|
Chief Kitsap
Kitsap (; ) was a leader of the Suquamish people during the 19th century. Kitsap was the orchestrator of a region-wide coalition that sought to end the constant slave raids perpetrated by the Cowichan. His wealth and prestige allowed him to build the Old Man House, one of the most famous longhouses on Puget Sound. Kitsap, who met one of the first European expeditions into Puget Sound, was quick to ally with European traders, and set a precedent for Suquamish attitudes toward white settlers in the future. Kitsap was famed for his prowess, military strategy, wealth, and medicine powers, and is remembered by the Suquamish both for his military achievements, and his violent nature, which made him many enemies. His military campaigns influenced Seattle, his nephew. His contemporary, pioneer Theodore O. William said that Kitsap was the most powerful chief on Puget Sound from 1790 to 1845. Kitsap County, Washington, and the Kitsap Peninsula are named for him. Life Early life Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Seattle
Seattle ( – June 7, 1866; , ; usually styled as Chief Seattle) was a leader of the Duwamish and Suquamish peoples. A leading figure among his people, he pursued a path of accommodation to white settlers, forming a personal relationship with Doc Maynard. The city of Seattle, in the U.S. state of Washington, was named after him. A widely publicized speech arguing in favor of ecological responsibility and respect for Native Americans' land rights had been attributed to him. Name The name Seattle is an anglicization of his name in his native Lushootseed language, . According to Upper Skagit elder Vi Hilbert, his name was traditionally pronounced . After his baptism in 1852, he gained the baptismal name of Noah Seattle. In English, his name is often also spelled Si'ahl, Sealth, Seathl or See-ahth as an attempt to be more accurate to the Lushootseed pronunciation. There is no "''th''" sound in the Lushootseed language. Life Youth Seattle was born between 1780 and 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
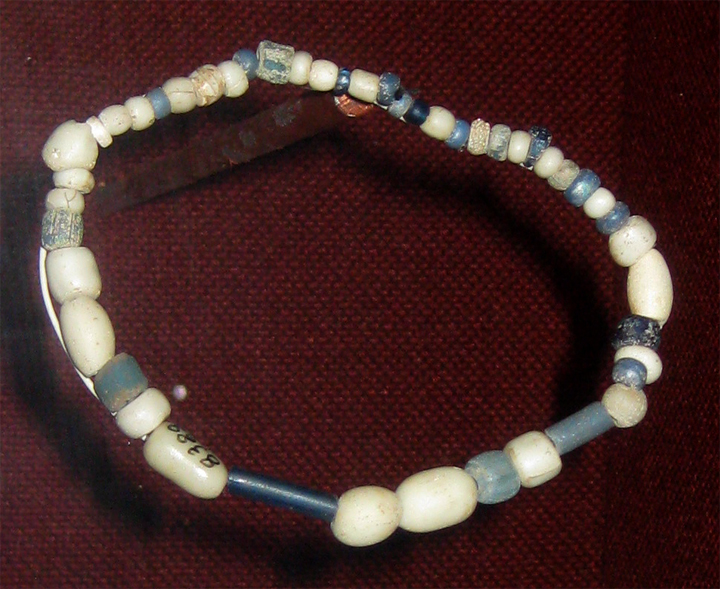
Trade Beads
Trade beads are beads that were used as a medium of barter within and amongst communities. They are considered to be one of the earliest forms of trade between members of the human race. It has also been surmised that bead trading was one of the reasons why humans developed language. Slave beads In sixteenth-century continental North America, trade beads (sometimes called aggry and slave beads) were decorative glass beads used as a token money to exchange for goods, services and slaves (hence the name). The beads were integrated in Native American jewelry using various beadwork techniques. Trade beads were also used by early Europeans to purchase African resources, including slaves in the African slave trade. Aggry beads are a particular type of decorated glass bead from Ghana. The practice continued until the early twentieth century. History Made to ease the passage of European explorers and then traders mainly across the African continent, the beads were made throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
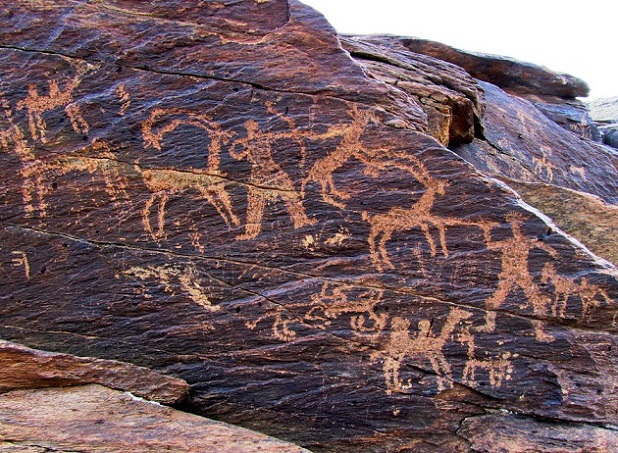
Petroglyph
A petroglyph is an image created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, or abrading, as a form of rock art. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions of the technique to refer to such images. Petroglyphs, estimated to be 20,000 years old are classified as protected monuments and have been added to the tentative list of UNESCO's World Heritage Sites. Petroglyphs are found worldwide, and are often associated with prehistoric peoples. The word comes from the Greek prefix , from meaning " stone", and meaning "carve", and was originally coined in French as . In scholarly texts, a ''petroglyph'' is a rock engraving, whereas a '' petrograph'' (or ''pictograph'') is a rock painting. In common usage, the words are sometimes used interchangeably. Both types of image belong to the wider and more general category of rock art or parietal art. Petroforms, or patterns and shapes made by man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirit Power
Spirit(s) commonly refers to: * Liquor, a distilled alcoholic drink * Spirit (animating force), the non-corporeal essence of living things * Spirit (supernatural entity), an incorporeal or immaterial being Spirit(s) may also refer to: Liquids * Tincture, an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol * Cologne spirit, also known as drinking alcohol * Petroleum spirit (other) ** Motor spirit, a clear petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel ** Petroleum ether, liquid hydrocarbon mixtures used chiefly as non-polar solvents ** White spirit or mineral spirits, a common organic solvent used in painting and decorating Philosophy, religion and folklore *Spirituality, pertaining to the soul or spirit *Holy Spirit, a divine force, manifestation of God in the Holy Trinity, or agent of divine action, according to Abrahamic Religions * Great Spirit, conception of a supreme being prevalent among some Native American and First Nations c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderbird (mythology)
The thunderbird is a mythological bird-like spirit in Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American indigenous peoples' history and culture. It is considered a supernatural being of power and strength. It is frequently depicted in the art, songs, and oral histories of many Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, Pacific Northwest Coast cultures, but is also found in various forms among some peoples of the American Southwest, East Coast of the United States, US East Coast, Great Lakes, and Plains Indians, Great Plains. Description The thunderbird is said to create thunder by flapping its wings (Algonquian), and lightning by flashing its eyes (Algonquian, Iroquois). Across cultures, thunderbirds are generally depicted as birds of prey, or hybrids of humans and birds. Thunderbirds are often viewed as protectors, sometimes intervening on people's behalf, but expecting veneration, prayers, and gifts. Archaeologically, sites containing depictions of thunderbirds hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frock Coat
A frock coat is a formal wear, formal men's coat (clothing), coat characterised by a knee-length skirt cut all around the base just above the knee, popular during the Victorian era, Victorian and Edwardian era, Edwardian periods (1830s–1910s). It is a fitted, long-sleeved coat with a centre vent at the back and some features unusual in post-Victorian dress. These include the reverse collar and lapels, where the outer edge of the lapel is often cut from a separate piece of cloth from the main body and also a high degree of waist suppression around the waistcoat, where the coat's diameter around the waist is less than around the chest. This is achieved by a high horizontal waist seam with side bodies, which are extra panels of fabric above the waist used to pull in the naturally cylindrical drape. As was usual with all coats in the 19th century, shoulder padding was rare or minimal. In the Age of Revolution around the end of the 18th century, men abandoned the justaucorps with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Top Hat
A top hat (also called a high hat, or, informally, a topper) is a tall, flat-crowned hat traditionally associated with formal wear in Western dress codes, meaning white tie, morning dress, or frock coat. Traditionally made of black silk or sometimes grey, the top hat emerged in Western fashion by the end of the 18th century. Although such hats fell out of fashion through the 20th century, being almost entirely phased out by the time of the counterculture of the 1960s, it remains a formal fashion accessory. A collapsible variant of a top hat, developed in the 19th century, is known as an opera hat. Perhaps inspired by the early modern era capotain, higher-crowned dark felt hats with wide brims emerged as a country leisurewear fashion along with the Age of Revolution around the 1770s. Around the 1780s, the justaucorps was replaced by the previously casual frocks and dress coats. With the introduction of the top hat in the early 1790s, the tricorne and bicorne hats b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually disappeared as the use of heavy armour declined, but ''musket'' continued as the generic term for smoothbore long guns until the mid-19th century. In turn, this style of musket was retired in the 19th century when rifled muskets (simply called rifles in modern terminology) using the Minié ball (invented by Claude-Étienne Minié in 1849) became common. The development of breech-loading firearms using self-contained Cartridge (firearms), cartridges, introduced by Casimir Lefaucheux in 1835, began to make muskets obsolete. The first reliable repeating rifles, the 1860 Henry rifle and its 1866 descendent the Winchester rifle, superseded muskets entirely. Repeating rifles quickly established themselves as the standard for rifle design, ending the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
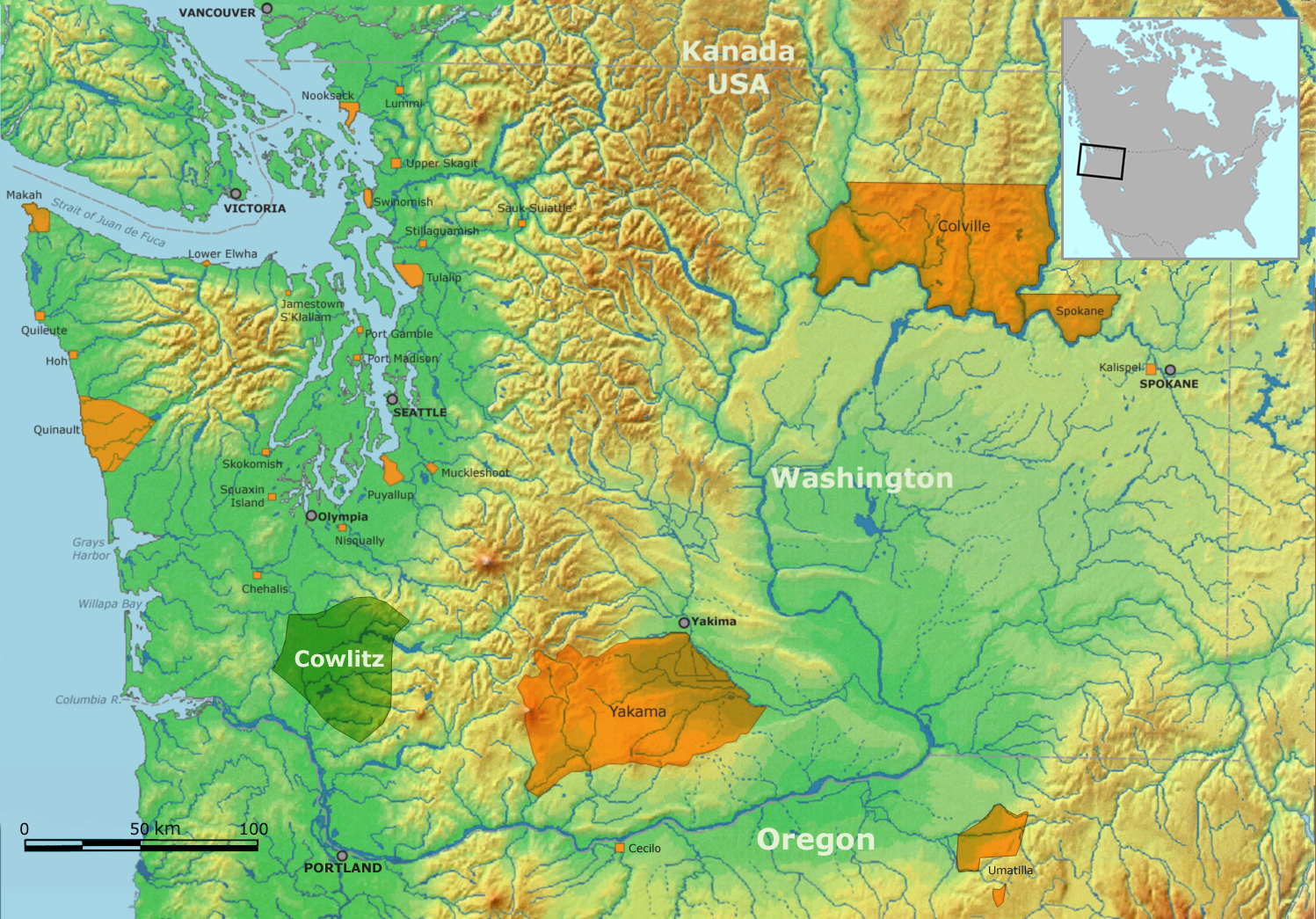
Cowlitz People
The term Cowlitz people covers two culturally and linguistically distinct indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest; the Lower Cowlitz or Cowlitz proper, and the Upper Cowlitz / Cowlitz Klickitat or Taitnapam. Lower Cowlitz refers to a southwestern Coast Salish people, which today are enrolled in the federally recognized tribes: Cowlitz Indian Tribe, Quinault Indian Nation, and Confederated Tribes of the Chehalis Reservation. The Upper Cowlitz or Taitnapam, is a Northwest Sahaptin speaking people, part of the Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation. Their traditional homelands are in western Washington state in the United States. Cowlitz tribal groups or bands There is an ongoing dispute over the Cowlitz people, their history, territory, ancestry, ethnicity, and language; which is important for land claims and treaty negotiations with the U.S. government by Cowlitz descendants. Some scholars believe that they were originally divided into four multi-linguistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suquamish Tribe
The Suquamish () are a Lushootseed-speaking Native American people, located in present-day Washington in the United States. They are a southern Coast Salish people. Today, most Suquamish people are enrolled in the federally recognized Suquamish Indian Tribe of the Port Madison Reservation, a signatory to the 1855 Treaty of Point Elliott. Chief Seattle, the famous leader of the Suquamish and Duwamish Tribes for whom the City of Seattle is named, signed the Point Elliot Treaty on behalf of both Tribes. The Suquamish Tribe owns the Port Madison Indian Reservation. Language and culture Suquamish people traditionally speak a dialect of Lushootseed, which belongs to the Salishan language family. Like many Northwest Coast indigenous peoples pre- European contact, the Suquamish enjoyed the rich bounty of land and sea west of the Cascade Mountains. They fished for salmon and harvested shellfish in local waters and Puget Sound. The cedar tree provided fiber used to weave waterpro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agate Pass
Agate Pass or Agate Passage is a high-current tidal strait in Puget Sound connecting Port Madison and mainland Kitsap County in the US state of Washington. It lies between Bainbridge Island and the mainland of the Kitsap Peninsula near Suquamish. It leads south towards Bremerton, extending about one mile (1.6 km) in a straight, southwesterly direction. The depth is about . The shores are wooded and fairly steep. The shoreline is mostly rocky and fringed with kelp to Point Bolin. The tidal currents have velocities up to six knots; the flood tide sets southwesterly, and the ebb tide northeasterly. The traditional winter village of the Suquamish people was located on Agate Pass. It was the site of Old Man House, the largest longhouse on Puget Sound, and is the location of Haleets, a petroglyph. Agate Pass was unknown to non-native people until it was discovered by the Wilkes Expedition in 1841. Before then, Europeans thought Bainbridge Island was a peninsula. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suquamish, Washington
Suquamish is a census-designated place (CDP) in Kitsap County, Washington, Kitsap County, Washington (state), Washington, United States. The population was 4,266 at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census. Comprising the Port Madison Indian Reservation, it is the burial site of Chief Seattle and was the site of the Suquamish tribe winter longhouse known as the Old Man House. Geography Suquamish is located in northern Kitsap County. The village of Suquamish is in the northeast part of the CDP, and Washington State Route 305 crosses the southern part, leading southeast across the Agate Pass Bridge to Bainbridge Island and west to Poulsbo, Washington, Poulsbo. According to the United States Census Bureau, the Suquamish CDP has a total area of , of which are land and , or 10.21%, are water. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 3,510 people, 1,459 households, and 948 families residing in the CDP. The population density was 513.1 people per square mile (198.1/km2) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |