|
Chen Zhi (Three Kingdoms)
Chen Zhi (died 28 September 258), courtesy name Fengzong, was an official of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He is mostly known for his association with the infamous Huang Hao that allowed him to dominate the imperial court, however he was also described as extremely talented and in favour of both, Fei Yi and Liu Shan. Life Chen Zhi was born in Runan Commandery (), which is present-day Pingyu County, Henan. He was a maternal grandson of an elder brother of Xu Jing, who briefly served as Minister over the Masses of the state of Shu during the early Three Kingdoms period. As he was orphaned at a young age, he was raised by his granduncle Xu Jing. Chen Zhi had quite a reputation in Shu by the time he reached adulthood (around 19 years old). He started his career as a low-level official in the selection bureau of the imperial secretariat of Shu. His appearance is described as awe-inspiring and his demeanour as restrained and strict. Moreover, he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Shan
Liu Shan (, 207–271), courtesy name Gongsi, was the second and last emperor of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. As he ascended the throne at the age of 16, Liu Shan was entrusted to the care of the Chancellor Zhuge Liang and Imperial Secretariat Li Yan. His reign of 40 years was the longest of all emperors in the Three Kingdoms era. During Liu Shan's reign, many campaigns were led against the rival state of Cao Wei, primarily by Zhuge Liang and his successor Jiang Wei, but to little avail, due to their drastic mismatch in terms of population and geographic extent. Liu Shan eventually surrendered to Wei in 263 after Deng Ai led a surprise attack on the Shu capital Chengdu. He was quickly relocated to the Wei capital at Luoyang, and enfeoffed as "Duke Anle". There he enjoyed his last years peacefully before dying in 271, most probably of natural causes. Widely known to later generations by his infant name "Adou" (), Liu Shan was commonly perceived as an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Situ (office)
Situ was one of the highest ranking government offices in ancient China. Established in the Western Zhou dynasty, it was originally written as (), meaning Administrator of Land. During the Han dynasty, the title became written with the different characters (), which is translated variously as Minister over the Masses or Excellency over the Masses. It was one of the three most important official posts during the Han dynasty, called the Three Excellencies. The nominal salary for the post was 20,000 ''Picul, dàn'' () of grain.Michael Loewe The Men Who Governed Han China Dictionary of the Qin, Former Han and Xin Periods (2004) The title is the origin of the Situ (surname), surname Situ. See also * Government of the Han dynasty * Tai Situpa (Grand Situ) * Translation of Han dynasty titles References Citations Sources * * Chinese-language titles, Situ Obsolete occupations Government of Imperial China Zhou dynasty Han dynasty {{Job-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annotations To Records Of The Three Kingdoms
''Annotated Records of the Three Kingdoms'' () by Pei Songzhi (372–451) is an annotation completed in the 5th century of the 3rd century historical text ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'', compiled by Chen Shou. After the fall of the Eastern Jin, Pei Songzhi became the Gentleman of Texts under the Liu Song dynasty, and was given the assignment of editing the book, which was completed in 429. This became the official history of the Three Kingdoms period, under the title ''Sanguozhi zhu'' (''zhu'' meaning "notes"). Pei went about providing detailed explanations to some of the geography and other elements mentioned in the original. More importantly, he made corrections to the work, in consultation with records he collected of the period. In regard to historical events and figures, as well as Chen Shou's opinions, he added his own commentary. From his broad research, he was able to create a history which was relatively complete, without many of the loose ends of the original. Some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pei Songzhi
Pei Songzhi (372–451), courtesy name Shiqi, was a Chinese historian and politician who lived in the late Eastern Jin dynasty and the Liu Song dynasty. His ancestral home was in Wenxi County, Shanxi Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ..., but he moved to the Jiangnan region later. He is best known for making annotations to the historical text '' Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi'') written by Chen Shou in the third century, providing additional details omitted from the original work. His commentary, completed in 429, became integral to later editions of the ''Sanguozhi'', making the joint work three times as long as the original.Yuet Keung Lo, "Pei Songzhi", in ''A Global Encyclopedia of Historical Writing'', edited by D. R. Woolf (Garland Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicles Of Huayang
The ''Chronicles of Huayang'' or ''Huayang Guo Zhi'' ( zh, t=華陽國志, s=华阳国志, first=t, l=Records of the Lands South of Mt. Hua) is the oldest extant gazetteer of a region of China. It was compiled by Chang Qu during the Jin dynasty. It contains roughly 110,000 characters. Its contents comprise history, geography and biographies of the Sichuan region. It was used by the Liu Song historian Pei Songzhi in his annotations to the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'', and by the Tang dynasty prince Li Xian when he wrote his commentaries on the '' Book of the Later Han''. The ''Chronicles of Huayang'' is also rendered in English as: * ''Annals of Huayang Country'' * ''Huayang National Annals'' * ''Records of the States South of Mount Hua'' * ''Annals of the Kingdoms South of Mount Hua'' Hong Liangji said that ''Chronicles of Huayang'' is one of the oldest extant Chinese gazetteers, along with the '. Contents There are twelve chapters in ''Chronicles of Huayang'', the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang Qu
Chang Qu (291–361), courtesy name Daojiang, was a Chinese historian of the Cheng-Han dynasty during the Sixteen Kingdoms period and the Jin dynasty (266–420). Chang Qu is best known for his magnum opus, the '' Chronicles of Huayang'' or ''Records of the States South of Mount Hua'' that he compiled between 348 and 354, the oldest extant regional history of China about his native region of Yizhou, or the modern-day Sichuan province. Life Chang Qu was born in Jiangyuan, , which is in present-day Chengdu, Sichuan during the Jin dynasty. The Chang of Jiangyuan were a prominent clan producing many scholars and masters of the prose who enjoyed writing. At the start of the 4th century, due to a peasant uprising in the Shu region, local nobles led their followers and retainers to migrate far away. The Chang clan led by Chang Kuan) went east to Jing and Xiang, following the path of Du Tao and others. At this time, Chang Qu was still a child, born from a minor and poor branch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Three Kingdoms
The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is a Chinese official history written by Chen Shou in the late 3rd century CE, covering the end of the Han dynasty (220 CE) and the subsequent Three Kingdoms period (220–280 CE). It is regarded as to be the authoritative source text for these periods. Compiled following the reunification of China under the Jin dynasty (266–420), the work chronicles the political, social, and military events within rival states Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu into a single text organized by individual biography. The ''Records'' are the primary source of information for the 14th-century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', considered to be one of the four classic novels emblematic of written vernacular Chinese. While large subsections of the work have been selected and translated into English, the entire corpus has yet to receive an unabridged English translation. Origin and structure The '' Book of Han'' and ''Records of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Shou
Chen Shou ( zh , t = 陳壽 ; 233–297), courtesy name Chengzuo (), was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer who lived during the Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. Chen Shou is best known for his most celebrated work, the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi''), which records the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period. Chen Shou wrote the ''Sanguozhi'' primarily in the form of biographies of notable persons of those eras. Today, Chen's ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is part of the '' Twenty-Four Histories'' canon of Chinese history. Historical sources on Chen Shou's life There are two biographies of Chen Shou. The first one is in the '' Chronicles of Huayang'', which was written by Chang Qu in the fourth century during the Eastern Jin dynasty. The second one is in the ''Book of Jin'', which was written by Fang Xuanling and others in the seventh century during the Tang dynasty. Life He started his career as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of People Of The Three Kingdoms
The following are lists of people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220–280) of Chinese history. Their names in Mandarin pinyin are sorted in alphabetical order. Fictional characters in the 14th-century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' and those found in other cultural references to the Three Kingdoms are listed separately in List of fictional people of the Three Kingdoms. Lists * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (A) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (B) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (C) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (D) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (E) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (F) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (G) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (H) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (I) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (J) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (K) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (L) * List of people of the Three Kingdoms (M) * Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
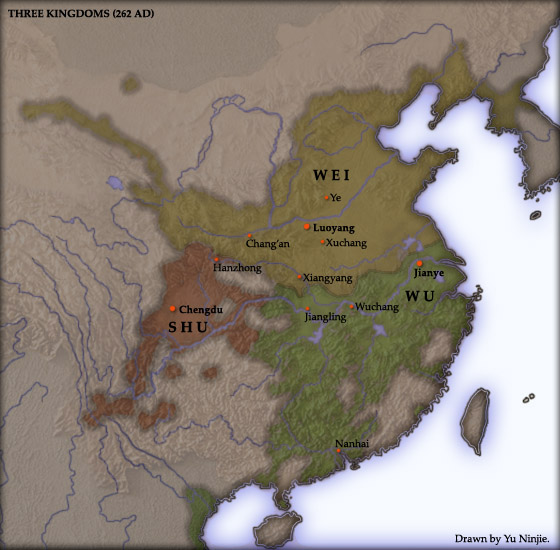
Conquest Of Shu By Wei
The Conquest of Shu by Wei was a military campaign launched by the dynastic state of Cao Wei against its rival Shu Han in late 263 during the Three Kingdoms period of China. The campaign culminated in the fall of Shu Han and the tripartite equilibrium maintained in China for over 40 years since the End of the Han dynasty, end of the Han dynasty#Eastern Han, Eastern Han dynasty in 220. The conquest laid the foundation for an eventual reunified China under the Jin dynasty (266–420)#Western Jin (266–316), Western Jin dynasty in 280. Background Following the End of the Han dynasty, end of the Eastern Han dynasty in 220, three contending states emerged in China and fought for control over the territories of the former Han Empire. Among the three, Cao Wei, Wei was the most powerful one in terms of military prowess, economic resources, manpower and geographical size. The other two, Shu Han, Shu and Eastern Wu, Wu, re-established their alliance against Wei in 223. Between 228 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twenty-Four Histories
The ''Twenty-Four Histories'', also known as the ''Orthodox Histories'' (), are a collection of official histories detailing the dynasties of China, from the legendary Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors in the 4th millennium BC to the Ming dynasty in the 17th century. The Han dynasty official Sima Qian established many of the conventions of the genre, but the form was not fixed until much later. Starting with the Tang dynasty, each dynasty established an official office to write the history of its predecessor using official court records, partly in order to establish its own link to the earliest times. As fixed and edited in the Qing dynasty, the whole set contains 3,213 volumes and about 40 million words. It is considered one of the most important sources on Chinese history and culture. The title ''Twenty-Four Histories'' dates from 1775, which was the 40th year in the reign of the Qianlong Emperor. This was when the last volume, the '' History of Ming'', was reworked and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang Wei
Jiang Wei (202 – 3 March 264), courtesy name Boyue, was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Born in Ji County (present-day Gangu County, Gansu), Jiang Wei started his career as a military officer in his native Tianshui Commandery, which was a territory of Cao Wei, Wei. In 228, when Wei's rival state Shu launched an invasion led by Zhuge Liang, Jiang Wei was distrusted by Ma Zun, then administrator of Tianshui Commandery. As such, Jiang Wei had to defect to Shu. Zhuge Liang, the Chancellor (China), Imperial Chancellor and regent of Shu, highly regarded Jiang Wei and appointed him as a general in Shu. After Zhuge Liang's death in 234, Jiang Wei continued serving as a military commander during the regencies Jiang Wan and Fei Yi, eventually rising to the highest military rank of General-In-Chief (大將軍) after Fei Yi's death in 253. Between 240 and 262, he continued Zhuge Liang's legacy of Zhuge Liang's N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |