|
Chernokozovo
Chernokozovo (russian: Чернокозово) is a rural locality (a '' selo'') in Naursky District of the Chechen Republic, Russia,Decree #500 located north of the Terek River. In 2019, the population of Chernokozovo was about 3,240 residents. At the beginning of the Second Chechen War, Chernokozovo was defended by Chechen separatist forces, while the Russians bombed and shelled it with the BM-21 Grad The BM-21 "Grad" (russian: БМ-21 "Град", lit= hail) is a self-propelled 122 mm multiple rocket launcher designed in the Soviet Union. The system and the M-21OF rocket were first developed in the early 1960s, and saw their first combat ... rocket artillery systems. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chernokozovo Detention Center
Chernokozovo detention center (russian: Чернокозово СИЗО, ''Chernokozovo SIZO'') is a prison in the village of Chernokozovo, Chechnya, Russia. The detention center is operated by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and currently has the status of penal colony. Chernokozovo SIZO was notorious during the Second Chechen War, serving as the main component of the " filtration camp" system operated by Russian federal forces. It was the site of reported human rights violations, particularly accusations of widespread arbitrary detention and torture. History The Soviet-era maximum-security penitentiary facility at Chernokozovo was closed down during the First Chechen War in December 1994. It was re-opened by the Russian federal forces during the Second Chechen War at the end of 1999, officially as a "temporary reception center for the persons detained on the grounds of vagrancy and begging". In fact, it served as an unofficial prison camp for captured separatist fighters, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filtration Camp System In Chechnya
Filtration camps or filtration points (the official name) were used by the Russian federal forces for their mass internment centers during the First Chechen Wars in 1994–1996 and then again during the Second Chechen War between 1999 and 2003. "Filtration" system The term "filtration point" re-appeared during the First Chechen War as name of the facilities illegally created for the purpose of holding the persons detained by the federal forces in the course of an operation "to restore constitutional order" in Chechen Republic territory in 1994–1996. During the Second Chechen War, beginning in 1999, some of the "filtration" facilities got legitimate status of investigative isolators (SIZO) subordinated to the Ministry of Justice and temporary detention isolators (IVS) subordinated to the Interior Ministry, but with an unclear legal status and no apparent basis in the criminal code of the Russian Federation. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types Of Inhabited Localities In Russia
The classification system of human settlement, inhabited localities in Russia and some other post-Soviet Union, Soviet states has certain peculiarities compared with those in other countries. Classes During the Soviet Union, Soviet time, each of the republics of the Soviet Union, including the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR, had its own legislative documents dealing with classification of inhabited localities. After the history of the Soviet Union (1985-1991), dissolution of the Soviet Union, the task of developing and maintaining such classification in Russia was delegated to the federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects.Articles 71 and 72 of the Constitution of Russia do not name issues of the administrative and territorial structure among the tasks handled on the federal level or jointly with the governments of the federal subjects. As such, all federal subjects pass :Subtemplates of Template RussiaAdmMunRef, their own laws establishing the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naursky District
Naursky District (russian: Нау́рский райо́н; ce, Невран кӀошт, ''Nevran khoşt'') is an administrativeDecree #500 and municipalLaw #47-RZ district ( raion), one of the fifteen in the Chechen Republic, Russia. It is located in the northwest of the republic. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the rural locality (a '' stanitsa'') of Naurskaya. Population: 51,143 ( 2002 Census); The population of Naurskaya accounts for 16.5% of the district's total population. History In the second half of the 18th century, the area was settled by the Russian and Ukrainian Cossacks. Several ''stanitsas'' were founded. In 1771, after being wounded at the siege of Bender, the future Cossack insurgency leader Yemelyan Pugachev came to live at Ishcherskaya with his family. The modern district was created in 1935 by the order of the Supreme Soviet. It was a part of Stavropol Krai prior to 1944 when it was transferred to newly created Grozny Oblas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
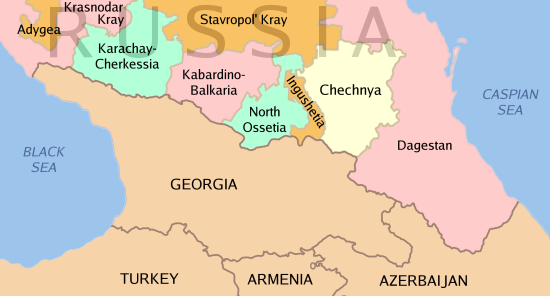
Chechen Republic
Chechnya ( rus, Чечня́, Chechnyá, p=tɕɪtɕˈnʲa; ce, Нохчийчоь, Noxçiyçö), officially the Chechen Republic,; ce, Нохчийн Республика, Noxçiyn Respublika is a republic of Russia. It is situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, close to the Caspian Sea. The republic forms a part of the North Caucasian Federal District, and shares land borders with the country of Georgia to its south; with the Russian republics of Dagestan, Ingushetia, and North Ossetia-Alania to its east, north, and west; and with Stavropol Krai to its northwest. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Checheno-Ingush ASSR split into two parts: the Republic of Ingushetia and the Chechen Republic. The latter proclaimed the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, which sought independence. Following the First Chechen War of 1994–1996 with Russia, Chechnya gained ''de facto'' independence as the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, although ''de jure'' it rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terek River
The Terek (; , Tiyrk; , Tərč; , ; , ; , ''Terk''; , ; , ) is a major river in the Northern Caucasus. It originates in the Mtskheta-Mtianeti region of Georgia and flows through North Caucasus region of Russia into the Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad s .... It rises near the juncture of the Greater Caucasus Mountain Range and the Khokh Range, to the southwest of Mount Kazbek, winding north in a white torrent between the town of Stepantsminda and the village of Gergeti toward the Russian region North Ossetia and the city of Vladikavkaz. It turns east to flow through Chechnya and Dagestan before Water divide, dividing into two branches which empty into the Caspian Sea. Below the city of Kizlyar it forms a swampy river delta around wide. The river is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Chechen War
The Second Chechen War (russian: Втора́я чече́нская война́, ) took place in Chechnya and the border regions of the North Caucasus between the Russian Federation and the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria, from August 1999 to April 2009. In August 1999, Islamist fighters from Chechnya infiltrated Russia's Dagestan region, violating Russia's borders. During the initial campaign, Russian military and pro-Russian Chechen paramilitary forces faced Chechen separatists in open combat and seized the Chechen capital Grozny after a winter siege that lasted from December 1999 until February 2000. Russia established direct rule over Chechnya in May 2000 although Chechen militant resistance throughout the North Caucasus region continued to inflict heavy Russian casualties and challenge Russian political control over Chechnya for several years. Both sides carried out attacks against civilians. These attacks drew international condemnation. In mid-2000, the Russian g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BM-21 Grad
The BM-21 "Grad" (russian: БМ-21 "Град", lit= hail) is a self-propelled 122 mm multiple rocket launcher designed in the Soviet Union. The system and the M-21OF rocket were first developed in the early 1960s, and saw their first combat use in March 1969 during the Sino-Soviet border conflict. ''BM'' stands for ''boyevaya mashina'' ( ru , боевая машина – combat vehicle), and the nickname means "hail". The complete system with the BM-21 launch vehicle and the M-21OF rocket is designated as the M-21 field-rocket system. The complete system is more commonly known as a Grad multiple rocket launcher system. In NATO countries the system, either the complete system or the launch vehicle only, was initially known as the M1964. Several other countries have copied the Grad or have developed similar systems. In Russian service its intended replacement is the 9A52-4 Tornado. Many similar 122 mm MLRS systems are made by different countries based on the BM-21 Grad. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |