|
Cherethites
In the Bible, the Cherethites ( ''Kərēṯī'') and Pelethites ( ''Pəlēṯī''), the former also spelled Kerethites, are two ethnic groups in the Levant. Their identity has not been determined with certainty.On the Cherethites, see The Cherethites are mentioned independently three times, and as the "Cherethites and Pelethites" seven times. They are interpreted to have been a group of elite mercenaries employed by King David, some of whom acted as his bodyguards, and others as part of his army. Historical translations In the Masoretic version of the Book of Ezekiel, a group referred to as "children of the land league" are stated as being allies of Egypt, but in the Septuagint version of the same passage, the group are described instead as "children of the Cherethites"; scholars believe that this is a reference to an alliance of the Philistines as a whole, rather than a subgroup. The Targum, and Syriac Peshitta, regarding the phrase as an appellative, render it "bowmen and sling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistine
Philistines (; Septuagint, LXX: ; ) were ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan during the Iron Age in a confederation of city-states generally referred to as Philistia. There is compelling evidence to suggest that the Philistines originated from a Greek immigrant group from the Aegean civilization, Aegean. The immigrant group settled in Canaan around 1175 BC, during the Late Bronze Age collapse. Over time, they intermixed with the indigenous Canaanite societies and assimilated elements from them, while preserving their own unique culture. In 604 BC, the Philistines, who had been under the rule of the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–605 BC), were ultimately vanquished by King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. Much like the kingdoms of Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Israel and Kingdom of Judah, Judah, the Philistines lost their autonomy by the end of the Iron Age, becoming vassals to the Assyrian people, Assyrians, Egyptians, and later Babylonians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ziklag
Ziklag () is the Bible, biblical name of a town in the Negev region in the southwest of what was the Kingdom of Judah. It was a provincial town in the Philistine kingdom of Gath (city), Gath when Achish was king. Its exact location has not been identified with any certainty. Identification At least 14 sites have been proposed as the location of Ziklag. At the end of the 19th century, both Elusa (Haluza), Haluza (by Wadi Asluj, south of Beersheba)Cheyne and Black, ''s:Encyclopaedia Biblica/Zereth Shahar-Zuzim#ZIKLAG, Encyclopedia Biblica'' and Khirbet Zuheiliqah (northwest of Beersheba and south-southeast of Gaza City) had been suggested as possible locations. Conder and Kitchener identified Khirbet Zuheiliqah as the location on the basis of ''Ziklag'' being a corruption of ''Zahaliku'', whence also ''Zuheiliqah''. The more recently proposed identifications for Ziklag are: *Albrecht Alt (1883–1956) proposed Tel Halif/Tell el-Khuweilifeh, just beside kibbutz Lahav, some northeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. The texts include instructions, stories, poetry, prophecies, and other genres. The collection of materials accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text varies. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible, called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning 'five books') in Greek. The second-oldest part was a collection of narrative histories and prophecies (the Nevi'im). The third co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Palestine
Roman Palestine was a period in the history of Palestine characterised by Roman rule in the Palestine region. Historians typically trace the period from the Hasmonean civil war in 63 BCE up until the end of the Byzantine rule with the Muslim conquest of the Levant in the 7th century. The period is commonly subdivided into a pagan Roman period and a Christian Byzantine period. The Roman period (narrow sense) can be subdivided into early and late phases, transitioning at either the First Jewish–Roman War c. 70 CE or the Bar Kokhba Revolt c. 135 CE. During this period, Palestine went through a series of administrative changes, beginning as a series of Roman client states under the Judean Hasmonean and Herodian dynasties before being gradually annexed into the Roman Empire as the fully incorporated Roman province of Judaea, as well as the Nabatean Kingdom in the peripherial areas. After 135 CE, Roman Palestine was re-organised into the Roman province of Syria Palaesti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-Jerome
Pseudo-Jerome is the name given to several authors misidentified as, or pseudepigraphically claiming to be, Saint Jerome. A principal writing identified as "Pseudo Jerome" is the ninth-century writing the ''Epistle of Pseudo-Jerome to Paula and Eustochium'', a sermon on the Assumption of Mary. Other works are also pseudonymously attributed to Jerome, including a ''Handbook on the Apocalypse'', a kind of preacher's manual containing glosses (brief 1-2 sentence explanations) of passages from the Book of Revelation. This work was likely composed by an Irish bishop writing from continental Europe Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ... in the late 7th century. References Christian manuscripts {{manuscript-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
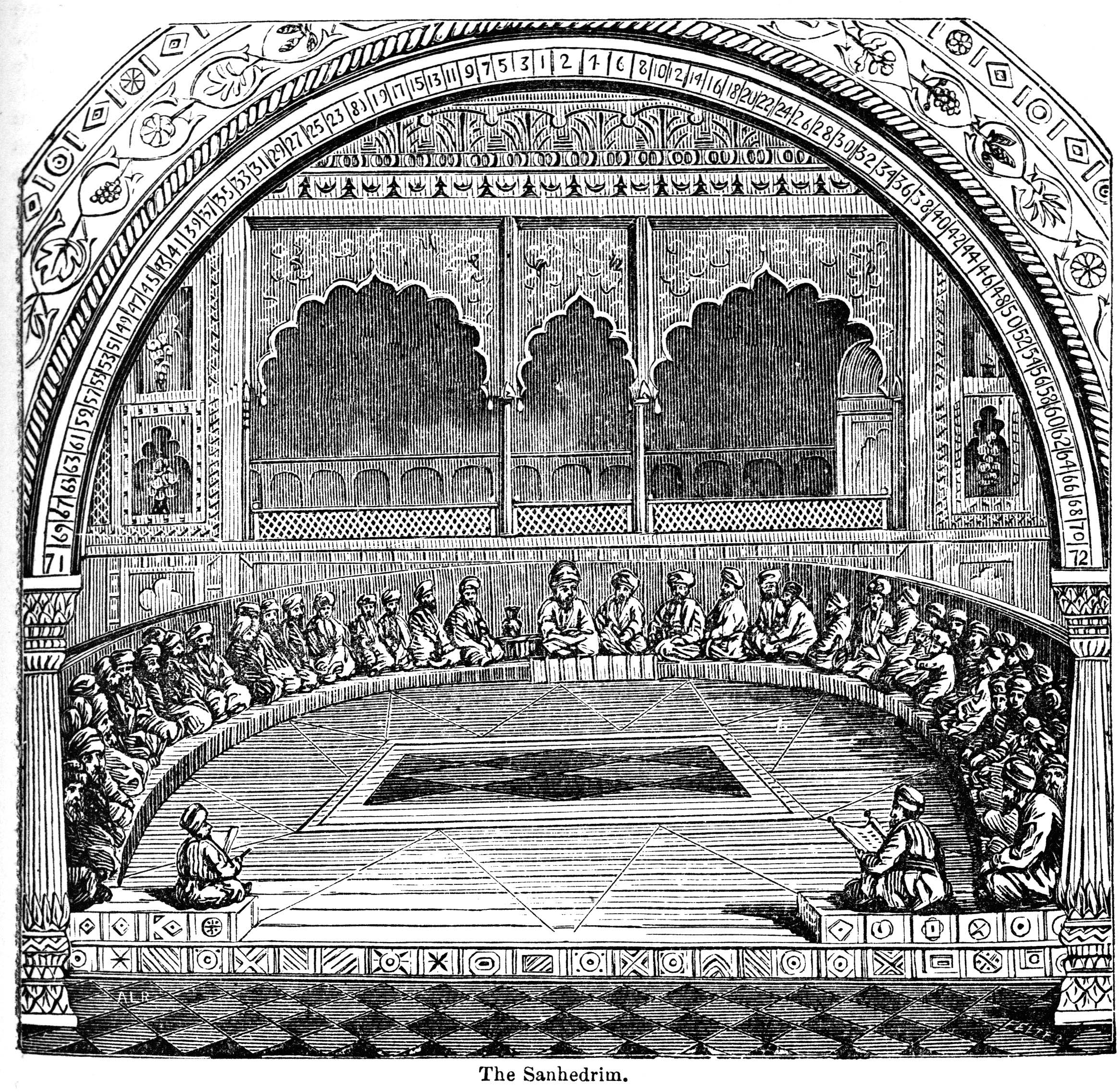
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Middle Aramaic , a loanword from , 'assembly,' 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was a Jewish legislative and judicial assembly of either 23 or 70 elders, existing at both a local and central level in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite courts called sanhedrins: Greater and Lesser. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city. There was only one Great Sanhedrin of 70 judges, which, among other roles, acted as a supreme court, taking appeals from cases that lesser courts decided. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier usually refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the Nasi, who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the Av Beit Din or the chief of the court, who was second to the Nasi and 69 general members. In the Second Temple period, the Great Sanhedrin met in the Temple in Jerusalem, in a bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggadah
Aggadah (, or ; ; 'tales', 'legend', 'lore') is the non-legalistic exegesis which appears in the classical rabbinic literature of Judaism, particularly the Talmud and Midrash. In general, Aggadah is a compendium of rabbinic texts that incorporates folklore, historical anecdotes, moral exhortations, and practical advice in various spheres, from business to medicine. Etymology The Hebrew word () is derived from the Hebrew root , meaning "declare, make known, expound", also known from the common Hebrew verb .Berachyahu Lifshitz, "Aggadah Versus Haggadah : Towards a More Precise Understanding of the Distinction", ''Diné Yisrael'' 24 (2007): page 23 (English section). The majority scholarly opinion is that the Hebrew word ''aggadah'' () and corresponding Aramaic ''aggadta'' (אֲגַדְתָּא) are variants of ''haggadah'' based on a common linguistic shift from ''haphalah'' to ''aphalah'' forms. However, a minority of scholars believe that these words derive from a separate Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athaliah
Athaliah ( ''Gotholía''; ) was the daughter of King Ahab and Queen Jezebel of Israel; she was queen consort of kingdom of Judah, Judah as the wife of Jehoram of Judah, King Jehoram, a descendant of King David, and was later queen regnant c. 841–835 BCE. Biblical narrative Accounts of Athaliah’s life are found in Books of Kings, 2 Kings 8:16–11:16 and Books of Chronicles, 2 Chronicles 2 Chronicles 22, 22:10–23:15 in the Hebrew Bible. According to the Deuteronomist, she was the daughter of king Omri of Israel Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...; however, she is usually considered to have been the daughter of King Ahab – the son of Omri – and his wife, Queen Jezebel. Some scholars believe Athaliah was the daughter of Omri, but that she grew up as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Biblica
''Encyclopaedia Biblica: A Critical Dictionary of the Literary, Political and Religion History, the Archeology, Geography and Natural History of the Bible'' (1899), edited by Thomas Kelly Cheyne and John Sutherland Black, J. Sutherland Black, is a critical encyclopedia of the Bible. In theology and biblical studies, it is often referenced as ''Enc. Bib.'', or as ''Cheyne and Black''. Description It has an article for every single name and place both in the Bible and in its traditional Biblical apocrypha, Apocrypha, as well as for each of the books of these, together with many improper nouns appearing in these (such as ''nebi'im'', 'mole', 'owl') and other more general subjects (such as 'music', 'tents', etc.). Many of these articles are given in great detail, and usually include mention of the various spellings for each word as used by the Masoretic Text, Septuagint (differentiating between each of the most important ancient manuscripts), and by other ancient versions; the larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Change
In historical linguistics, a sound change is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic change) or a more general change to the speech sounds that exist (''phonological change''), such as the merger of two sounds or the creation of a new sound. A sound change can eliminate the affected sound, or a new sound can be added. Sound changes can be environmentally conditioned if the change occurs in only some sound environments, and not others. The term "sound change" refers to diachronic changes, which occur in a language's sound system. On the other hand, " alternation" refers to changes that happen synchronically (within the language of an individual speaker, depending on the neighbouring sounds) and do not change the language's underlying system (for example, the ''-s'' in the English plural can be pronounced differently depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Language
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until after 200 CE and as the liturgical language of Judaism (since the Second Temple period) and Samaritanism. The language was revived as a spoken language in the 19th century, and is the only successful large-scale example of linguistic revival. It is the only Canaanite language, as well as one of only two Northwest Semitic languages, with the other being Aramaic, still spoken today. The earliest examples of written Paleo-Hebrew date back to the 10th century BCE. Nearly all of the Hebrew Bible is written in Biblical Hebrew, with much of its present form in the dialect that scholars believe flourished around the 6th century BCE, during the time of the Babylonian captivity. For this reason, Hebrew has been referred to by Jews as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negev
The Negev ( ; ) or Naqab (), is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southern end is the Gulf of Aqaba and the resort town, resort city and port of Eilat. It contains several development towns, including Dimona, Arad, Israel, Arad, and Mitzpe Ramon, as well as a number of small Negev Bedouin, Bedouin towns, including Rahat, Tel Sheva, and Lakiya. There are also several kibbutzim, including Revivim and Sde Boker; the latter became the home of Israel's first Prime Minister of Israel, prime minister, David Ben-Gurion, after his retirement from politics. Although historically part of a separate region (known during the Roman Empire, Roman period as Arabia Petraea), the Negev was added to the proposed area of Mandatory Palestine, of which large parts later became Israel, on 10 July 1922, having been conceded by British representative St John Philby "in Emirate of Transjordan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |