|
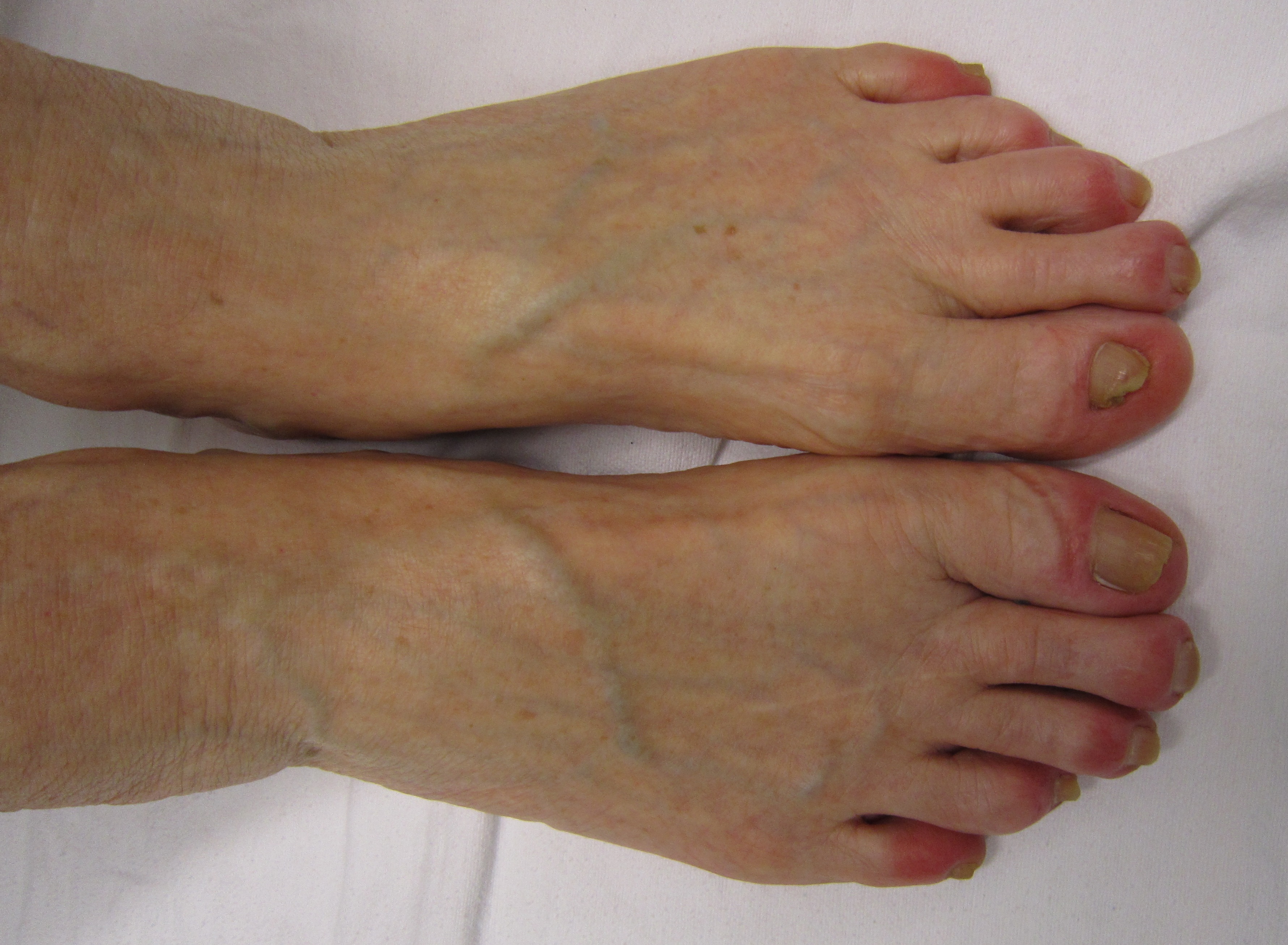
Chilblains
Chilblains, also known as pernio, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to capillary beds in the skin, most often in the hands or feet, when blood perfuses into the nearby tissue, resulting in redness, itching, inflammation, and possibly blisters. It occurs most frequently when predisposed individuals, predominantly women, are exposed to cold and humidity. Ulcerated chilblains are referred to as kibes. Temperature-related chilblains can be prevented by keeping the feet and hands warm in cold weather and avoiding exposing these areas to extreme temperature changes. Once the diagnosis of chilblains is made, first-line treatment includes avoiding cold, damp environments and wearing gloves and warm socks. Chilblains can be idiopathic (spontaneous and unrelated to another disease), but similar symptoms may also be a manifestation of another serious medical condition that must be investigated. Related medical conditions include Raynaud syndrome, erythromelalgia, fros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
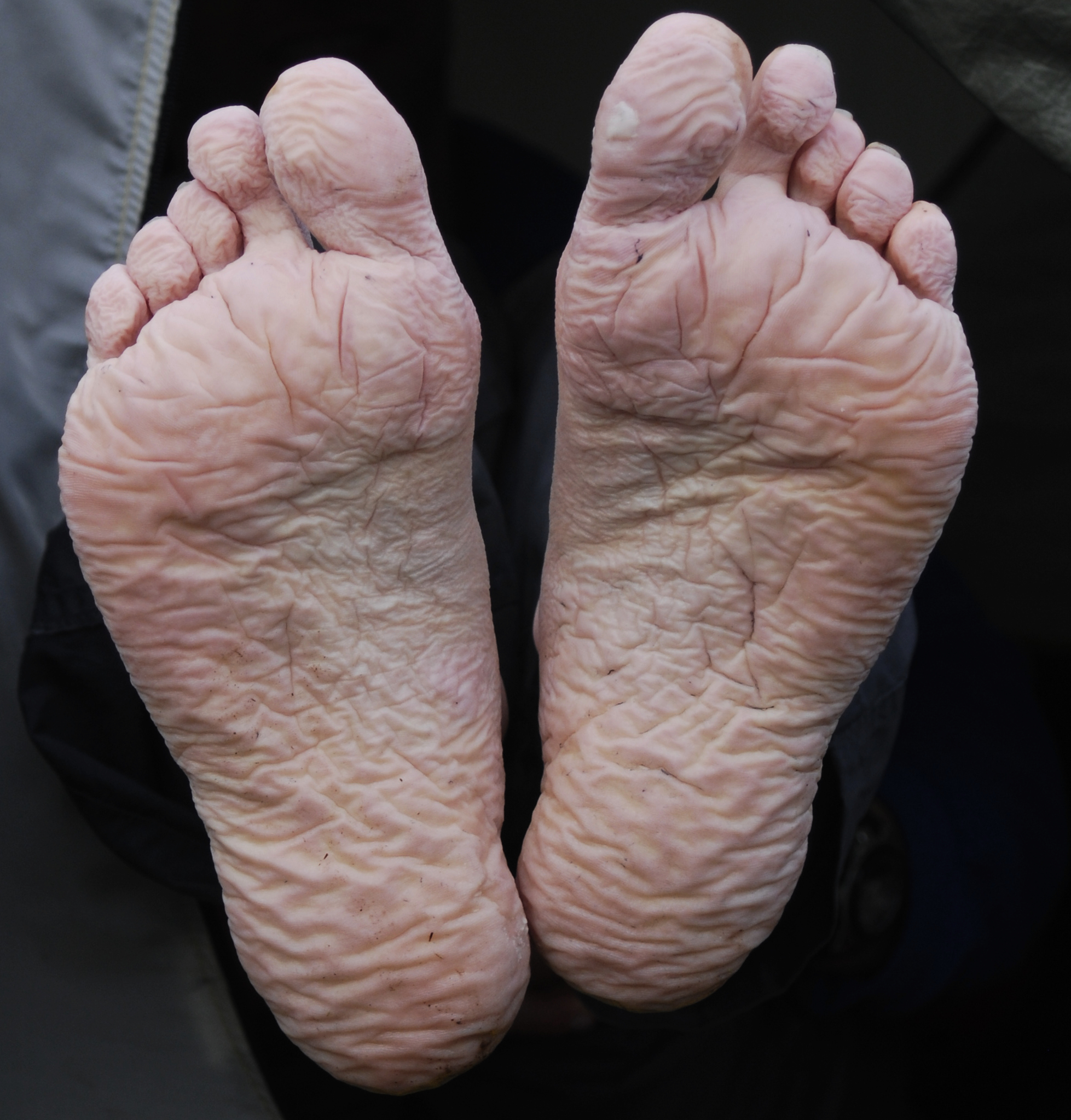
Frostbite
Frostbite is a skin injury that occurs when someone is exposed to extremely low temperatures, causing the freezing of the skin or other tissues, commonly affecting the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin areas. Most often, frostbite occurs in the hands and feet. The initial symptoms are typically a feeling of cold and tingling or numbing. This may be followed by clumsiness with a white or bluish color to the skin. Swelling or blistering may occur following treatment. Complications may include hypothermia or compartment syndrome. People who are exposed to low temperatures for prolonged periods, such as winter sports enthusiasts, military personnel, and homeless individuals, are at greatest risk. Other risk factors include drinking alcohol, smoking, mental health problems, certain medications, and prior injuries due to cold. The underlying mechanism involves injury from ice crystals and blood clots in small blood vessels following thawing. Diagnosis is based on sympt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raynaud Syndrome
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically the fingers, and, less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rarely, the nose, ears, nipples, or lips are affected. The episodes classically result in the affected part turning white and then blue. Often, numbness or pain occurs. As blood flow returns, the area turns red and burns. The episodes typically last minutes but can last several hours. The condition is named after the physician Auguste Gabriel Maurice Raynaud, who first described it in his doctoral thesis in 1862. Episodes are typically triggered by cold or emotional stress. Primary Raynaud's is idiopathic (spontaneous and of unknown cause) and not correlated with another disease. Secondary Raynaud's is diagnosed given the presence of an underlying condition and is associated with an older age of onset. In comparison to primary Raynaud's, ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench Foot
Trench foot, also known by #Names, other names, is a type of immersion foot syndromes, foot damage due to moisture. Initial symptoms often include tingling or itching which can progress to numbness. The feet may become erythema, red or cyanosis, bluish in color. As the condition worsens the feet can start to swell and smell of decay. Complications may include skin breakdown or infection. Trench foot occurs due to prolonged exposure of the feet to cold, damp, and often unsanitary conditions. Unlike frostbite, trench foot usually occurs at temperatures above freezing, and can be classed as a form of non-freezing cold injury. Onset can be as rapid as 10 hours. Risk factors include overly tight boots and not moving. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve vasoconstriction, constriction of blood vessels resulting in insufficient blood flow to the feet. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and physical examination, examination. Prevention involves keeping the feet warm, dry, and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Nose
The human nose is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum, which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two. The nose has an important function in breathing. The nasal mucosa lining the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses carries out the necessary conditioning of inhaled air by warming and moistening it. Nasal conchae, shell-like bones in the walls of the cavities, play a major part in this process. Filtering of the air by nasal hair in the nostrils prevents large particles from entering the lungs. Sneezing is a reflex to expel unwanted particles from the nose that irritate the mucosal lining. Sneezing can Transmission (medicine), transmit infections, because aerosols are created in which the Respiratory droplets, droplets can harbour pathogens. Another major function of the nose is olfactio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itch
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response patterns are different. Pain creates a withdrawal reflex, whereas itches leads to a scratch reflex. Unmyelinated nerve fibers for itches and pain both originate in the skin. Information for them is conveyed centrally in two distinct systems that both use the same nerve bundle and spinothalamic tract. Classification Most commonly, an itch is felt in one place. If it is felt all over the body, then it is called ''generalized itch'' or ''generalized pruritus''. Generalized itch is infrequently a symptom of a serious underlying condition, such as cholestatic liver disease. If the sensation of itching persists for six weeks or longer, then it is called ''chronic itch'' or ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythema
Erythema (, ) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology include nervous blushes. Types * Erythema ab igne * Erythema chronicum migrans * Erythema induratum * Erythema infectiosum (or fifth disease) * Erythema marginatum * Erythema migrans * Erythema multiforme (EM) * Erythema nodosum * Erythema toxicum * Erythema elevatum diutinum * Erythema gyratum repens * Keratolytic winter erythema * Palmar erythema Causes It can be caused by infection, massage, electrical treatment, acne medication, allergies, exercise, solar radiation (sunburn), photosensitization, acute radiation syndrome, mercury toxicity, blister agents, niacin administration, or waxing and tweezing of the hairs—any of which can cause the affected capillaries to dilate, resulting in redness. Erythema is a common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanch (medical)
When skin is blanched, it takes on a whitish appearance as blood flow to the region is prevented. This occurs during and is the basis of the physiologic test known as diascopy. Blanching of the fingers is also one of the most clinically evident signs of Raynaud's phenomenon. Blanching is prevented in gangrene as the red blood corpuscles are extravasated and impart red color to the gangrenous part. See also * Diascopy *Pallor Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eye ... References Dermatologic terminology {{dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid (lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid, either serum or plasma. However, blisters can be filled with blood (known as "blood blisters") or with pus (for instance, if they become infected). Smaller blisters are called ''blebs''. The word "blister" entered English in the 14th century. It came from the Middle Dutch and was a modification of the Old French , which meant a leprous nodule—a rise in the skin due to leprosy. In dermatology, the words cutaneous condition#Vesicle, ''vesicle'' and ''bulla'' refer to blisters of smaller or greater size, respectively. Some sources recommend not to pop a blister. If popped, bacteria can enter. Excess skin should not necessarily be removed as the top layer protects the soft tissue underneath. However, some sources a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nifedipine
Nifedipine ( ), sold under the brand name Procardia among others, is a calcium channel blocker medication used to manage angina, high blood pressure, Raynaud's phenomenon, and premature labor. It is one of the treatments of choice for Prinzmetal angina. It may be used to treat severe high blood pressure in pregnancy. Its use in preterm labor may allow more time for steroids to improve the baby's lung function and provide time for transfer of the mother to a well qualified medical facility before delivery. It is a calcium channel blocker of the dihydropyridine type. Nifedipine is taken by mouth and comes in fast- and slow-release formulations. Common side effects include lightheadedness, headache, feeling tired, leg swelling, cough, and shortness of breath. Serious side effects may include low blood pressure and heart failure. Nifedipine is considered safe in pregnancy and breastfeeding. Nifedipine was patented in 1967, and approved for use in the United States in 1981. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finger
A finger is a prominent digit (anatomy), digit on the forelimbs of most tetrapod vertebrate animals, especially those with prehensile extremities (i.e. hands) such as humans and other primates. Most tetrapods have five digits (dactyly, pentadactyly),#Cha1998, Chambers 1998 p. 603#OxfIll, Oxford Illustrated pp. 311, 380 and short digits (i.e. significantly shorter than the metacarpal/metatarsals) are typically referred to as toes, while those that are notably elongated are called fingers. In humans, the fingers are flexibly joint, articulated and opposable, serving as an important organ of somatosensory, tactile sensation and fine motor skill, fine movements, which are crucial to the dexterity of the hands and the ability to grasp and object manipulation, manipulate objects. Land vertebrate fingers As terrestrial vertebrates were evolution, evolved from lobe-finned fish, their forelimbs are phylogeny, phylogenetically equivalent to the pectoral fins of fish. Within the taxon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
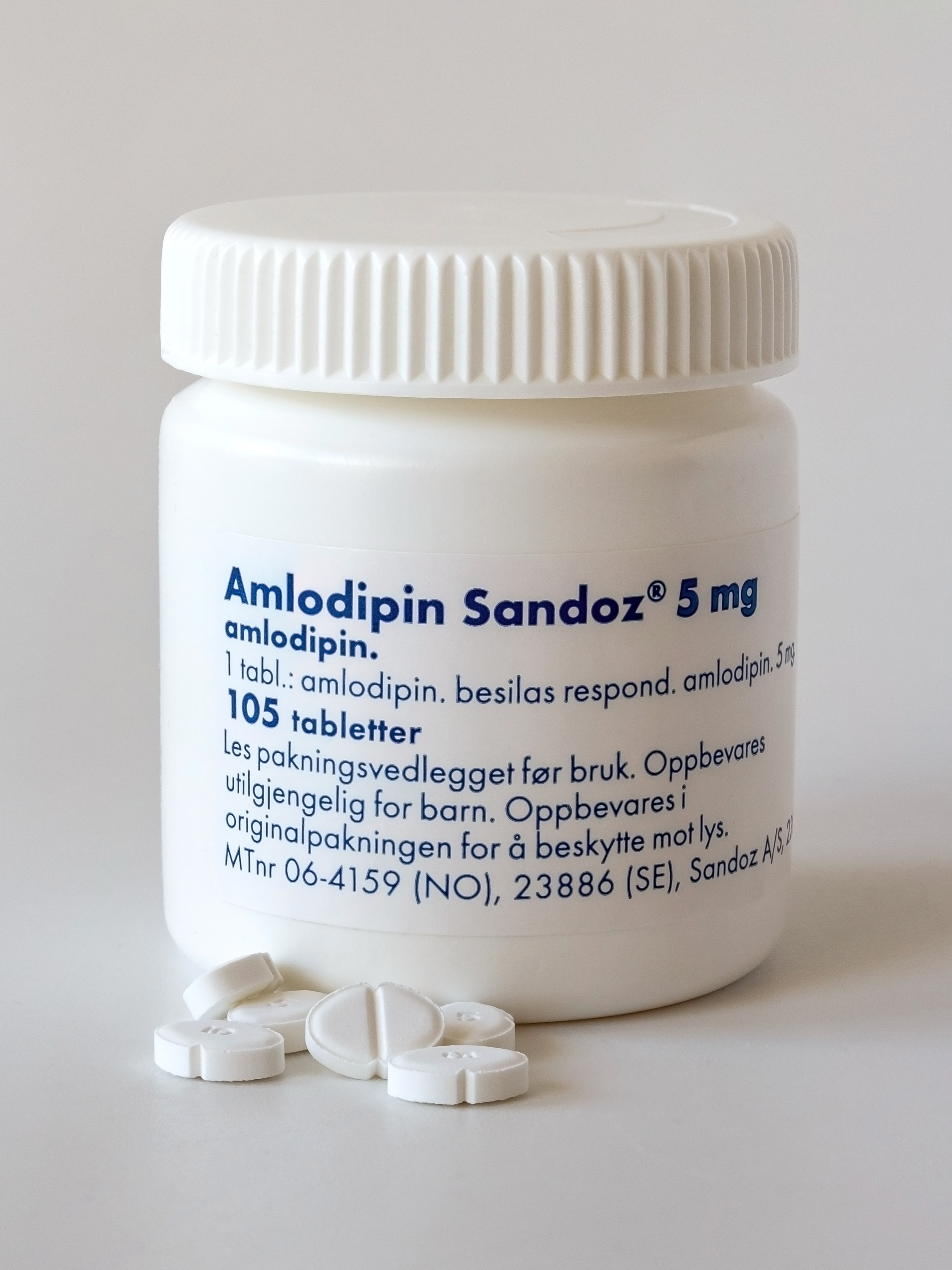
Amlodipine
Amlodipine, sold under the brand name Norvasc among others, is a calcium channel blocker medication used to treat hypertension, high blood pressure, coronary artery disease (CAD) and variant angina (also called Prinzmetal angina or coronary artery vasospasm, among other names). It is taken Oral administration, orally (swallowed by mouth). Common side effects include edema, swelling, fatigue (medical), feeling tired, abdominal pain, and nausea. Serious side effects may include hypotension, low blood pressure or myocardial infarction, heart attack. Whether use is safe during pregnancy or breastfeeding is unclear. When used by people with liver problems, and in elderly individuals, doses should be reduced. Amlodipine works partly by vasodilation (relaxing the arteries and increasing their diameter). It is a long-acting calcium channel blocker of the dihydropyridine type. Amlodipine was patented in 1982, and approved for medical use in 1990. It is on the WHO Model List of Essent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |