|
Charles M. Hudson (author)
Charles Melvin Hudson Jr. (1932–2013) was an anthropologist, a professor of anthropology and history at the University of Georgia. He was a leading scholar on the history and culture of Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the present-day United States. He is known for his book mapping the expedition of Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in the mid-16th century in the Southeast, based on both the expedition's records and sites identified through archeology and anthropology. He also published books with detailed discussion of two 16th-century Spanish expeditions in the Southeast: ''Knights of Spain, Warriors of the Sun: Hernando De Soto and the South's Ancient Chiefdoms'' (1997) and ''The Juan Pardo Expeditions: Exploration of the Carolinas and Tennessee, 1566–1568'' (2005). Life Born in 1932, Hudson grew up on a farm in Owen County, Kentucky, and attended local schools. He served in the U.S. Air Force during the Korean War. After the war, he used the G.I. Bill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeSoto Map HRoe 2008
De Soto commonly refers to * Hernando de Soto (c. 1500 – 1542), Spanish explorer * DeSoto (automobile), an American automobile brand from 1928 to 1961 De Soto, DeSoto, Desoto, or de Soto may also refer to: Places in the United States of America ;Populated places * De Soto, Georgia * De Soto, Illinois * De Soto, Iowa * De Soto, Kansas * De Soto, Mississippi * De Soto, Missouri * De Soto, Nebraska * De Soto, Wisconsin * DeSoto, Indiana * DeSoto, Texas ;Administrative divisions * De Soto Parish, Louisiana * DeSoto County, Florida * DeSoto County, Mississippi ;Parks and geographic features * De Soto National Forest in Mississippi * DeSoto Falls (Alabama) * DeSoto Falls (Georgia) * DeSoto Lake, a lake in Georgia * DeSoto National Wildlife Refuge, in Nebraska and Iowa * Fort De Soto Park in St. Petersburg, Florida * De Soto National Memorial in Bradenton, Florida * DeSoto Site Historic State Park in Tallahassee, Florida People * de Soto (surname) Other uses *The DeSoto, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society For Ethnohistory
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label that was previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of North Carolina At Chapel Hill Alumni
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Kentucky Alumni
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the Midd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historians Of Native Americans
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human species; as well as the study of all history in time. Some historians are recognized by publications or training and experience.Herman, A. M. (1998). Occupational outlook handbook: 1998–99 edition. Indianapolis: JIST Works. Page 525. "Historian" became a professional occupation in the late nineteenth century as research universities were emerging in Germany and elsewhere. Objectivity Among historians Ancient historians In the 19th century, scholars used to study ancient Greek and Roman historians to see how generally reliable they were. In recent decades, however, scholars have focused more on the constructions, genres, and meanings that ancient historians sought to convey to their audiences. History is always written with contemporary concerns and ancient hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Male Non-fiction Writers
American(s) may refer to: * American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America" ** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America ** American ancestry, people who self-identify their ancestry as "American" ** American English, the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States ** Native Americans in the United States, indigenous peoples of the United States * American, something of, from, or related to the Americas, also known as "America" ** Indigenous peoples of the Americas * American (word), for analysis and history of the meanings in various contexts Organizations * American Airlines, U.S.-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas * American Athletic Conference, an American college athletic conference * American Recordings (record label), a record label that was previously known as Def American * American University, in Washington, D.C. Sports teams S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2013 Deaths
This is a list of lists of deaths of notable people, organized by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked below. 2025 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 Earlier years ''Deaths in years earlier than this can usually be found in the main articles of the years.'' See also * Lists of deaths by day * Deaths by year (category) {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coosa Chiefdom
The Coosa Chiefdom was a powerful Native American paramount chiefdom in what are now Gordon and Murray counties in Georgia, in the United States."Late Prehistoric/Early Historic Chiefdoms (ca. A.D. 1300-1850)" . '' New Georgia Encyclopedia''. Retrieved July 22, 2010. It was inhabited from about 1400 until about 1600, and dominated several smaller chiefdoms. The total population of Coosa's area of influence, reaching into present-day Tennessee and Alabama, has been estimated at 50,000. and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
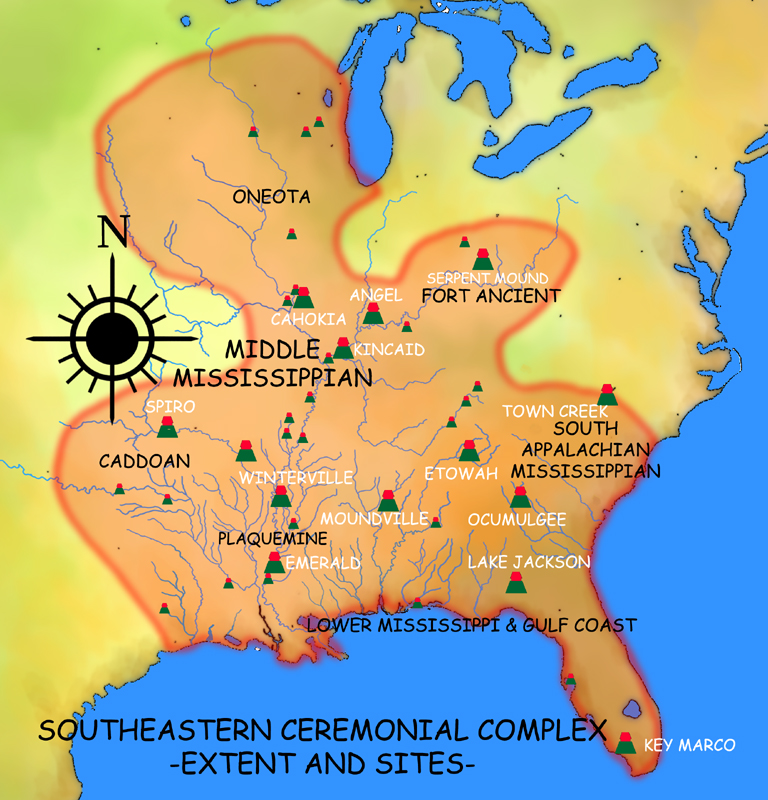
Southeastern Ceremonial Complex
Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (formerly Southern Cult, Southern Death Cult or Buzzard Cult), abbreviated S.E.C.C., is the name given by modern scholars to the regional stylistic similarity of artifacts, iconography, ceremonies, and mythology of the Mississippian culture. It coincided with their adoption of maize agriculture and chiefdom-level complex social organization from 1200 to 1650 CE. Due to some similarities between S.E.C.C. and contemporary Mesoamerican cultures (i.e., artwork with similar aesthetics or motifs; maize-based agriculture; and the development of sophisticated cities with large pyramidal structures), scholars from the late 1800s to mid-1900s suspected there was a connection between the two locations. One hypothesis was that Meso-Americans enslaved by conquistador Tristán de Luna y Arellano (1510–1573) may have spread artistic and religious elements to North America. However, later research indicates the two cultures have no direct links and that thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian Culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center, located in what is present-day southern Illinois. The Mississippian way of life began to develop in the Mississippi River Valley (for which it is named). Cultures in the tributary Tennessee River Valley may have also begun to develop Mississippian characteristics at this point. Almost all dated Mississippian sites predate 1539–1540 (when Hernando de Soto explored the area), with notable exceptions being Natchez communities. These maintained Mississippian cultural practices into the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Anthropological Society
The Southern Anthropological Society (SAS) is an organization in the United States. It publishes a journal titled ''Southern Anthropologist'' and issues a newsletter. It awards a James Mooney Award (James Mooney James Mooney (February 10, 1861 – December 22, 1921) was an American ethnographer who lived for several years among the Cherokee. Known as "The Indian Man", he conducted major studies of Southeastern Indians, as well as of tribes on the Great ...) and Zora Neal Hurston Award ( Zora Neal Hurston). The Mooney Award recognizes the best among books about southern anthropological matters. The group was established in 1966. It holds an annual meeting. William E. Carter was involved in the group. Robbie Ethridge and Dickson D. Bruce are among recipients of the Mooney award. References Website * Professional associations based in the United States Anthropology-related professional associations Educational organizations established in 1966 1966 establishments in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behaviour, while cultural anthropology studies cultural meaning, including norms and values. The term sociocultural anthropology is commonly used today. Linguistic anthropology studies how language influences social life. Biological anthropology, Biological (or physical) anthropology studies the biology and evolution of Human evolution, humans and their close primate relatives. Archaeology, often referred to as the "anthropology of the past," explores human activity by examining physical remains. In North America and Asia, it is generally regarded as a branch of anthropology, whereas in Europe, it is considered either an independent discipline or classified under related fields like history and palaeontology. Etymology The abstract noun ''wikt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |