|
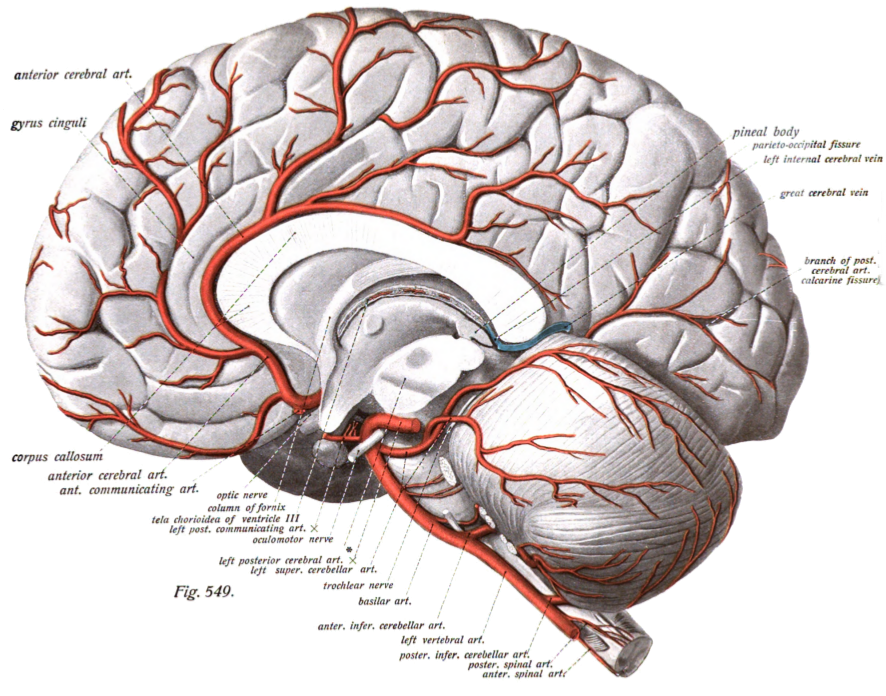
Chiasmatic Cistern
The chiasmatic cistern or suprasellar cistern is a small subarachnoid cistern related to the optic chiasm. Anatomy The cistern is situated superior to the optic chiasm, and inferior to the rostrum of corpus callosum. The cistern is an extension of/communicates inferiorly with the interpeduncular cistern. The cistern of lamina terminalis connects the chiasmatic cistern with the pericallosal cistern. Contents It contains the anterior aspect of the optic chiasm and both optic nerves (CN II), the pituitary stalk, the origin of the anterior cerebral artery, and the anterior communicating artery. References External links NIF Search - Chiasmatic Cisternvia the Neuroscience Information Framework The Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/ genomic resources and provides many aut ... Meninges {{neuroana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarachnoid Cistern
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space is situated between the two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Structure Although the pia mater adheres to the surface of the brain, closely following the contours of its gyri and sulci, the arachnoid mater only covers its superficial surface, bridging across the gyri. This leaves wider spaces between the pia and arachnoid and the cavities are known as the subarachnoid cisterns. Although they are often described as distinct compartments, the subarachnoid cisterns are not truly anatomically distinct. Rather, these subarachnoid cisterns are separated from each other by a trabeculated porous wall with various-sized openings. Cisterns There are many cisterns in the brain with several large ones noted with their own name. At the base of the spinal cord is another subarachno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Chiasm
In neuroanatomy, the optic chiasm, or optic chiasma (; , ), is the part of the brain where the optic nerves cross. It is located at the bottom of the brain immediately inferior to the hypothalamus. The optic chiasm is found in all vertebrates, although in cyclostomes (lampreys and hagfishes), it is located within the brain. This article is about the optic chiasm of vertebrates, which is the best known nerve chiasm, but not every chiasm denotes a crossing of the body midline (e.g., in some invertebrates, see Chiasm (anatomy)). A midline crossing of nerves inside the brain is called a decussation (see Definition of types of crossings). Structure In all vertebrates, the optic nerves of the left and the right eye meet in the body midline, ventral to the brain. In many vertebrates the left optic nerve crosses over the right one without fusing with it. In vertebrates with a large overlap of the visual fields of the two eyes, i.e., most mammals and birds, but also amphibians, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostrum Of Corpus Callosum
The corpus callosum (Latin for "tough body"), also callosal commissure, is a wide, thick nerve tract, consisting of a flat bundle of commissural fibers, beneath the cerebral cortex in the brain. The corpus callosum is only found in placental mammals. It spans part of the longitudinal fissure, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres, enabling communication between them. It is the largest white matter structure in the human brain, about in length and consisting of 200–300 million axonal projections. A number of separate nerve tracts, classed as subregions of the corpus callosum, connect different parts of the hemispheres. The main ones are known as the genu, the rostrum, the trunk or body, and the splenium. Structure The corpus callosum forms the floor of the longitudinal fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres. Part of the corpus callosum forms the roof of the lateral ventricles. The corpus callosum has four main parts – individual nerve trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpeduncular Cistern
The interpeduncular cistern (or basal cistern) is the subarachnoid cistern situated between the dorsum sellae (anteriorly) and the two cerebral peduncles at the front of the midbrain. Its roof is represented by the floor of the third ventricle (i.e. posterior perforated substance, and the two mammillary bodies). Its floor is formed by the arachnoid membrane extending between the temporal lobes of either side. Anteriorly, it extends to the optic chiasm. The cistern communicates superiorly with the chiasmatic cistern, and inferiorly with the pontine cistern. The chiasmatic cistern, cistern of lamina terminalis, and supracallosal cistern are all extensions of the interpeduncular cistern. Anatomy Contents The cistern contains: * the posterior portion of the circle of Willis: ** basilar artery (including its bifurcation), ** (origins of the) posterior cerebral arteries, ** posterior communicating arteries, * (the origin of the) posterior thalamo-perforating arteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistern Of Lamina Terminalis
The cistern of lamina terminalis is one of the subarachnoid cisterns. It is situated (depending upon the source) either superior to the lamina terminalis, or rostral/anterior to the lamina terminalis and anterior commissure between the two frontal lobes of the cerebrum. It is situated rostral/anterior to the third ventricle. The cistern is an extension of interpeduncular cistern. The cistern of lamina terminalis interconnects the chiasmatic cistern and pericallosal cistern. The cistern contains the anterior cerebral arteries, the anterior communicating artery, hypothalamic artery, the origin of the fronto-orbital arteries, and Heubner's artery. See also * Terminal cisterna Terminal cisternae (singular: terminal cisterna) are enlarged areas of the sarcoplasmic reticulum surrounding the transverse tubules. Function Terminal cisternae are discrete regions within the muscle cell. They store calcium (increasing t ... References Meninges {{neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericallosal Cistern
The pericallosal cistern is one of the subarachnoid cisterns. It is situated atop the corpus callosum, extending from its splenium (rostrally/anteriorly) to its genu (caudally/posteriorly). Rostrally, it communicates with the cistern of lamina terminalis (which in turn communicates with the chiasmatic cistern The chiasmatic cistern or suprasellar cistern is a small subarachnoid cistern related to the optic chiasm. Anatomy The cistern is situated superior to the optic chiasm, and inferior to the rostrum of corpus callosum. The cistern is an extensi ...). References Meninges {{neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual system, visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, Pretectal area, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus. Structure The optic nerve has been classified as the second of twelve paired cranial nerves, but it is technically a myelinated tract of the central nervous system, rather than a classical nerve of the peripheral nervous system because it is derived from an out-pouching of the diencephalon (optic stalks) during embryonic development. As a consequence, the fibers of the optic nerve are covered with myelin produced by oligodendrocytes, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Cerebral Artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery. Anterior cerebral artery syndrome refers to symptoms that follow a stroke occurring in the area normally supplied by one of the arteries. It is characterized by Paresis, weakness and sensory loss in the lower leg and foot opposite to the lesion and behavioral changes. Structure The anterior cerebral artery is divided into 5 segments. Its smaller branches: the callosal (supracallosal) arteries are considered to be the A4 and A5 segments. * A1 originates from the internal carotid artery and extends to the ''anterior communicating artery'' (AComm). The ''anteromedial central'' (med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Communicating Artery
In human anatomy, the anterior communicating artery is a blood vessel of the brain that connects the left and right anterior cerebral arteries. Anatomy The anterior communicating artery connects the two anterior cerebral arteries across the commencement of the longitudinal fissure. Sometimes this vessel is wanting, the two arteries joining to form a single trunk, which afterward divides; or it may be wholly, or partially, divided into two. Its length averages about 4 mm, but varies greatly. It gives off some of the anteromedial ganglionic vessels, but these are principally derived from the anterior cerebral artery. It is part of the cerebral arterial circle, also known as the circle of Willis. Physiology Anatomical variations of the anterior communicating artery are relatively common. The artery is sometimes duplicated, multiplicated, fenestrated ("net-like") or very short, giving the impression that two anterior cerebral arteries are fused at the point where the anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience Information Framework
The Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/ genomic resources and provides many authoritative links throughout the neuroscience portal of Wikipedia. Description The Neuroscience Information Framework (NIF) is an initiative of the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research, which was established in 2004 by the National Institutes of Health. Development of the NIF started in 2008, when the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine obtained an NIH contract to create and maintain "a dynamic inventory of web-based neurosciences data, resources, and tools that scientists and students can access via any computer connected to the Internet". The project is headed by Maryann Martone, co-director of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR), part of the multi-disciplinary Center for Research in Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |