|
Chemical Bonding Of Water
Water () is a simple triatomic bent molecule with C2v molecular symmetry and bond angle of 104.5° between the central oxygen atom and the hydrogen atoms. Despite being one of the simplest triatomic molecules, its chemical bonding scheme is nonetheless complex as many of its bonding properties such as bond angle, ionization energy, and electronic state energy cannot be explained by one unified bonding model. Instead, several traditional and advanced bonding models such as simple Lewis and VSEPR theory, VSEPR structure, valence bond theory, molecular orbital theory, isovalent hybridization, and Bent's rule are discussed below to provide a comprehensive bonding model for , explaining and rationalizing the various electronic and physical properties and features manifested by its peculiar bonding arrangements. Lewis structure and valence bond theory The Lewis structure of describes the bonds as two sigma bonds between the central oxygen atom and the two peripheral hydrogen atoms w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H2O 2D Labelled
H, or h, is the eighth Letter (alphabet), letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, including the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''aitch'' (pronounced , plural ''aitches''), or regionally ''haitch'' (pronounced , plural ''haitches'')''.''"H" ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "aitch" or "haitch", op. cit. Name English For most English speakers, the name for the letter is pronounced as and spelled "aitch" or occasionally "eitch". The pronunciation and the associated spelling "haitch" are often considered to be H-dropping#H-insertion, h-adding and are considered non-standard in England. It is, however, a feature of Hiberno-English, and occurs sporadically in various other dialects. The perceived name of the letter affects the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Orbital
In quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital () is a Function (mathematics), function describing the location and Matter wave, wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function describes an electron's Charge density, charge distribution around the Atomic nucleus, atom's nucleus, and can be used to calculate the probability of finding an electron in a specific region around the nucleus. Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a set of values of three quantum numbers , , and , which respectively correspond to electron's energy, its angular momentum, orbital angular momentum, and its orbital angular momentum projected along a chosen axis (magnetic quantum number). The orbitals with a well-defined magnetic quantum number are generally complex-valued. Real-valued orbitals can be formed as linear combinations of and orbitals, and are often labeled using associated Spherical harmonics#Harmonic polynomial representation, harmonic polynomials (e.g., ''xy'', ) which describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isovalent Hybridization
In chemistry, isovalent or second order hybridization is an extension of orbital hybridization, the mixing of atomic orbitals into hybrid orbitals which can form chemical bonds, to include fractional numbers of atomic orbitals of each type (s, p, d). It allows for a quantitative depiction of bond formation when the molecular geometry deviates from ideal bond angles. Only bonding with 4 equivalent substituents results in exactly hybridization. For molecules with different substituents, we can use isovalent hybridization to rationalize the differences in bond angles between different atoms. In the molecule methyl fluoride for example, the HCF bond angle (108.73°) is less than the HCH bond angle (110.2°). This difference can be attributed to more character in the C−F bonding and more character in the C−H bonding orbitals. The hybridisation of bond orbitals is determined by Bent's rule: "Atomic s character concentrates in orbitals directed toward electropositive substituents". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory (quantum Mechanics)
In quantum mechanics, perturbation theory is a set of approximation schemes directly related to mathematical perturbation for describing a complicated quantum system in terms of a simpler one. The idea is to start with a simple system for which a mathematical solution is known, and add an additional "perturbing" Hamiltonian representing a weak disturbance to the system. If the disturbance is not too large, the various physical quantities associated with the perturbed system (e.g. its energy levels and eigenstates) can be expressed as "corrections" to those of the simple system. These corrections, being small compared to the size of the quantities themselves, can be calculated using approximate methods such as asymptotic series. The complicated system can therefore be studied based on knowledge of the simpler one. In effect, it is describing a complicated unsolved system using a simple, solvable system. Approximate Hamiltonians Perturbation theory is an important tool for de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
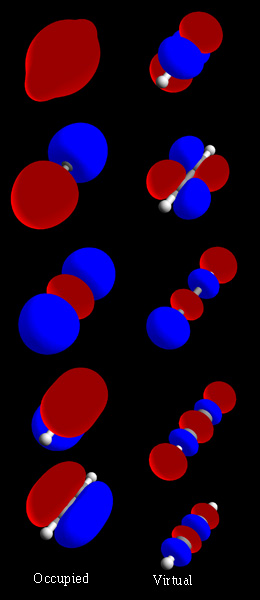
Hybridized MO H2O
Hybridization (or hybridisation) may refer to: *Hybridization (biology), the process of combining different varieties of organisms to create a hybrid *Orbital hybridization, in chemistry, the mixing of atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals *Nucleic acid hybridization, the process of joining two complementary strands of nucleic acids - RNA, DNA or oligonucleotides *In evolutionary algorithms, the merging two or more optimization techniques into a single algorithm **Memetic algorithm, a common template for hybridization *In linguistics, the process of one variety blending with another variety *The alteration of a vehicle into a hybrid electric vehicle *In globalization theory, the ongoing blending of cultures *Hybridization in political election campaign communication, the combining of campaign techniques developed in different countries *In paleoanthropology, the hypothesis of Neanderthal and human hybridization See also *Hybrid (other) *Hybridity Hybridity, in its mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irreducible Representation
In mathematics, specifically in the representation theory of groups and algebras, an irreducible representation (\rho, V) or irrep of an algebraic structure A is a nonzero representation that has no proper nontrivial subrepresentation (\rho, _W,W), with W \subset V closed under the action of \. Every finite-dimensional unitary representation on a Hilbert space V is the direct sum of irreducible representations. Irreducible representations are always indecomposable (i.e. cannot be decomposed further into a direct sum of representations), but the converse may not hold, e.g. the two-dimensional representation of the real numbers acting by upper triangular unipotent matrices is indecomposable but reducible. History Group representation theory was generalized by Richard Brauer from the 1940s to give modular representation theory, in which the matrix operators act on a vector space over a field K of arbitrary characteristic, rather than a vector space over the field of real number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Group
In geometry, a point group is a group (mathematics), mathematical group of symmetry operations (isometry, isometries in a Euclidean space) that have a Fixed point (mathematics), fixed point in common. The Origin (mathematics), coordinate origin of the Euclidean space is conventionally taken to be a fixed point, and every point group in dimension ''d'' is then a subgroup of the orthogonal group O(''d''). Point groups are used to describe the Symmetry (geometry), symmetries of geometric figures and physical objects such as molecular symmetry, molecules. Each point group can be Group representation, represented as sets of orthogonal matrix, orthogonal matrices ''M'' that transform point ''x'' into point ''y'' according to . Each element of a point group is either a Rotation (mathematics), rotation (determinant of ), or it is a Reflection (mathematics), reflection or improper rotation (determinant of ). The geometric symmetries of crystals are described by space groups, which allow T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walsh Diagram
Walsh diagrams, often called angular coordinate diagrams or correlation diagrams, are representations of calculated orbital binding energies of a molecule versus a distortion coordinate (bond angles), used for making quick predictions about the geometries of small molecules. By plotting the change in molecular orbital levels of a molecule as a function of geometrical change, Walsh diagrams explain why molecules are more stable in certain spatial configurations (e.g. why water adopts a bent conformation). A major application of Walsh diagrams is to explain the regularity in structure observed for related molecules having identical numbers of valence electrons (e.g. why H2O and H2S look similar), and to account for how molecules alter their geometries as their number of electrons or spin quantum number, spin state changes. Additionally, Walsh diagrams can be used to predict distortions of molecular geometry from knowledge of how the LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) affects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Orbital Diagram
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals, although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals. This tool is very well suited for simple diatomic molecules such as dihydrogen, dioxygen, and carbon monoxide but becomes more complex when discussing even comparatively simple polyatomic molecules, such as methane. MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. They can also predict bond strength, as well as the electronic transitions that can take place. History Qualitative MO theory was introduced in 1928 by Robert S. Mulliken and Friedrich Hund. A mathematical description w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delocalized Electron
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond.IUPAC Gold Boo''delocalization''/ref> The term delocalization is general and can have slightly different meanings in different fields: * In organic chemistry, it refers to resonance in conjugated systems and aromatic compounds. * In solid-state physics, it refers to free electrons that facilitate electrical conduction. * In quantum chemistry, it refers to molecular orbital electrons that have extended over several adjacent atoms. Resonance In the simple aromatic ring of benzene, the delocalization of six π electrons over the C6 ring is often graphically indicated by a circle. The fact that the six C-C bonds are equidistant is one indication that the electrons are delocalized; if the structure were to have isolated double bonds alternating with discrete single bonds, the bond would likewise have alternating longer and short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The terms ''atomic orbital'' and ''molecular orbital'' were introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 to mean ''one-electron orbital wave functions''. At an elementary level, they are used to describe the ''region'' of space in which a function has a significant amplitude. In an isolated atom, the orbital electrons' location is determined by functions called atomic orbitals. When multiple atoms combine chemically into a molecule by forming a valence chemical bond, the electrons' locations are determined by the molecule as a whole, so the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The electrons from the constituent atoms occupy the molecular orbitals. Mathematically, molecular orbitals are an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |