|
Charles Girdlestone
Charles Girdlestone (1797–1881) was an English clergyman and biblical commentator. Life The second son of Samuel Rainbow Girdlestone, a chancery barrister, was born in London in March 1797; Edward Girdlestone, canon of Bristol, was his younger brother. He was educated at Tunbridge School, under Vicesimus Knox, and in 1815 entered Wadham College, Oxford, where he held two exhibitions, one for Hebrew, the other for botany. In 1818 he graduated B.A., with a first class in classics and a second in mathematics, at the same time as Edward Greswell, Josiah Forshall, and Richard Bethell, also of Wadham. He was elected to an open fellowship at Balliol College, and was appointed catechetical, logical, and mathematical lecturer in the college. He was ordained deacon in 1820 and priest in 1821, taking his M.A. degree in the same year. About this time he became tutor to the twin sons of Sir John Stanley of Alderley Park; it was this connection which led to his being appointed rector of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Girdlestone
Edward Girdlestone (6 September 1805 – 4 December 1884) was an English cleric, who became known as "The Agricultural Labourers' Friend" for his activism of the late 1860s and early 1870s. Life He was the youngest son of Samuel Rainbow Girdlestone, a chancery barrister, born in London 6 September 1805, and younger brother of Charles Girdlestone. He matriculated at Balliol College, Oxford, 10 June 1822, and in 1823 was admitted a scholar of his college, became B.A. in 1826, M.A. in 1829, and was ordained to the curacy of Deane, Lancashire, in 1828. Having taken priest's orders he became vicar of Deane in 1830. Lord-chancellor Cranworth conferred on Girdlestone in 1854 the place of canon residentiary of Bristol Cathedral, and he consequently succeeded to the vicarage of St. Nicholas with St. Leonard, Bristol, in 1855. He resigned it in 1858 for the vicarage of Wapley with Codrington, South Gloucestershire, Codrington, Gloucestershire. In 1862 he became vicar of Halberton, Devon, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
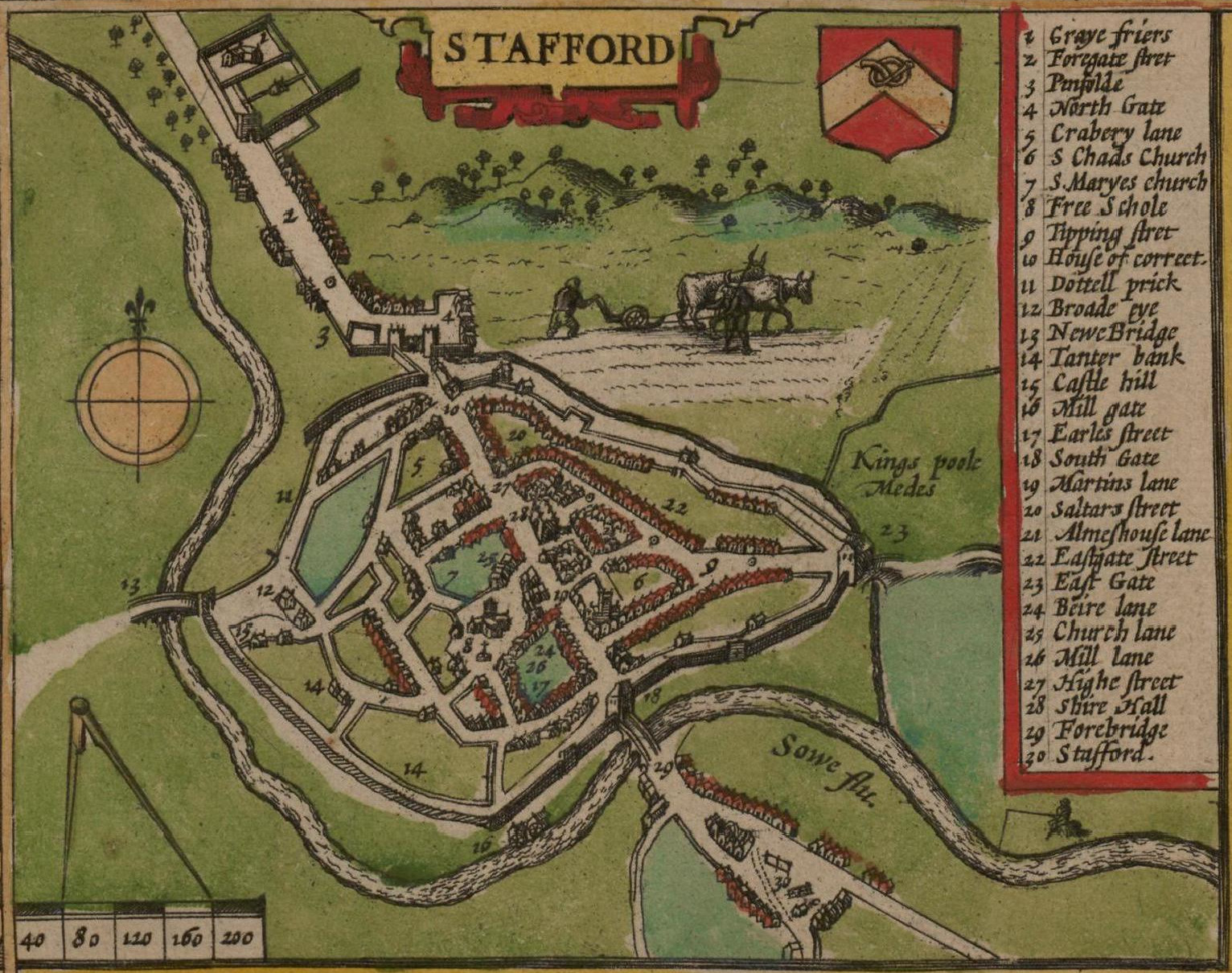
Stafford
Stafford () is a market town and the county town of Staffordshire, England. It is located about south of Stoke-on-Trent, north of Wolverhampton, and northwest of Birmingham. The town had a population of 71,673 at the 2021–2022 United Kingdom censuses, 2021 census, and is the main settlement within the larger Borough of Stafford, which had a population of 136,837 in 2021. Stafford has Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon roots, being founded in 913, when Æthelflæd, List of monarchs of Mercia, Lady of the Mercians founded a defensive burh, it became the county town of Staffordshire soon after. Stafford became an important market town in the Middle Ages, and later grew into an important industrial town due to the proliferation of shoemaking, engineering and electrical industries. History Ancient Prehistoric finds suggest scattered settlements in the area, whilst south-west of the town lies an British Iron Age, Iron Age hill fort at Berry Ring. There is also evidence of Roman Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1881 Deaths
Events January * January 1– 24 – Siege of Geok Tepe: Russian troops under General Mikhail Skobelev defeat the Turkomans. * January 13 – War of the Pacific – Battle of San Juan and Chorrillos: The Chilean army defeats Peruvian forces. * January 15 – War of the Pacific – Battle of Miraflores: The Chileans take Lima, capital of Peru, after defeating its second line of defense in Miraflores. * January 24 – William Edward Forster, chief secretary for Ireland, introduces his Coercion Bill, which temporarily suspends habeas corpus so that those people suspected of committing an offence can be detained without trial; it goes through a long debate before it is accepted February 2. Note that Coercion bills had been passed almost annually in the 19th century, with a total of 105 such bills passed from 1801 to 1921. * January 25 – Thomas Edison and Alexander Graham Bell form the Oriental Telephone Company. February * Febru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1797 Births
Events January–March * January 3 – The Treaty of Tripoli, a peace treaty between the United States and Ottoman Tripolitania, is signed at Algiers (''see also'' 1796). * January 7 – The parliament of the Cisalpine Republic adopts the Italian green-white-red tricolour as their official flag (this is considered the birth of the flag of Italy). * January 13 – Action of 13 January 1797, part of the War of the First Coalition: Two British Royal Navy frigates, HMS ''Indefatigable'' and HMS ''Amazon'', drive the French 74-gun ship of the line '' Droits de l'Homme'' aground on the coast of Brittany, resulting in over 900 deaths. * January 14 – War of the First Coalition – Battle of Rivoli: French forces under General Napoleon Bonaparte defeat an Austrian army of 28,000 men, under '' Feldzeugmeister'' József Alvinczi, near Rivoli (modern-day Italy), ending Austria's fourth and final attempt to relieve the fortress city of Mantua. * Jan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wycliffe Hall, Oxford
Wycliffe Hall () is a permanent private hall of the University of Oxford affiliated with the Church of England, specialising in philosophy, theology, and religion. It is named after the Bible translator and reformer John Wycliffe, who was master of Balliol College, Oxford in the 14th century. Founded in 1877, Wycliffe Hall provides theological training to women and men for ordained and lay ministries in the Church of England as well as other Anglican and non-Anglican churches. There are also a number of independent students studying theology, education and philosophy at undergraduate or postgraduate level. The hall is rooted in and has a history of Evangelical Anglicanism and includes strong influences of Charismatic, Conservative and Open Evangelical traditions. The hall has contributed the greatest number of Lords Spiritual to the Parliament, surpassing all other colleges of the University of Oxford in this century. The hall is the third-oldest Anglican theological college ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Baker Girdlestone
Robert Baker Girdlestone (1836–1923) was an Anglican cleric who ministered at St John's Downshire Hill, Hampstead. He studied at Charterhouse, London, and Christ Church, Oxford, and was first principal of Wycliffe Hall, Oxford. A Hebrew scholar and head of the translation department of the British and Foreign Bible Society, he is best known for his reference work ''Synonyms of the Old Testament''. Life Robert Baker Girdlestone was the seventh son of Charles Girdlestone, a Fellow of Balliol College, Oxford. R. B. Girdlestone was minister of St. John's Downshire Hill, Hampstead, then head of the translation department of the British and Foreign Bible Society, and first principal of Wycliffe Hall, Oxford, in the post from 1877 to 1889. Family His third son Gathorne Robert Girdlestone (1881–1950) was the first Nuffield Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery, and thereby the first professor of orthopaedics Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternative spelling orthopaedics) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somerset
Somerset ( , ), Archaism, archaically Somersetshire ( , , ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel, Gloucestershire, and Bristol to the north, Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. The largest settlement is the city of Bath, Somerset, Bath, and the county town is Taunton. Somerset is a predominantly rural county, especially to the south and west, with an area of and a population of 965,424. After Bath (101,557), the largest settlements are Weston-super-Mare (82,418), Taunton (60,479), and Yeovil (49,698). Wells, Somerset, Wells (12,000) is a city, the second-smallest by population in England. For Local government in England, local government purposes the county comprises three Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas: Bath and North East Somerset, North Somerset, and Somerset Council, Somerset. Bath and North East Somerset Council is a member of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weston-super-Mare
Weston-super-Mare ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the North Somerset unitary district, in the county of Somerset, England. It lies by the Bristol Channel south-west of Bristol between Worlebury Hill and Bleadon Hill. Its population at the 2021 census was 82,418. The area around the town has been occupied since the Iron Age. It was still a small village until the 19th century when it developed as a seaside resort. A Weston-super-Mare railway station, railway station and two piers were built. In the second half of the 20th century it was connected to the M5 motorway but the number of people holidaying in the town declined and some local industries closed, although the number of day visitors has risen. Attractions include the Grand Pier, Weston-super-Mare, Grand Pier, Weston Museum and The Helicopter Museum. Cultural venues include The Playhouse, Weston-super-Mare, The Playhouse, the Winter Gardens Pavilion, Weston-super-Mare, Winter Gardens and the The Blakehay Theat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locum Tenens
A locum, or locum tenens, is a person who temporarily fulfills the duties of another; the term is especially used for physicians or clergy. For example, a ''locum tenens physician'' is a physician who works in the place of the regular physician. In the Catholic Church, an example of a ''locum tenens'' is an apostolic administrator, often a bishop who temporarily governs a vacant see until a new ordinary is appointed. ''Locum tenens'' is a Latin phrase meaning "place holding", akin to the Greek ''topoteretes'', or French ''lieutenant''. United Kingdom healthcare In the United Kingdom, the NHS The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern ... on average has 3,500 locum doctors working in hospitals on any given day, with another 17,000 locum general practitioners ( GPs). On the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingswinford
Kingswinford is a town of the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley in the English West Midlands (county), West Midlands, situated west-southwest of central Dudley. In 2011 the area had a population of 25,191, down from 25,808 at the 2001 Census. The current economic focus of Kingswinford is education and housing for commuters. Positioned at the far western edge of the West Midlands Urban Area it borders on a rural area extending past the River Severn; but its position at the edge of the Black Country and its long standing in the area means it has had significant industrial influence in the past. This is illustrated by the influence in creating local workhouses, which shows a population of 15,000 plus in the 1831 census. History Kingswinford has Ancient counties of England, historically been in Staffordshire. The larger Kingswinford manor mentioned in the Domesday Book of 1086 was located in the Hundred_(county_division), hundred of Seisdon Hundred, Seisdon in Staffordshire, with ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tithes Commutation Act 1836
The Tithe Act 1836 ( 6 & 7 Will. 4. c. 71), sometimes called the Tithe Commutation Act 1836, is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It is one of the Tithe Acts 1836 to 1891. It replaced the ancient system of payment of tithes in kind with monetary payments. It is especially noted for the tithe maps which were needed for the valuation process required by the act. British Parliamentary Paper 1837 XLI 405 was published to give guidance on how landscape features were to be indicated on the maps. It is entitled ′Conventional signs to be used in the plans made under the Act for the Commutation of Tithes in England and Wales′What is a cross road? by Susan Taylor Tithe payments Tithes were originally paid as one-tenth of the produce of the land (crops, eggs, cattle, timber, fishing, etc.) to the rector, as alms and as payment for his services. The tithes were often stored in a tithe barn attached to the parish. At the dissolution of the monasteries some of the land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward John Stanley
Edward John Stanley, 2nd Baron Stanley of Alderley, (13 November 180216 June 1869), known as The Lord Eddisbury between 1848 and 1850, was a British politician. He served as Postmaster General between 1860 and 1866. Early life and education Stanley was the eldest of twin sons born to John Stanley, 1st Baron Stanley of Alderley, and Lady Maria Josepha, daughter of John Holroyd, 1st Earl of Sheffield. His twin brother, Hon. William Owen Stanley (1802–1884), was a Liberal Party politician. He was educated at Eton College and Christ Church, Oxford. Political career Stanley entered the House of Commons as Whig Member of Parliament (MP) for Hindon in 1831 and was later member for North Cheshire between 1832 and 1841, and between 1847 and 1848. He served under Lord Melbourne as Patronage Secretary to the Treasury from 1835 to 1841, as Under-Secretary of State for the Home Department in 1841 and as Paymaster General in 1841 and under Lord John Russell as Under-Secretary of Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |