|
Checker House Railway Station
Checker House railway station was a station between Retford and Worksop, Nottinghamshire, England which served the village of Ranby from 1852 to 1931. The platforms were immediately to the east of the A1 road, and there was a goods station to the west of the road, which remained open until 1963. The line remains open for services on the Sheffield–Lincoln line but nothing remains of the passenger station or platforms, although part of a loading gauge was still visible in 2021. The site was included in Bassetlaw District Council's local plan in 2019, as they were considering locations for a garden village development, and the favoured site was immediately to the south of the railway line. If the village is built, it will probably include a station at or near the site of Checker House station, but it may be called Morton. History The line between and opened on 16 July 1849, but did not initially include a station at Checker House, which opened three years later on 1 April 1852 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheffield And Lincolnshire Junction Railway
The Sheffield and Lincolnshire Junction Railway was an early British railway company which opened in 1849 between Sheffield and Gainsborough and Lincoln. It amalgamated with the Sheffield, Ashton-Under-Lyne and Manchester Railway and the Great Grimsby and Sheffield Junction Railway, the three being renamed the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway in 1847. It is now the Sheffield to Lincoln Line. Plans The line originated with a plan in 1836 to connect the SA&MR at Sheffield with the proposed Midland Counties Railway at a time when the latter was planning to run to Chesterfield. This was changed to proposal for Sheffield Union Railway to connect instead with the North Midland Railway at Woodhouse Mill. This plan, in turn, was superseded by one for a connection to Chesterfield. At this point, in 1844, it was suggested that the people of Sheffield would be better served by extending the SA&MR eastwards. This was supported, not only by the SA&MR, but by the councillors of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great North Road (Great Britain)
The Great North Road was the main highway between England and Scotland from medieval times until the 20th century. It became a coaching route used by mail coaches travelling between London, York and Edinburgh. The modern A1 road (Great Britain), A1 mainly parallels the route of the Great North Road. Coaching inns, many of which survive, were staging posts providing accommodation, stabling for horses and replacement mounts. Nowadays virtually no surviving coaching inns can be seen while driving on the A1, because the modern route bypasses the towns in which the inns are found. Route The traditional start point for the Great North Road was Smithfield, London, Smithfield Market on the edge of the City of London. The initial stretch of the road was St John Street, London, St John Street which begins on the boundary of the city (the site of the former Smithfield, London#West Smithfield Bars, West Smithfield Bars), and runs through north London. Less than a hundred metres up St John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Great Central Railway Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retford Railway Station
Retford railway station is on the East Coast Main Line serving the town of Retford, Nottinghamshire, England. It is down the line from and is situated between and on the main line. It has four platforms, two of which serve the main line and the other two, located at a lower level and at right angles to the first pair, serve the Sheffield to Lincoln Line. Facilities The station is staffed throughout the week, with most amenities (booking office, toilets, coffee shop and vending machine) in the main building on platforms 1. The ticket office is staffed Monday - Friday 05:35 - 18:00, Saturday 05:35 - 16:10 and Sunday 08:20 - 16:10. A self-service ticket machine is also provided for use when the booking office is closed and for collecting pre-paid tickets. Train running information is offered via automated announcements, CIS displays and timetable posters. There are also customer help points on both low-level platforms, along with waiting shelters. All platforms are fully a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worksop Railway Station
Worksop railway station is a Grade II listed railway station which serves the town of Worksop in Nottinghamshire, England. History The station was designed by Weightman & Hadfield, Sheffield in the Jacobean style, and built by James Drabble, Carlton in Lindrick. It was opened on 7 July 1849 by the Sheffield and Lincolnshire Junction Railway, part of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway. It was extended and further buildings added in 1900. It is today an intermediate stop on the regional service between and ( from ) operated by Northern Trains, and is the northern terminus of East Midlands Railway' Robin Hood Line between Worksop and via (the section from the latter town was re-opened to passengers on 25 May 1998, after originally losing them to the Beeching Axe in October 1964). The station buildings on each side are still in use - operator Northern runs the booking office on platform 1, Network Rail has office accommodation on platform 1 and the remaining ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
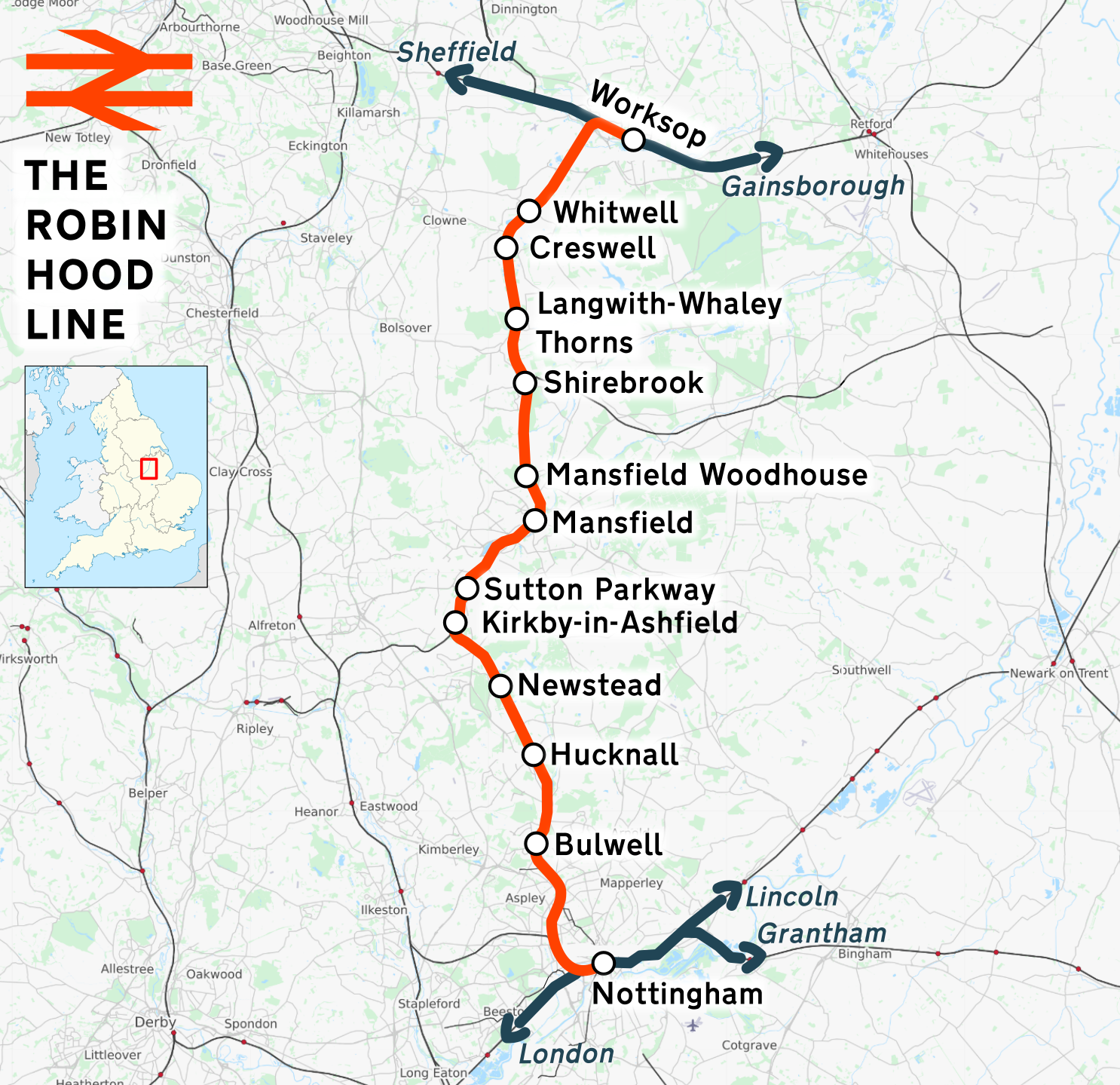
Robin Hood Line
The Robin Hood Line is a railway line running from Nottingham to Worksop, Nottinghamshire, in England. The stations between Shirebrook and Whitwell (inclusive) are in the county of Derbyshire. Passenger services are operated by East Midlands Railway. The line in its present form opened to passengers in stages between 1993 and 1998. Following the Beeching cuts of the 1960s, the line had been freight-only. The cuts had left Mansfield as one of the largest towns in Britain without a railway station. History The majority of the current Robin Hood Line re-uses the former Midland Railway (MR) route from Nottingham to Worksop. However, due to rationalisation leading to track removal in order to save the costs of maintaining the tunnel north of Annesley, the through route was severed in the 1970s. Northwards from Nottingham, the freight-only line remained intact as far as Newstead, where it had served the now closed Newstead Colliery. Southwards from Worksop, the line followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Box
A hot box is the term used when an axle bearing overheats on a piece of railway rolling stock. The term is derived from the journal-bearing trucks used before the mid-20th century. The axle bearings were housed in a box that used oil-soaked rags or cotton (collectively called "packing") to reduce the friction of the axle against the truck frame. When the oil leaked or dried out, the bearings overheated, often starting a fire that could destroy the entire railroad car (and cars coupled to it) if not detected early enough. The packing and bearing had to be regularly inspected by yard crews, and packing was often added at major stops. The journal bearing was replaceable, but if neglected, it would heat to a temperature where the babbitt bearing alloy would melt away, leaving the brass carrier riding on the steel axle, and result in a "taper journal". This would eventually lead to the axle fracturing and the car above falling onto the wheel, or failure of the taper journal, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert McGregor & Sons
Robert McGregor & Sons, also known just as Mc Gregor was a large civil engineering company based in Boothstown, in what is now Greater Manchester, England. History It was founded in Manchester in 1927. It specialised in building concrete surfaces for roads using a machine known as a concrete paver. It worked with the company Cementation Construction Ltd. It developed the CPP60 concrete paver. It became part of Norwest Holst Civil Engineering, when bought in October 1978 for £3m. Structure It was based on the A572 in Walkden in Greater Manchester (Salford). It also had a site in at Birdholme in Chesterfield, Derbyshire. Products Roads it built include: * A1(M) Birtley bypass (£2.5 million) * A1 Grantham bypass, October 1962 * A1 Newark-on-Trent bypass, July 1964 * A1 Improvement from North of Muskham to South of Carlton including Cromwell By-pass, January 1966 (£772,000) * A1 Sutton-on-Trent, Weston, and Tuxford By-Pass, July 1967, £4m * A38 Alfreton- M1 bypass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln Corporation Waterworks
Lincoln Corporation Waterworks and its predecessors and successors have provided a public water supply and sewerage and sewage treatment services to the city of Lincoln, England, Lincoln, England. The Ancient Rome, Romans are known to have built a conduit from the Roaring Meg stream to a water tower in East Bight. Further development took place when the Lincoln Waterworks Act 1846 (9 & 10 Vict. c. cxi) was passed to establish the Lincoln Water Company, following a national outbreak of cholera in 1831-32. The main source of supply was formed by impounding Prial Drain to form Hartsholme Lake. The water was filtered by sand filters at Boultham, and was pumped to a service reservoir at Westgate. Lincoln Corporation wanted to gain control of their water supply, and bought out the water company in 1871. The enabling act of Parliament (United Kingdom), act of Parliament, the Lincoln Waterworks Act 1871 (34 & 35 Vict. c. cxlix) also allowed them to construct a sewerage network, which fed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |