|
Chen Wo
Chen Wo (陳偓) was an official of the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period state Southern Han, serving as a chancellor during the reign of its third emperor Liu Sheng (Emperor Zhongzong). Little is known about Chen Wo's background. It was known that prior to chancellorship, he rose in Southern Han's official ranks up to the office of deputy minister of census (戶部侍郎, ''Hubu Shilang''). In 944, he was given the provisional chancellor designation ''Zhi Zhengshi'' (知政事).''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms''vol. 64 After Liu Sheng had his brother Liu Hongchang the Prince of Yue, who was then the main chancellor, assassinated in 944, he made Chen a full chancellor with the designation ''Tong Zhongshu Menxia Pingzhangshi'' (同中書門下平章事).''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 284. According to the ''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms'', as chancellor, Chen "did not have any shortcomings or strengths; he was only filling the position." It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the ''Book of Documents'' (early chapters, 11th century BC), the ''Bamboo Annals'' (c. 296 BC) and the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (c. 91 BC) describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Oracle Bone script, Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze, Yangtze River. These Yellow river civilization, Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world's oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the Cradle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
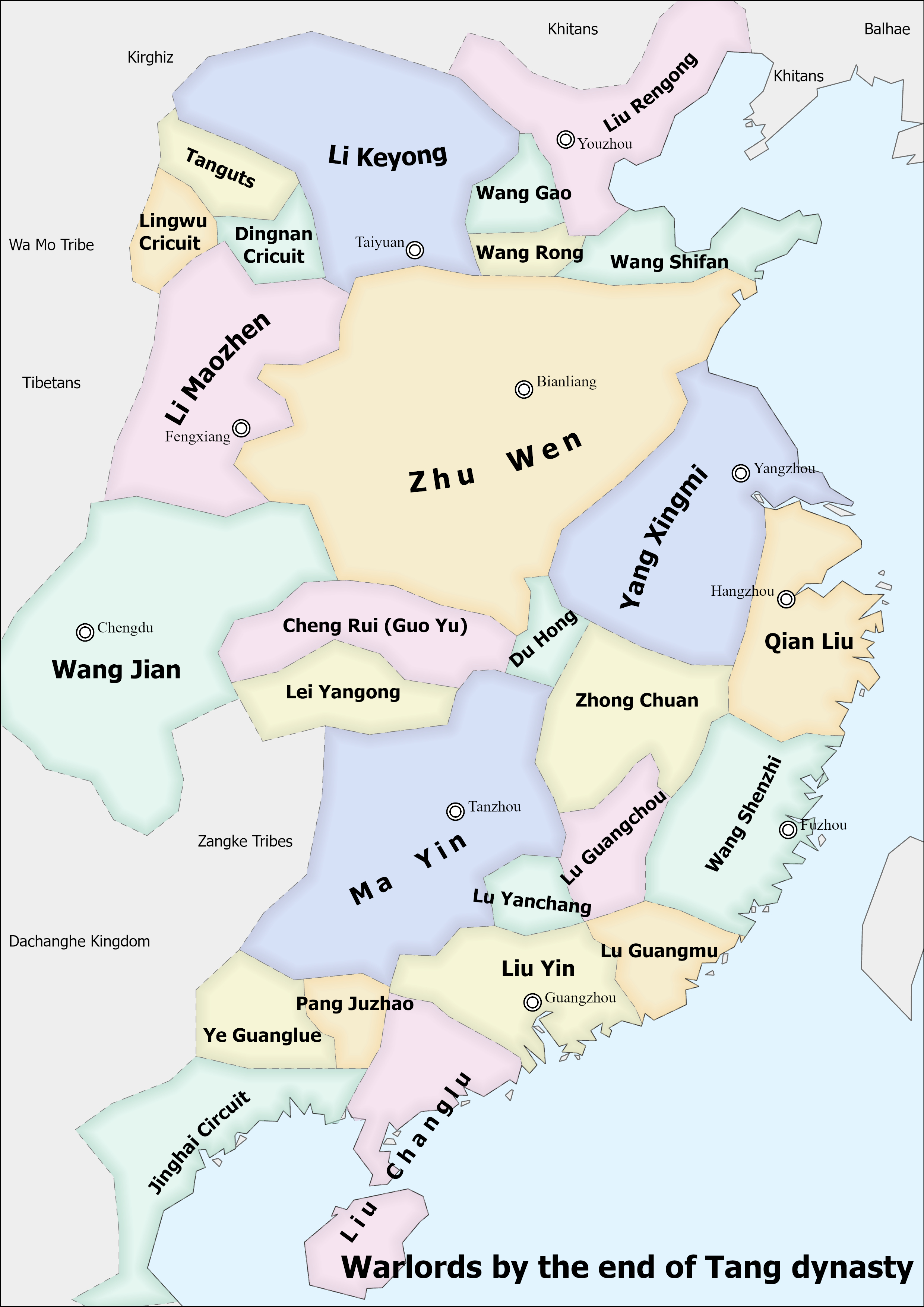
Five Dynasties And Ten Kingdoms Period
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concurrent dynastic states were established elsewhere, mainly in South China. It was a prolonged period of multiple political divisions in Chinese imperial history. Traditionally, the era is seen as beginning with the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907 and reaching its climax with the founding of the Song dynasty in 960. In the following 19 years, Song gradually subdued the remaining states in South China, but the Liao dynasty still remained in China's north (eventually succeeded by the Jin dynasty), and the Western Xia was eventually established in China's northwest. Many states had been ''de facto'' independent long before 907 as the Tang dynasty's control over its officials waned, but the key event was their recognition as sovereign by forei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Han
Southern Han (; 917–971), officially Han (), originally Yue (), was one of the ten kingdoms that existed during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was located on China's southern coast, controlling modern Guangdong and Guangxi. The kingdom greatly expanded its capital Xingwang Fu (, present-day Guangzhou). It attempted but failed to annex the independent polity of Jinghai which was controlled by the Vietnamese. Founding of the Southern Han Liu Yin was named regional governor and military officer by the Tang court in 905. Though the Tang fell two years later, Liu did not declare himself the founder of a new kingdom as other southern leaders had done. He merely inherited the title of Prince of Nanping in 909. It was not until Liu Yin's death in 917 that his brother, Liu Yan, declared the founding of a new kingdom, which he initially called "Yue" (); he changed the name to Han () in 918. This was because his surname Liu () was the imperial surname of the Han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancellor Of Tang Dynasty
The Grand chancellor (China), chancellor () was a semi-formally designated office position for a number of high-level officials at one time during the Tang dynasty of China. This list also includes List of chancellors of Wu Zetian, chancellors of the short-lived Zhou dynasty (690–705), Wu Zhou dynasty, which is typically treated as an interregnum of the Tang dynasty by historians. Origins Ouyang Xiu, the author of the ''New Book of Tang'', asserts that the Tang dynasty inherited its bureaucracy from its dynastic predecessor, the Sui dynasty, under which the founder Emperor Wen of Sui divided his government into five main bureaus: * ''Shàngshūshěng'' (尚書省) – The Department of State Affairs * ''Ménxiàshěng'' (門下省) – The Menxia Sheng, Chancellery * ''Nèishǐshěng'' (內史省) – The Legislative Bureau (note different tone than the eunuch bureau below) * ''Mìshūshěng'' (秘書省) – The Palace Library * ''Nèishìshěng'' (內侍省) – The Eunuch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Sheng (Southern Han)
Liu Sheng (; 920–958), born Liu Hongxi (劉弘熙), may be nicknamed Jun (雋),''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms''vol. 61 formally Emperor Zhongzong of (Southern) Han ((南)漢中宗), was the third emperor of the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period state Southern Han. He succeeded his brother, Liu Bin (Emperor Shang), whom he had ordered assassinated to allow himself to take the throne. Background Liu Hongxi was born in 920, as the fourth son of Liu Yan, who was then already the emperor of Southern Han (as Emperor Gaozu)—and therefore, was likely born at Southern Han's capital Xingwang (興王, in modern Guangzhou, Guangdong). The first historical reference to Liu Hongxi was in 932, when Liu Yan created his sons imperial princes—with Liu Hongxi receiving the title of Prince of Jin. As his two oldest brothers Liu Yaoshu (劉耀樞) and Liu Guitu (劉龜圖)—both of whom also received princely titles in 932 and therefore were likely still alive t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring And Autumn Annals Of The Ten Kingdoms
The ''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms'', also known by its Chinese title ''Shiguo Chunqiu'' (), is a history of the Ten Kingdoms that existed in southern China after the fall of the Tang Dynasty and before the reunification of China by the Song Dynasty. The book was written and compiled by the Qing Dynasty scholar Wu Renchen ( 1628 – 1689). Wu took part in the compilation of '' Mingshi'', the official history of the Ming Dynasty, and felt that the official dynastic histories have neglected the Ten Kingdoms. The book contains 114 volumes (scrolls). Contents The book consists of 114 volumes covering the histories of the Ten Kingdoms: #14 volumes - Wu (907–937) #20 volumes - Southern Tang (937–975) #13 volumes - Former Shu (907–925) #10 volumes - Later Shu (934–965) #9 volumes - Southern Han (917–971) #10 volumes - Chu (907–951) #13 volumes - Wuyue (907–978) #10 volumes - Min (909–945) #4 volumes - Jingnan (924–963) #5 volumes - Northern Han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Hongchang
Liu Hongchang (劉弘昌) (died 944), formally the Prince of Yue (越王), was an imperial prince and chancellor of the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period state Southern Han. He was a son of Southern Han's founding emperor Liu Yan (Emperor Gaozu), and at one point, Liu Yan considered bypassing his older brothers Liu Bin (né Liu Hongdu, Emperor Shang) and Liu Sheng (né Liu Hongxi, Emperor Zhongzong) and making him the successor to the throne. During the subsequent reign of Liu Sheng, Liu Sheng, fearing his capability, had him assassinated. Background It is not known when Liu Hongchang was born, and it is not known who his mother was. However, it is known that he was Liu Yan's fifth son.''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms''vol. 61 In 932, Liu Yan created 19 of his sons, including Liu Hongchang, imperial princes, with Liu Hongchang receiving the title of Prince of Yue.''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 278. Liu Hongchang was described to be filially pious, car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zizhi Tongjian
''Zizhi Tongjian'' () is a pioneering reference work in Chinese historiography, published in 1084 AD during the Northern Song dynasty in the form of a chronicle recording Chinese history from 403 BC to 959 AD, covering 16 dynasties and spanning almost 1400 years. The main text is arranged into 294 scrolls (''juan'' , equivalent to a chapter) totaling about 3 million Chinese characters. In 1065 AD, Emperor Yingzong of Song commissioned his official Sima Guang (1019–1086 AD) to lead a project to compile a universal history of China, and granted him funding and the authority to appoint his own staff. His team took 19 years to complete the work and in 1084 AD it was presented to Emperor Yingzong's successor Emperor Shenzong of Song. It was well-received and has proved to be immensely influential among both scholars and the general public. Endymion Wilkinson regards it as reference quality: "It had an enormous influence on later Chinese historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |