|
Cheng Ji (Wuyue)
Xian Ji ( 847–913, courtesy name Hongji), known as Cheng Ji before 908, was a general during the late Tang dynasty and early Wuyue Wuyue (; ), 907–978, was an independent coastal kingdom founded during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–960) of Chinese history. It was ruled by the Haiyan Qian clan (海盐钱氏), whose family name remains widespread in t ... kingdom, serving as a chief strategist for Qian Liu, Wuyue's first king. Cheng Ji was very close to Qian Liu, and his son Cheng Rensu married Qian Liu's daughter. Cheng Ji was captured by warlord Yang Xingmi in 896 but refused to submit. He was eventually returned to Qian Liu. References * 840s births 913 deaths {{China-mil-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hang Prefecture
Hangzhou or Hang Prefecture (589–1129) was a '' zhou'' (prefecture) in imperial China located in modern northern Zhejiang, China, around modern Hangzhou. The prefecture was called Yuhang Commandery from 607 to 621 and from 742 to 758. Hang Prefecture was the capital of the Wuyue kingdom (907–978), inside which it was known as Xi Prefecture (Western Prefecture), and during its last years of the kingdom, as Qiantang Prefecture. Hang Prefecture sat at the head of the Hangzhou Bay, which opens to the East China Sea. It was also the southern terminus of the Grand Canal and the eastern terminus of the Qiantang River. During the Northern Song (960–1127) it was the capital of Liangzhe Circuit. In 1129 it became Lin'an Prefecture, which would become the capital of the Southern Song (1127–1279) in 1138. Counties For most of its history, Hang Prefecture administered the following 7–9 counties (縣), some of whose names changed frequently: History During Sui and the Sui–Tang tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devastating An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
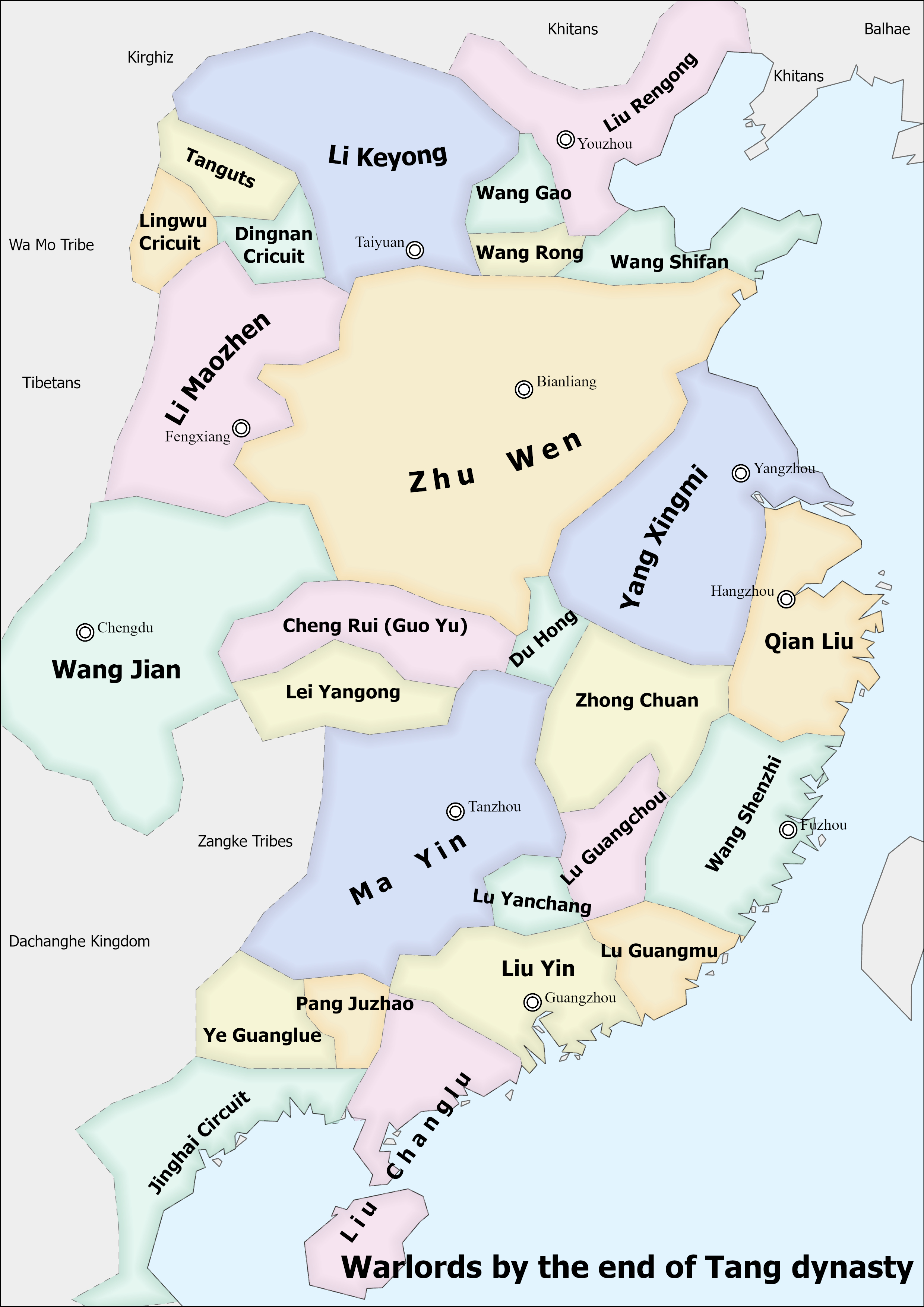
Wuyue
Wuyue (; ), 907–978, was an independent coastal kingdom founded during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (907–960) of Chinese history. It was ruled by the Haiyan Qian clan (海盐钱氏), whose family name remains widespread in the kingdom's former territory. Founding Beginning in 887, the Qian family provided military leaders (or ''jiedushi'') to the Tang dynasty. Qian Liu was named Prince of Yue in 902, with the title of Prince of Wu added two years later. In 907, when the Tang dynasty fell and was replaced in the north by the Later Liang, military leaders in the south formed their own kingdoms. Qian Liu used his position to proclaim himself the King of Wuyue. This signaled the beginning of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period which would last until the founding of the Song dynasty in 960. Origin of name The name Wuyue comes from the combination of Wu Kingdom and Yue Kingdom, two ancient kingdoms during the Spring and Autumn period from 770 to 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtesy Name
A courtesy name (), also known as a style name, is a name bestowed upon one at adulthood in addition to one's given name. This practice is a tradition in the East Asian cultural sphere, including China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ..., Japan, Korea, and Vietnam.Ulrich TheobaldNames of Persons and Titles of Rulers/ref> A courtesy name is not to be confused with an art name, another frequently mentioned term for an alternative name in East Asia, which is closer to the concept of a pen name or a pseudonym. Usage A courtesy name is a name traditionally given to Chinese men at the age of 20 East Asian age reckoning, ''sui'', marking their coming of age. It was sometimes given to women, usually upon marriage. The practice is no longer common in modern Chinese socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Xingmi
Yang Xingmi (; 852'' Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms''vol. 1 – December 24, 905Academia Sinicabr>Chinese-Western Calendar Converter''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 265.), né Yang Xingmin (楊行愍, name changed 886), courtesy name Huayuan (), formally Prince Wuzhong of Wu (吳武忠王, "martial and faithful"),Yang Xingmi's title of ''Wang'' (王) is translatable in English as either "prince" or "king." It will be largely translated as "prince" here as he made no attempt to claim his domain to be a state independent from Tang Dynasty, and it was not until the time of his son Yang Longyan (King Xuan), by which time the Tang imperial line had long been extinguished, that the Wu state formally declared itself independent, that the Wu rulers claimed the title of ''Guowang'' (lit., "state prince/king"). However, "king" will be used for the posthumous honors that Yang Longyan bestowed on him as Yang Longyan was then claiming the ''Guowang'' title. See ''Zizhi Tongjian'', vo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Annals Of The Ten Kingdoms
The ''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese title ''Shiguo Chunqiu'' (), is a history of the Ten Kingdoms that existed in southern China after the fall of the Tang Dynasty and before the reunification of China by the Song Dynasty. The book was written and compiled by the Qing Dynasty scholar Wu Renchen ( 1628 – 1689). Wu took part in the compilation of '' Mingshi'', the official history of the Ming Dynasty, and felt that the official dynastic histories have neglected the Ten Kingdoms. The book contains 114 volumes (scrolls). Contents The book consists of 114 volumes covering the histories of the Ten Kingdoms: #14 volumes - Wu (907–937) #20 volumes - Southern Tang (937–975) #13 volumes - Former Shu (907–925) #10 volumes - Later Shu (934–965) #9 volumes - Southern Han (917–971) #10 volumes - Chu (907–951) #13 volumes - Wuyue (907–978) #10 volumes - Min (909–945) #4 volumes - Jingnan (924–963) #5 volumes - Northern Han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
840s Births
84 may refer to: * 84 (number) 84 (eighty-four) is the natural number following 83 and preceding 85. In mathematics 84 is: * the sum of the first seven triangular numbers (making it a tetrahedral number). * a Dodecahedral number. * the sum of a twin prime (41 + 43). * a ... * one of the years 84 BC, AD 84, 1984, AD 2084 * Eighty Four, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated census-designated place in Washington County, Pennsylvania, United States * Seksendört, a Turkish pop group whose name means 84 See also * * List of highways numbered {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_King_of_Wuyue.jpg)