|
Childhood Obesity
Childhood obesity is a condition where excess adipose tissue, body fat negatively affects a child's health or well-being. As methods to determine body fat directly are difficult, the diagnosis of obesity is often based on Body mass index, BMI. Due to the rising prevalence of obesity in children and its many adverse health effects it is being recognized as a serious public health concern. The term ''overweight'' rather than ''obese'' is often used when discussing childhood obesity, as it is less Social stigma of obesity, stigmatizing, although the term ''overweight'' can also refer to a different BMI category. The prevalence of childhood obesity is known to differ by sex and gender. Classification Body mass index (BMI) is acceptable for determining obesity for children two years of age and older. It is determined by the ratio of weight to height. The normal range for BMI in children vary with age and sex. While a BMI above the 85th percentile is defined as overweight, a BM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipose Tissue
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of White blood cell, immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and Thermal insulation, insulates the body. Previously treated as being hormonally inert, in recent years adipose tissue has been recognized as a major endocrine organ, as it produces hormones such as leptin, estrogen, resistin, and cytokines (especially TNF-alpha, TNFα). In obesity, adipose tissue is implicated in the chronic release of pro-inflammatory markers known as adipokines, which are responsible for the development of metabolic syndromea constellation of diseases including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. Adipose tissue is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea (sleep apnoea or sleep apnœa in British English) is a sleep-related breathing disorder in which repetitive Apnea, pauses in breathing, periods of shallow breathing, or collapse of the upper airway during sleep results in poor ventilation and sleep disruption. Each pause in breathing can last for a few seconds to a few minutes and often occurs many times a night. A choking or snorting sound may occur as breathing resumes. Common symptoms include daytime sleepiness, snoring, and non restorative sleep despite adequate sleep time. Because the disorder disrupts normal sleep, those affected may experience sleepiness or feel tired during the day. It is often a chronic condition. Sleep apnea may be categorized as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), in which breathing is interrupted by a blockage of air flow, central sleep apnea (CSA), in which regular unconscious breath simply stops, or a combination of the two. OSA is the most common form. OSA has four key contributors; these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperandrogenism
Hyperandrogenism is a medical condition characterized by high levels of androgens. It is more common in women than men. Symptoms of hyperandrogenism may include acne, seborrhea, hair loss on the scalp, increased body or facial hair, and infrequent or absent menstruation. Complications may include high blood cholesterol and diabetes. It occurs in approximately 5% of women of reproductive age. Polycystic ovary syndrome accounts for about 70% of hyperandrogenism cases. Other causes include Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, insulin resistance, hyperprolactinemia, Cushing's disease, certain types of cancers, and certain medications. Diagnosis often involves blood tests for testosterone, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, and prolactin, as well as a pelvic ultrasound. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Symptoms of hyperandrogenism can be treated with birth control pills or antiandrogens, such as cyproterone acetate or spironolactone. Other measures may include hair removal techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Metabolic syndrome is associated with the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. In the U.S., about 25% of the adult population has metabolic syndrome, a proportion increasing with age, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and prediabetes are closely related to one another and have overlapping aspects. The syndrome is thought to be caused by an underlying disorder of energy utilization and storage, but the cause of the syndrome is an area of ongoing medical research. Researchers debate whether a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome implies differential treatment or increases risk of cardiovascular disease beyond what is suggested by the sum of its individual components. Signs and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid, parathyroid, pituitary, pineal, and adrenal glands, and the (male) testis and (female) ovaries. The hypothalamus, pancreas, and thymus also function as endocrine glands, among other functions. (The hypothalamus and pituitary glands are organs of the neuroendocrine system. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamusit is located in the brain adjacent to the pituitary glandis to link the endocrine system to the nervous system via the pituitary gland.) Other organs, such as the kidneys, also have roles within the endocrine system by secreting certain hormones. The study of the endocrine system and its disorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTV News
CTV News is the news division of the CTV Television Network in Canada. The name ''CTV News'' is also applied as the title of local and regional newscasts on the network's owned-and-operated stations (O&Os), which are closely tied to the national news division. Local newscasts on CTV 2 are also branded as ''CTV News'', although in most cases they are managed separately from the newscasts on the main CTV network. History On 1 September 2011, chief news anchor Lloyd Robertson retired after 35 years at the helm of the flagship. In September 2023 BellMedia celebrated long-time news anchor Sandie Rinaldo's 50th year with the franchise. On 26 September 2024 CTV News admitted that it had altered or manipulated a clip of Pierre Poilievre broadcast the previous Sunday. It fired two news editors and apologized "unreservedly". On 2 October he ended his boycott of the broadcaster. in 1961 CTV News was launched by the government. National programs CTV's national news division produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils. Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all animal Cell (biology)#Eukaryotic cells, cells and is an essential structural and cholesterol signaling, signaling component of animal cell membranes. In vertebrates, hepatocyte, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. In the brain, astrocytes produce cholesterol and transport it to neurons. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as ''Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. Cholesterol also serves as a Precursor (chemistry), precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood, especially when bound to low-density lipoprotein (LDL, often referred to as "bad cholesterol"), may increase the risk of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Arteries
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries. Structure The common carotid arteries are present on the left and right sides of the body. These arteries originate from different arteries but follow symmetrical courses. The right common carotid originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk; the left from the aortic arch in the thorax. These split into the external and internal carotid arteries at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, at around the level of the fourth cervical vertebra. The left common carotid artery can be thought of as having two parts: a thoracic (chest) part and a cervical (neck) part. The right common carotid originates in or close to the neck and contains only a small thoracic portion. There are studies in the bioengineering literature that have looked into characterizing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
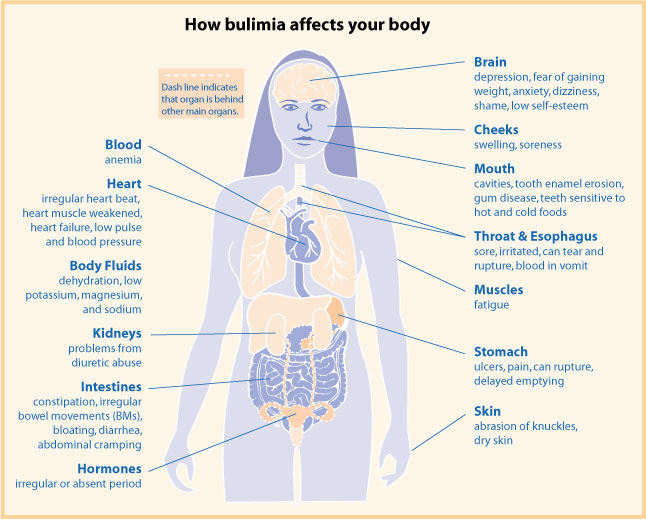
Bulimia
Bulimia nervosa, also known simply as bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating (eating large quantities of food in a short period of time, often feeling out of control) followed by compensatory behaviors, such as self-induced vomiting or fasting, to prevent weight gain. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, laxatives, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise. Most people with bulimia are at normal weight and have higher risk for other mental disorders, such as depression, anxiety, borderline personality disorder, bipolar disorder, and problems with drugs to alcohol. There is also a higher risk of suicide and self-harm. Bulimia is more common among those who have a close relative with the condition. The percentage risk that is estimated to be due to genetics is between 30% and 80%. Other risk factors for the disease include psychological stress, cultural pressure to attain a certain body type, poor self-esteem, and obesit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anorexia
Anorexia nervosa (AN), often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by Calorie restriction, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. Individuals with anorexia nervosa have a fear of being overweight or being seen as such, despite the fact that they are typically underweight. The DSM-5 describes this perceptual symptom as "disturbance in the way in which one's body weight or shape is experienced". In research and clinical settings, this symptom is called "body image disturbance" or Body dysmorphic disorder, body dysmorphia. Individuals with anorexia nervosa also often deny that they have a problem with low weight due to their altered perception of appearance. They may weigh themselves frequently, eat small amounts, and only eat certain foods. Some patients with anorexia nervosa Binge eating, binge eat and Purging disorder, purge to influence their weight or shape. Purging can manifest a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eating Disorders
An eating disorder is a mental disorder defined by abnormal eating behaviors that adversely affect a person's health, physical or mental health, mental health. These behaviors may include eating too much food or too little food. Types of eating disorders include binge eating disorder, where the person suffering keeps eating large amounts in a short period of time typically while not being hungry; anorexia nervosa, where the person has an intense fear of gaining weight and restricts food or overexercises to manage this fear; bulimia nervosa, where individuals eat a large quantity (binging) then try to rid themselves of the food (purging); pica (disorder), pica, where the patient eats non-food items; rumination syndrome, where the patient regurgitation (digestion), regurgitates undigested or minimally digested food; avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), where people have a reduced or selective food intake due to some psychological reasons; and a group of other specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
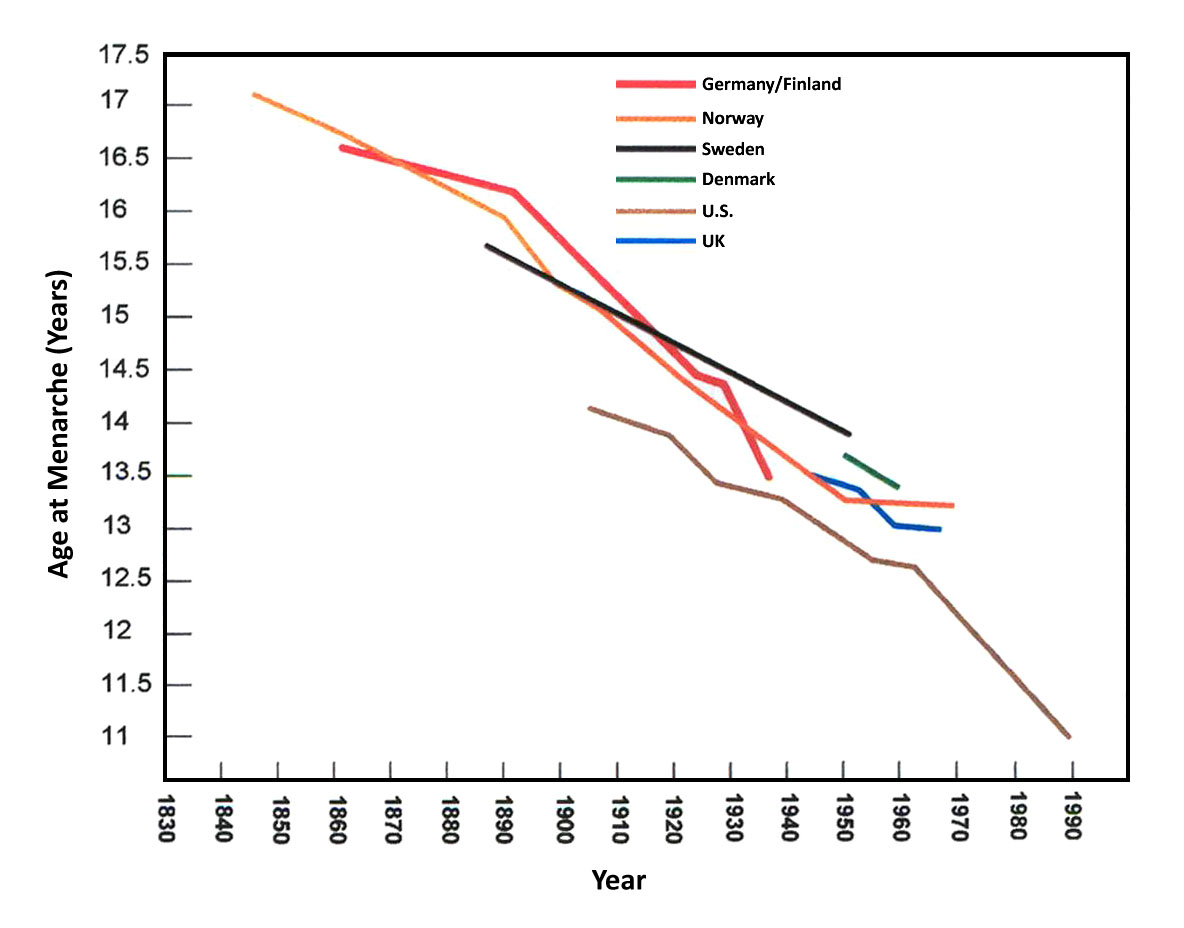
Menarche
Menarche ( ; ) is the first menstrual cycle, or first menstruation, menstrual bleeding, in female humans. From both social and medical perspectives, it is often considered the central event of female puberty, as it signals the possibility of fertility. Girls experience menarche at different ages, but the most common age is 12. Having menarche occur between the ages of 9–14 in the West is considered normal.US National Health Statistics Report September 2020 The timing of menarche is influenced by female biology, as well as Genetics, genetic, environmental factors, and nutritional factors. The mean age of menarche has declined over the last century, but the magnitude of the decline and the factors responsible remain subjects of contention. The worldwide average age of menarche is very difficult to estimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |