the least biodiverse state with just 2 ecoregions. Freshwater ecoregions Baja California Complex * Baja California Colorado River Complex * Colorado Delta * Sonoran Sinaloan Coastal Complex * Sinaloan Coastal Rio Bravo Complex * Rio Bravo * Pecos * Guzman * Mapimí * Cuatro Ciénegas * Llanos El ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
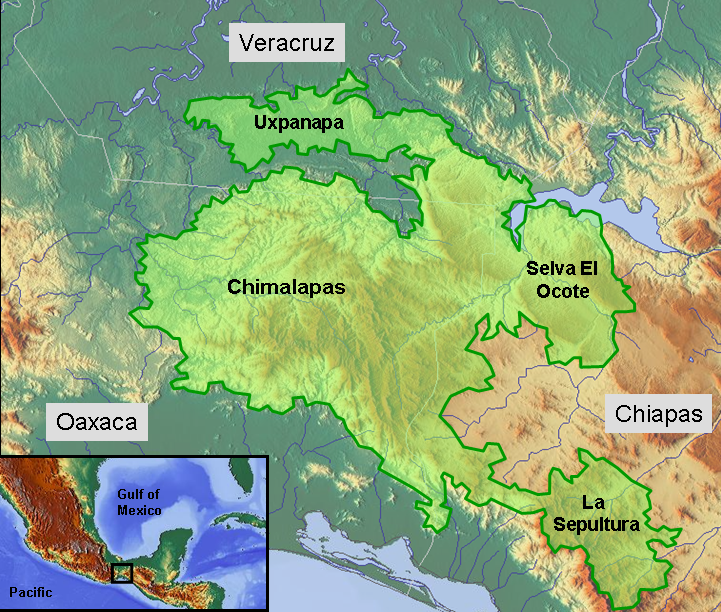
Selva Zoque
The Selva Zoque (), which includes the Chimalapas rain forest, is an area of great ecological importance in Mexico. Most of the forest lies in the state of Oaxaca but parts are in Chiapas and Veracruz. It is the largest tract of tropical rainforest in Mexico, and contains the majority of terrestrial biodiversity in the country. The forest includes the Selva El Ocote, a federally-protected biosphere reserve, but is otherwise not yet protected. Despite the rich ecology of the region, a 2003 study that focused on bird populations stated that "the fauna of the heart of the Chimalapas, including its vast rainforests, have seen little or no study". As it is an impoverished region, efforts to preserve the ecology are often at odds with demands to improve the economy. Geography The forest lies between 16°00'32"N, 17°32'00"N, 93°21'40"W and 94°53'53"W in the eastern part of the mountain range that forms the spine of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec. The terrain is rugged and includes a com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimalapas Territory Conflict
For more than 500 years, the indigenous Zoque people of Chimalapas in Southern Mexico have been victim of invasions in their territory. Chimalapas is a region with a large biodiversity and due to that it is of interest to, among others, the federal government, state governments, and a variety of companies. Therefore, throughout history several claims have been laid on this area. This goes against the will of the Zoque people, who want to take care of this land as they have done ever since they started living in this area. Area Chimalapas is primarily located in southeastern Oaxaca and partially in western Chiapas. It is one of the bioregions of top importance in all of Mesoamerica. A variety of ecosystems exists in this area, including rainforests, cloud forests, and pine forests. Chimalapas is also inhabited by a large variety of animal and plant species. Although Chimalapas has a great biodiversity, is not a wildlife reserve or a protected space. The Mexican government has repeate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ecoregions In Mexico
The following is a list of ecoregions in Mexico as identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). A different system of ecoregional analysis is used by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation, a trilateral body linking Mexican, Canadian and United States environmental regime. Terrestrial ecoregions The terrestrial ecoregions of Mexico span two biogeographic realms - the Nearctic and Neotropic - which together constitute the entire biogeography of the Americas. Veracruz is the most biodiverse state with 10 ecoregions across 5 biomes and 2 realms. Chiapas comes in a close second with 10 ecoregions across 4 biomes in the same realm. By contrast, Morelos is the least biodiverse state with just 2 ecoregions. Freshwater ecoregions Baja California Complex * Baja California Colorado River Complex * Colorado Delta * Sonoran Sinaloan Coastal Complex * Sinaloan Coastal Rio Bravo Complex * Rio Bravo * Pecos * Guzman * Mapimí * Cuatro Ciénegas * Llanos El Salado * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa María Chimalapa
Santa María Chimalapa is a town and municipality in Oaxaca in southeastern Mexico and the easternmost and largest municipality in Oaxaca, but is also the least densely populated municipality in Oaxaca. It is part of the Juchitán District in the west of the Istmo de Tehuantepec region. Geography The municipality has an area of 3572.31 km², much of it covered by tropical rain forest. The climate is warm sub humid, with summer rainfall of 23,000 mm. The town is at a height of 180 metres above sea level and is supplied with water by El Rio Corte, originating in the Selva Zoque forests to the east. Flora and fauna The forests contain many species of tree including cedar, mahogany, Nopo, Guanacaste, cedrillo, coabillo, ceiba, pine, hormiguillo, rattan, oak, oak, lime, nanche, pineapple, custard apple, tangerine and coffee. Wild fauna include boar, paca, deer, jaguar, raccoon, skunk, monkey, pheasant, parrot, owl, toucan, white eagle, rattlesnake, coral snake deaf. Dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peso
The peso is the monetary unit of several Hispanophone, Spanish-speaking countries in Latin America, as well as the Philippines. Originating in the Spanish Empire, the word translates to "weight". In most countries of the Americas, the symbol commonly known as dollar sign, "$", was originally used as an abbreviation of "pesos" and later adopted by the dollar. The dollar itself actually originated from the peso or Spanish dollar in the late 18th century. The sign "Philippine peso sign, ₱" is used in the Philippines. The silver ''peso'' worth eight ''Spanish real, reales'' was also known in English as a Spanish dollar or "piece of eight" and was widely used for international trade from the 16th to the 19th century. Origin and history 1537–1686 piece of eight The name ''peso'' was given to the 8-Spanish real, real silver coin introduced in 1497, minted at 8 pesos to a Castilian mark (230.0465 grams) of silver 134/144 fine (25.56 g fine silver). It was minted in large quantiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
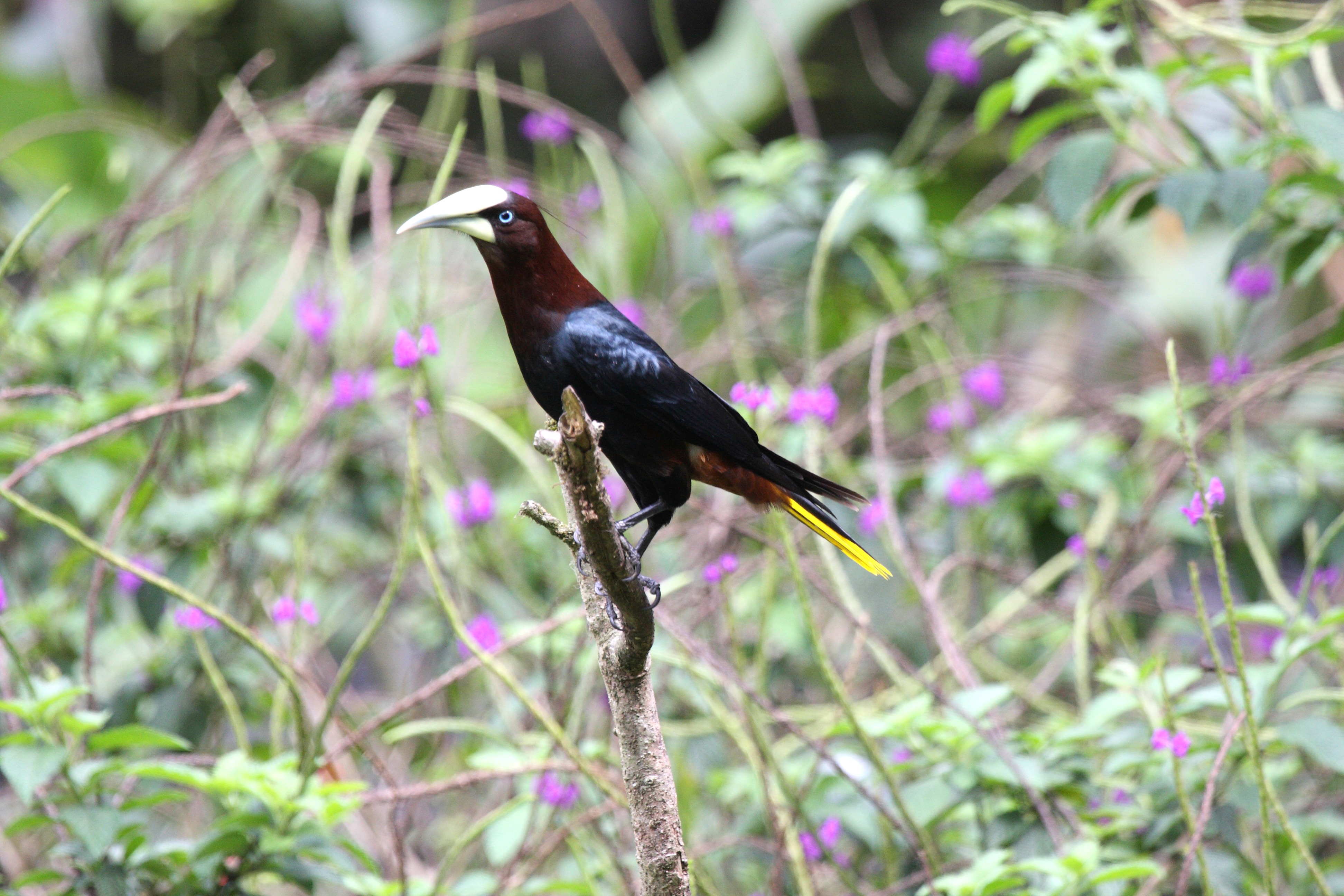
Chestnut-headed Oropendola
The chestnut-headed oropendola (''Psarocolius wagleri'') is a New World tropical icterid bird. The scientific name of the species commemorates Johann Georg Wagler, who established ''Psarocolius'', the oropendola genus. Description The male is long and weighs ; the smaller female is long and weighs . The wings are very long. Adult males are mainly black with a chestnut head and rump and a tail which is bright yellow apart from two dark central feathers. The iris is blue and the long bill is whitish. Females are similar, but smaller and duller than males. Young birds are duller than adults and have brown eyes. The populations south of an area around the border of Honduras and Nicaragua are sometimes separated as a subspecies ''P. w. ridgwayi'', but the separation of this form has been questioned. The distinctive songs of the male include a gurgle followed by a crash ''guu-guu-PHRRRRTTT''. Both sexes have loud ''chek'' and ''chuk'' calls. Range and ecology It is a resident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Mealy Amazon
The southern mealy amazon or southern mealy parrot (''Amazona farinosa farinosa'') is among the largest parrots in the genus ''Amazona'', the amazon parrots. It is a mainly green parrot with a total length of . It is native to tropical Central and South America. This parrot and the northern mealy amazon (''Amazona farinosa guatemalae'') are considered conspecific. Taxonomy The southern mealy amazon was described by the French polymath Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon in 1780 in his ''Histoire Naturelle des Oiseaux'' from a specimen collected in Cayenne, French Guiana. The bird was also illustrated in a hand-coloured plate engraved by François-Nicolas Martinet in the ''Planches Enluminées D'Histoire Naturelle'' which was produced under the supervision of Edme-Louis Daubenton to accompany Buffon's text. Neither the plate caption nor Buffon's description included a scientific name but in 1783 the Dutch naturalist Pieter Boddaert coined the binomial name ''Psittacus farino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keel-billed Motmot
The keel-billed motmot (''Electron carinatum'') is a Vulnerable species of bird in the motmot family Momotidae. It is found in Belize, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, and Nicaragua. Taxonomy and systematics The keel-billed motmot was formally described as ''Pionites carinatus''. It was later referred to as ''Prionirhynchus carinatus'' but eventually was renamed ''Electron carinatum''. The keel-billed motmot is thought to be closely related to the broad-billed motmot (''E. platyrhynchum''); they are the only members of the genus ''Electron''. The two may be conspecific. Their plumage is very different but their structure and vocalizations are very similar.Snow, D., G. M. Kirwan, and C. J. Sharpe (2020). Keel-billed Motmot (''Electron carinatum''), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.kebmot1.01 retrieved April 5, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |