|
Chemoreceptors
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance ( endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemoreceptor is a neuron, or in the form of a neurotransmitter that can activate a nerve fiber if the chemoreceptor is a specialized cell, such as taste receptors, or an internal peripheral chemoreceptor, such as the carotid bodies. In physiology, a chemoreceptor detects changes in the normal environment, such as an increase in blood levels of carbon dioxide (hypercapnia) or a decrease in blood levels of oxygen (hypoxia), and transmits that information to the central nervous system which engages body responses to restore homeostasis. In bacteria, chemoreceptors are essential in the mediation of chemotaxis. Cellular chemoreceptors In prokaryotes Bacteria utilize complex long helical proteins as chemoreceptors, permitting signals to travel lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Chemoreceptor
Peripheral chemoreceptors (of the carotid and aortic bodies) are so named because they are sensory extensions of the peripheral nervous system into blood vessels where they detect changes in chemical concentrations. As transducers of patterns of variability in the surrounding environment, carotid and aortic bodies count as chemosensors in a similar way as taste buds and photoreceptors. However, because carotid and aortic bodies detect variation within the body's internal organs, they are considered interoceptors. Taste buds, olfactory bulbs, photoreceptors, and other receptors associated with the five traditional sensory modalities, by contrast, are exteroceptors in that they respond to stimuli outside the body. The body also contains proprioceptors, which respond to the amount of stretch within the organ, usually muscle, that they occupy. As for their particular function, peripheral chemoreceptors help maintain homeostasis in the cardiorespiratory system by monitoring concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
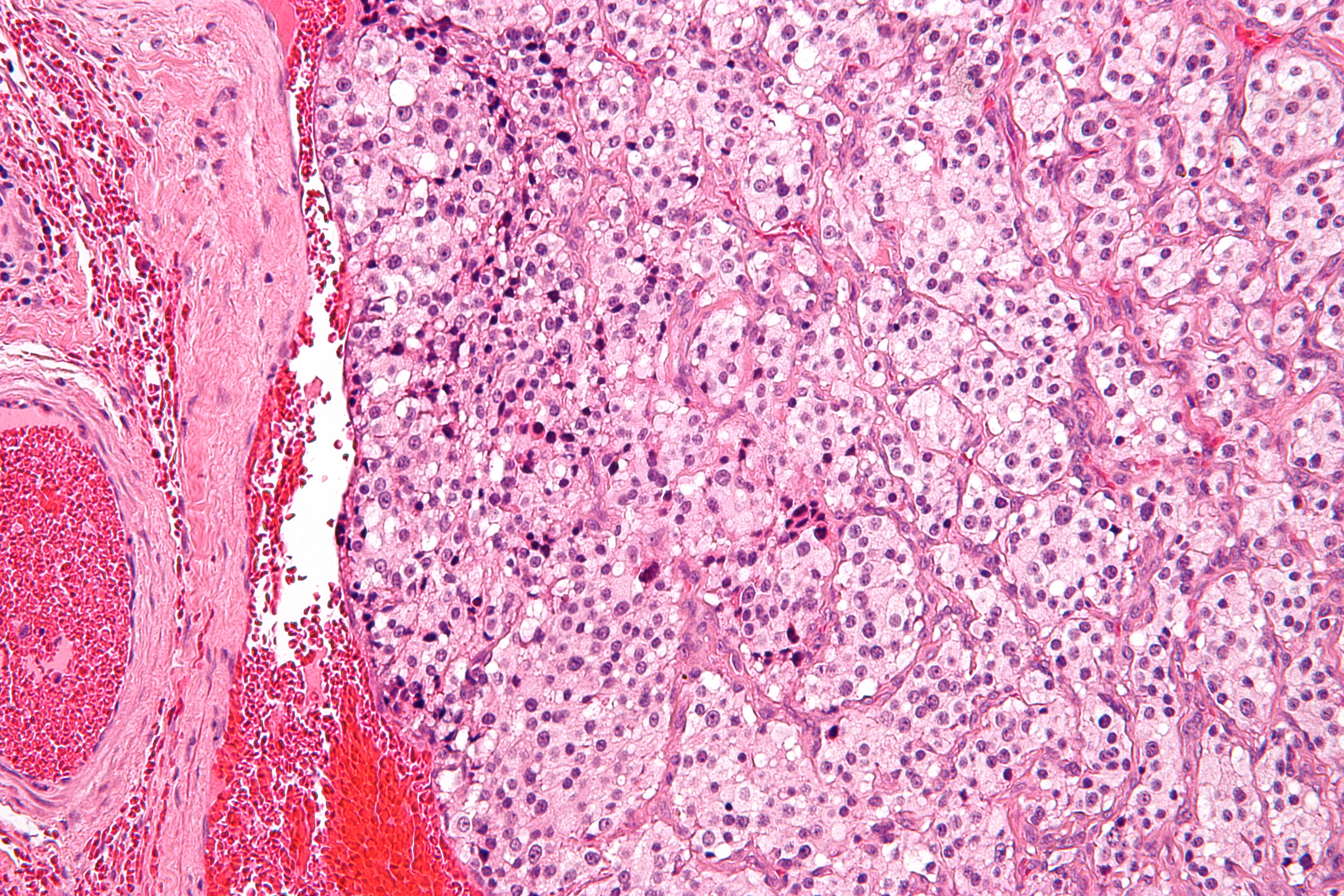
Carotid Body
The carotid body is a small cluster of peripheral chemoreceptor cells and supporting sustentacular cells situated at the bifurcation of each common carotid artery in its tunica externa. The carotid body detects changes in the composition of arterial blood flowing through it, mainly the partial pressure of arterial oxygen, but also of carbon dioxide. It is also sensitive to changes in blood pH, and temperature. Structure The carotid body is situated on the posterior aspect of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. The carotid body is made up of two types of cells, called glomus cells: glomus type I cells are peripheral chemoreceptors, and glomus type II cells are sustentacular supportive cells. * Glomus type I cells are derived from the neural crest. They release a variety of neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine, ATP, and dopamine that trigger EPSPs in synapsed neurons leading to the respiratory center. They are innervated by axons of the glossopharyngeal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from ''chemical substance, chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell organism, single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function and health (e.g., migration of White blood cell, leukocytes during injury or infection). In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis, and the aberrant change of the overall property of these networks, which contro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning for the organism and includes many variables, such as body temperature and fluid balance, being kept within certain pre-set limits (homeostatic range). Other variables include the pH of extracellular fluid, the concentrations of sodium, potassium, and calcium ions, as well as the blood sugar level, and these need to be regulated despite changes in the environment, diet, or level of activity. Each of these variables is controlled by one or more regulators or homeostatic mechanisms, which together maintain life. Homeostasis is brought about by a natural resistance to change when already in optimal conditions, and equilibrium is maintained by many regulatory mechanisms; it is thought to be the central motivation for all organic action. All home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Neuron
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded receptor potentials. This process is called sensory transduction. The cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord. The sensory information travels on the afferent nerve fibers in a sensory nerve, to the brain via the spinal cord. Spinal nerves transmit external sensations via sensory nerves to the brain through the spinal cord. The stimulus can come from exteroreceptors outside the body, for example those that detect light and sound, or from interoreceptors inside the body, for example those that are responsive to blood pressure or the sense of body position. Types and function Sensory neurons in vertebrates are predominantly pseudounipolar or bipolar, and different types of sensory neurons have different sensory receptors that respond t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytosol
The cytosol, also known as cytoplasmic matrix or groundplasm, is one of the liquids found inside cells ( intracellular fluid (ICF)). It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments. In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is surrounded by the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. The cytosol is thus a liquid matrix around the organelles. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others take place within organelles. The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with two subtypes, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core, called the axoneme, determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand Binding Domain
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroids, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These intracellular receptors work with other proteins to regulate the expression of specific genes, thereby controlling the development, homeostasis, and metabolism of the organism. Nuclear receptors bind directly to DNA regulating the expression of adjacent genes; hence these receptors are classified as transcription factors. The regulation of gene expression by nuclear receptors often occurs in the presence of a ligand—a molecule that affects the receptor's behavior. Ligand binding to a nuclear receptor results in a conformational change activating the receptor. The result is up- or down-regulation of gene expression. A unique property of nuclear receptors that differentiates them from other classes of receptors is their direct control of genomic DNA. Nuclear receptors play key roles in both embryonic deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogen-associated Molecular Pattern
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are small molecular motifs conserved within a class of microbes, but not present in the host. They are recognized by toll-like receptors (TLRs) and other pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) in both plants and animals. This allows the innate immune system to recognize pathogens and thus, protect the host from infection. This initiation of the immune response consists of the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. PAMPs can initiate the maturation of immune cells, which can travel to the primary lymph node and trigger the adaptive immune system that involves the production of antibodies against specific antigens. Although the term "PAMP" is relatively new, the concept that molecules derived from microbes must be detected by receptors from multicellular organisms has been held for many decades, and references to an "endotoxin receptor" are found in much of the older literature. The recognition of PAMPs by the PRRs triggers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damage-associated Molecular Pattern
Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) are molecules within cells that are a component of the innate immune response released from damaged or dying cells due to trauma or an infection by a pathogen. They are also known as danger signals, and alarmins because they serve as warning signs to alert the organism to any damage or infection to its cells. DAMPs are endogenous danger signals that are discharged to the extracellular space in response to damage to the cell from mechanical trauma or a pathogen. Once a DAMP is released from the cell, it promotes a noninfectious inflammatory response by binding to a pattern recognition receptor (PRR). Inflammation is a key aspect of the innate immune response; it is used to help mitigate future damage to the organism by removing harmful invaders from the affected area and start the healing process. As an example, the cytokine Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signaling Pathway
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) is the process by which a cell interacts with itself, other cells, and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Typically, the signaling process involves three components: the signal, the receptor, and the effector. In biology, signals are mostly chemical in nature, but can also be physical cues such as pressure, voltage, temperature, or light. Chemical signals are molecules with the ability to bind and activate a specific receptor. These molecules, also referred to as ligands, are chemically diverse, including ions (e.g. Na+, K+, Ca2+, etc.), lipids (e.g. steroid, prostaglandin), peptides (e.g. insulin, ACTH), carbohydrates, glycosylated proteins (proteoglycans), nucleic acids, etc. Peptide and lipid ligands are particularly important, as most hormones belong to these classes of chemicals. Peptides are usually polar, hydrophilic molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |