|
Chervonohrad Raion 2020
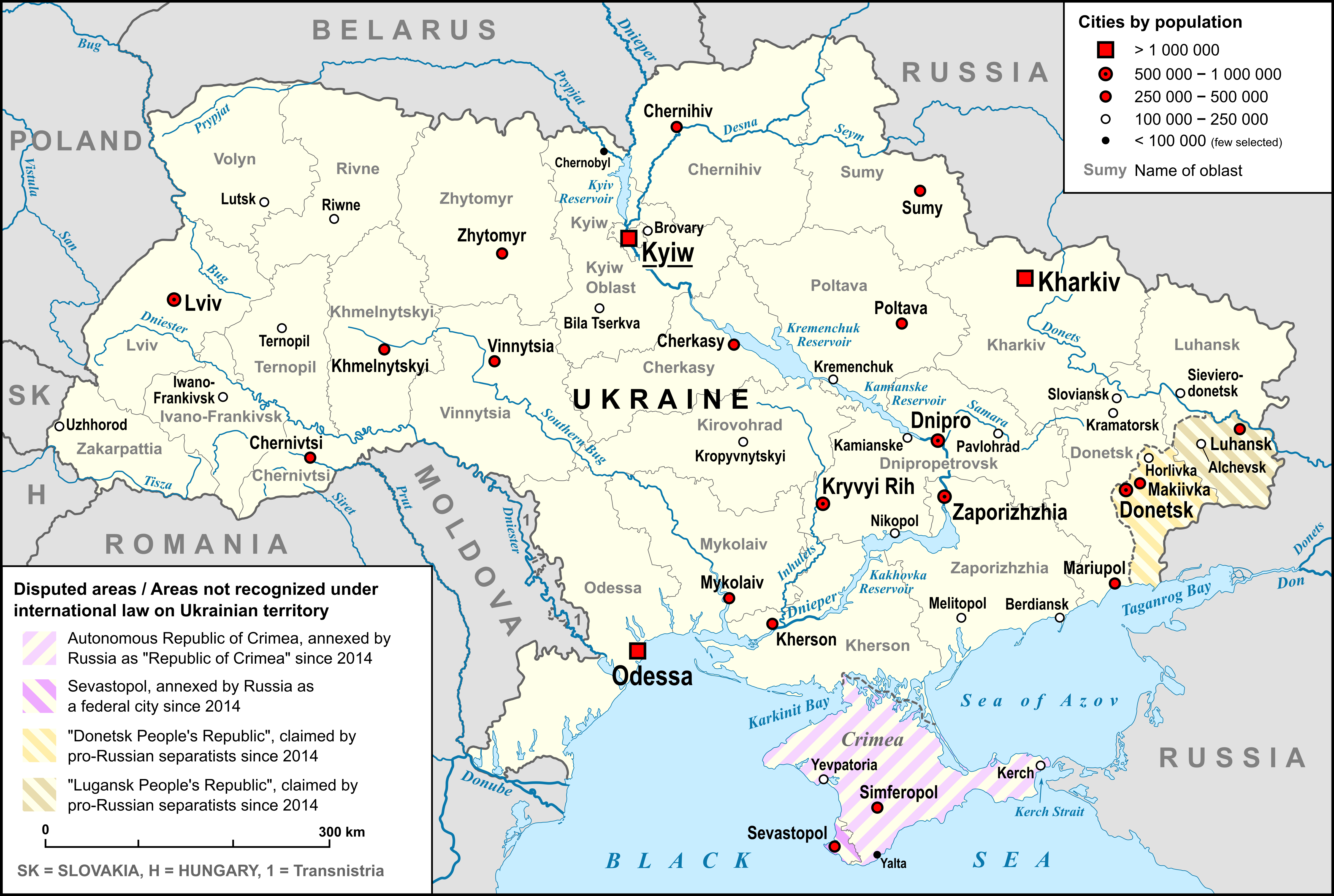
Sheptytskyi (, ), formerly Chervonohrad (, ), historically Krystynopol, is a historical mining town and the administrative center of Sheptytskyi Raion, Lviv Oblast of western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Sheptytskyi urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Sheptytskyi lies about 62 km north of Lviv, 7 km from Sokal, 28 km northeast of the town of Voroniv, and has a population of History In May 1685, the Crown hetman and Kraków Voivode Feliks Kazimierz Potocki purchased land along the Bug River. In 1692, he founded a city on the lands of the village Novyi Dvir (, ) and named it "Krystynopol" after his wife Krystyna Lubomirska (the suffix "-pol" derives from Greek "polis"). Potocki made the city his family center. He died here on 22 September 1702. His grandson Franciszek Salezy Potocki built a palace and in 1763 founded a monastery of Basilians (barocco church of Saint George; prior to 1946 – a place of miracles with wondrous icon of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Ukraine
There are 463 populated places in Ukraine, populated places in Ukraine that have been officially granted city status () by the Verkhovna Rada, the country's parliament, as of 23 April 2025. Settlements with more than 10,000 people are eligible for city status although the status is typically also granted to settlements of historical or regional importance. Smaller settlements are Populated places in Ukraine#Rural settlements, rural settlements () and villages (). Historically, there were systems of city rights, granted by the territorial lords, which defined the status of a place as a ''misto'' or ''selo''. In the past, cities were self-governing and had several privileges. The list of cities is roughly ordered by population and the 2022 estimates are compared to the 2001 Ukrainian census, except for Chernobyl for which the population is an unofficial estimate. The City with special status, cities with special status are shown in ''italic''. The average population size is 62,000. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sokal
Sokal (, ) is a city located on the Bug River in Sheptytskyi Raion, Lviv Oblast of western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Sokal urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The population is approximately History The first written mention of Sokal dates from 1377. In 1424, it received Magdeburg rights from Siemowit IV, Duke of Masovia, and in 1462, the town became part of Bełz Voivodeship, Lesser Poland Province. On August 2, 1519, following the defeat of a Polish-Lithuanian army under Hetman Konstanty Ostrogski by Crimean Tatars, the town was razed by the invaders. Mikolaj Sep-Szarzynski later dedicated one of his poems to this battle. In 1619, Armenians in Sokal were first mentioned. The town remained part of Poland until the First Partition of Poland, when it was annexed by the Habsburg Empire, as part of Galicia. It was the capital of the Sokal district, one of the 78 ''Bezirkshauptmannschaften'' in the Austrian Galicia province (Crown land) in 1900. Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciszek Salezy Potocki
Franciszek Salezy Potocki (1700 – 22 October 1772) was a Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Polish szlachta, nobleman, diplomat, politician and knight of the Order of the White Eagle (Poland), Order of the White Eagle, awarded on 3 August 1750, in Warsaw. Potocki was the wealthiest magnate of his time and the owner of large properties in Dnieper Ukraine, then part of the Crown of Poland, Polish Crown. Nicknamed "Little King of Ruthenia" ("''królik Rusi''"). Franciszek became Krajczy, Krajczy of the Crown in 1736, Field Clerk of the Crown and voivode of Wołyń Voivodeship (1569–1795), Volhynian Voivodship in 1755, voivode of Kijów Voivodship in 1755–1771 and starost of Belz, Hrubieszów, Ropczyce, Sokal, Jablonów, Jabłonów and Opalin. Bibliography * Urzędnicy województwa bełskiego i ziemi chełmskiej XIV-XVIII wieku. Spisy. Oprac. Henryk Gmiterek i Ryszard Szczygieł. Kórnik 1992, p. 255. * Teka Gabriela Junoszy Podoskiego, t. III, Poznań 1856, p. 303. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polis
Polis (: poleis) means 'city' in Ancient Greek. The ancient word ''polis'' had socio-political connotations not possessed by modern usage. For example, Modern Greek πόλη (polē) is located within a (''khôra''), "country", which is a πατρίδα (patrida) or "native land" for its citizens. In ancient Greece, the polis was the native land; there was no other. It had a constitution and demanded the supreme loyalty of its citizens. χώρα was only the countryside, not a country. Ancient Greece was not a sovereign country, but was territory occupied by Hellenes, people who claimed as their native language some dialect of Ancient Greek. Poleis did not only exist within the area of the modern Republic of Greece. A collaborative study carried by the Copenhagen Polis Centre from 1993 to 2003 classified about 1,500 settlements of the Archaic and Classical ancient-Greek-speaking population as poleis. These ranged from the Caucasus to Southern Spain, and from Southern Russia to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek (, ; , ) is an Indo-European languages, Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic languages, Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy (in Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the list of languages by first written accounts, longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting importance in the European canon. Greek is also the language in which many of the foundational texts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry grammatical information (inflectional endings) or lexical information ( derivational/lexical suffixes)''.'' Inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. Derivational suffixes fall into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation. Particularly in the study of Semitic languages, suffixes are called affirmatives, as they can alter the form of the words. In Indo-European studies, a distinction is made between suffixes and endings (see Proto-Indo-European root). A word-final segment that is somewhere between a free morpheme and a bound morpheme is known as a suffixoidKremer, Marion. 1997. ''Person reference and gender in translation: a contrastive investigation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krystyna Lubomirska (d
The House of Lubomirski is a Princely Houses of Poland, Polish princely family. The Lubomirski family's coat of arms is the Drużyna coat of arms, which is similar to the Szreniawa coat of arms but without a cross. Origin and the coat of arms The Lubomirski family have been actors in the history of Poland since the 10th century. There are two theories regarding the family's origin. One, by Adam Boniecki, a Polish heraldist, assumes that there were two branches of the family. One settled at the Szreniawa River in Proszowice County while the other established itself in Szczyrzyc County. The time of this division of the family is not known, but most likely it was before the adoption of Religion in Poland, Christianity by Poland. The Szreniawici family used a similar coat of arms, which means that the two families had the same ancestry. At the time of Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I, the members of the Lubomirski family demonstrated bravery in battle against paganism, pagans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bug River
The Bug or Western Bug is a major river in Central Europe that flows through Belarus (border), Poland, and Ukraine, with a total length of .Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Poland 2017 Statistics Poland, p. 85-86 A of the Narew, the Bug forms part of the |
Feliks Kazimierz Potocki
Feliks Kazimierz "Szczęsny" Potocki (1630–1702) was a Polish noble, magnate, and military leader. He was the son of Hetman and magnate Stanisław "Rewera" Potocki and Zofia Kalinowska, and brother of Hetman Andrzej Potocki. He married the daughter of Hetman and Marshal of the Crown Prince Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski, Princess Krystyna Lubomirska, in 1661. Shortly before his death he married again, in 1700, his second wife being Konstancja Roża Łos. He was Podstoli of the Crown from 1663, voivode of Sieradz Voivodship from 1669, Kijów Voivodship (Kyiv, also Kiev) from 1682, Kraków Voivodship from 1683, Field Crown Hetman from 1692, castellan of Kraków and Great Crown Hetman from 1702. Starost of Bełz, Krasnystaw, Hrubieszów, Ropczyce, Sokal, Tłumacz and Nisko. He fought in wars against Cossacks, Sweden, Transylvania, and Muscovy from 1655 to 1664. He commanded cavalry regiment in Battle of Chudnov (1660) and Battle of Podhajce (1667). As the Marshal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivode
Voivode ( ), also spelled voivod, voievod or voevod and also known as vaivode ( ), voivoda, vojvoda, vaivada or wojewoda, is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe in use since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the medieval rulers of the Romanian-inhabited states and of governors and military commanders of Poles, Hungarian, Lithuanian, Balkan, Russian people and other Slavic-speaking populations. In the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, ''voivode'' was interchangeably used with '' palatine''. In the Tsardom of Russia, a voivode was a military governor. Among the Danube principalities, ''voivode'' was considered a princely title. Etymology The term ''voivode'' comes from two roots. , means "war, fight," while , means "leading", thus in Old Slavic together meaning "war leader" or "warlord". The Latin translation is for the principal commander of a military force, serving as a deputy for the monarch. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 (2023), with approximately 8 million additional people living within a radius. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596, and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Kraków Old Town, Old Town was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1978, one of the world's first sites granted the status. The city began as a Hamlet (place), hamlet on Wawel Hill and was a busy trading centre of Central Europe in 985. In 1038, it became the seat of King of Poland, Polish monarchs from the Piast dynasty, and subsequently served as the centre of administration under Jagiellonian dynasty, Jagiellonian kings and of the Polish–Lithuan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hetmans Of The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
Hetmans of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth () were the highest-ranking military officers, second only to the King, in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The first Polish title of Grand Crown Hetman was created in 1505. The title of hetman was given to the leader of the Polish Army and until 1581 it was awarded only for a specific campaign or war. Later it became a permanent title, as did all the titles in the Jagiellon Poland, Kingdom of Poland and Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It could not be revoked unless treachery had been proven (from 1585). Hetmans were not paid for their services by the Royal Treasury. Field and Great Hetmans From the end of 16th century there were two hetmans in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and two hetmans in Crown of the Polish Kingdom, the Crown: a Field Hetman and a Great Hetman (sometimes translated as Grand Hetman). As a result, there were in total four hetman titles: Great Crown Hetman, Field Crown Hetman, Great Lithuanian Het ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |