|
Charles Baird (engineer)
Charles Baird (20 December 1766 – 10 December 1843) was a Scottish engineer who played an important part in the industrial and business life of 19th-century St. Petersburg. His company specialised in steam-driven machinery and was responsible for Russia's first steamboat. Biography Born at Westerton, Bothkennar, Stirlingshire, a farm owned by the Gascoigne family, Charles was one of the nine children of Nicol Baird, who later became a toll collector and then superintendent of works for the Forth and Clyde Canal. He was originally baptised Gascoigne Baird in January 1767. His younger brother Hugh Baird also became an engineer. Charles Baird started his working life in 1782 as an apprentice at the Carron Ironworks near Falkirk. By the age of 19 Baird had a supervisory post in the gun department, and in 1786 he accompanied a Carron Company manager, Charles Gascoigne, a son of the owner's family, to Russia to establish the Aleksandrovsk gun factory at Petrozavodsk, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The St
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Handyside
William Handyside (1793–1850) was a Scottish engineer who was involved in several important construction projects in St. Petersburg. Biography Born in Edinburgh on 25 July 1793, to merchant Hugh Handyside and his wife Margaret, he was the eldest brother of Andrew Handyside and nephew of Charles Baird. On a visit to Scotland in 1810, Baird invited William, then a trainee architect, to join his flourishing business in St. Petersburg and live in his household. His first projects included installing machinery at the imperial arsenal and glassworks and helping build the ''Elizaveta'' steamship, launched in 1815. He was a talented engineer and contributed to the development of Baird Works' steamship and steam engine manufacturing. He developed a gas lighting system for the factory and the sugar refining process conceived by Baird. When the company started working with Wilhelm von Traitteur and Pierre Bazaine on the first Russian suspension bridges in the 1820s, Handyside design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Baird
Francis Baird (1802–1864) was an engineer of Scottish ancestry in Saint Petersburg, who took over his father's business manufacturing machinery, ships, and metalwork for some of the city's major structures. Life He was born on 28 February 1802, one of Charles Baird's three sons, and the only one to live beyond his thirties. He joined his father's company in St. Petersburg at the age of 17 and also went to the University of Edinburgh. In 1823 he was elected to the Institution of Civil Engineers, one of its earliest members. He married Dorothea Halliday in 1828 and they had ten children. Some of the time he worked with his cousin William Handyside, who had a leading role in several engineering projects, and it is not entirely clear how much he helped Handyside with the specialist castings for the Alexander Column and Saint Isaac's Cathedral. He is credited with casting the great cannons in the Kremlin and the angel on the Alexander monument. As well as the iron foundry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Nasmyth
James Hall Nasmyth (sometimes spelled Naesmyth, Nasmith, or Nesmyth) (19 August 1808 – 7 May 1890) was a Scottish engineer, philosopher, artist and inventor famous for his development of the steam hammer. He was the co-founder of Nasmyth, Gaskell and Company manufacturers of machine tools. He retired at the age of 48, and moved to Penshurst, Kent where he developed his hobbies of astronomy and photography. Early life Nasmyth was born at 47 York Place, Edinburgh where his father Alexander Nasmyth was a landscape and portrait painter. One of Alexander's hobbies was mechanics and he employed nearly all his spare time in his workshop where he encouraged his youngest son to work with him in all sorts of materials. James was sent to the Royal High School (Edinburgh), Royal High School where he had as a friend, Jimmy Patterson, the son of a local iron founder. Being already interested in mechanics he spent much of his time at the foundry and there he gradually learned to work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serfdom
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed during late antiquity and the Early Middle Ages in Europe and lasted in some countries until the mid-19th century. Unlike slaves, serfs could not be bought, sold, or traded individually, though they could, depending on the area, be sold together with land. Actual slaves, such as the kholops in Russia, could, by contrast, be traded like regular slaves, abused with no rights over their own bodies, could not leave the land they were bound to, and marry only with their lord's permission. Serfs who occupied a plot of land were required to work for the lord of the manor who owned that land. In return, they were entitled to protection, justice, and the right to cultivate certain fields within the manor to maintain their own subsistence. Serfs wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
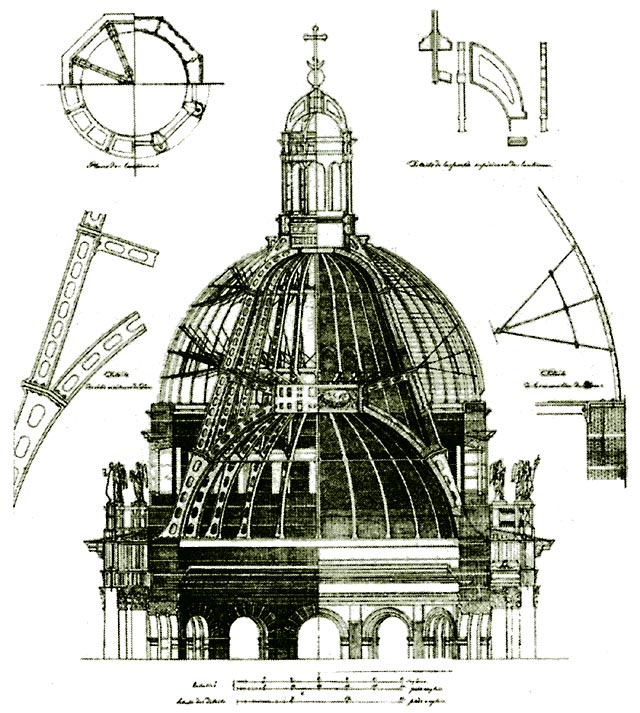
Saint Isaac's Cathedral
Saint Isaac's Cathedral () is a large architectural landmark cathedral that currently functions as a museum with occasional church services in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is dedicated to Saint Isaac of Dalmatia, a patron saint of Peter the Great, who had been born on the feast day of that saint. It was originally built as a cathedral but was turned into a museum by the Soviet government in 1931 and has remained a museum ever since, with church services held in a side chapel since the 1990s. In 2017, the Governor of Saint Petersburg offered to transfer the cathedral back to the Russian Orthodox Church, but this was not accomplished due to the protests of St Petersburg citizens opposing the offer. History The church on St Isaac's Square was ordered by Tsar Alexander I, to replace an earlier structure by Vincenzo Brenna, and was the fourth consecutive church standing at this place. A specially appointed commission examined several designs, including that of the French-born a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Column
The Alexander Column (, ''Aleksandrovskaya kolonna''), also known as Alexandrian Column (, ''Aleksandriyskaya kolonna''), is the focal point of Palace Square in Saint Petersburg, Russia. The monument was raised after the Russian victory in the war with Napoleon's France. The column is named for Emperor Alexander I of Russia, who reigned from 1801 to 1825. Column The Alexander Column was designed by the French-born architect Auguste de Montferrand, built between 1830 and 1834 designed by Swiss-born architect Antonio Adamini, and unveiled on 30 August 1834 (St. Alexander of Constantinople's Day). The monument is claimed to be the tallest of its kind in the world at tall and is topped with a statue of an angel holding a cross, as a triumphal column it may be the highest but the Monument to the Great Fire of London is a freestanding column high. The column is a single piece of red granite, long and about in diameter. The granite monolith was obtained from Virolahti, Finl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste De Montferrand
Auguste de Montferrand (; ; January 23, 1786 – July 10, 1858) was a French classicist architect who worked primarily in Russia. His two best known works are the Saint Isaac's Cathedral and the Alexander Column in Saint Petersburg. Early life Family Montferrand was born in the parish of Chaillot, France (now the 16th ''arrondissement'' of Paris). He was styled at birth Henri Louis Auguste Leger Ricard de Montferrand; the aristocratic ''de'' was probably his parents' invention. Decades later, Montferrand admitted in his will that, although his father owned Montferrand estate (his family was from the town of Montferrand), the title is disputable "and if there is any doubt, I can accept other names, first of all Ricard, after my father". Montferrand's father, Benois Ricard, was a horse trainer who died when Montferrand was a child; his grandfather, Leger Ricard, was a bridge engineer. Montferrand's mother, Marie Francoise Louise Fistioni, remarried to Antoine de Commarieux, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moika
The Moyka (, also latinised as Moika) is a short river in Saint Petersburg which splits from the Neva River. Along with the Neva, the Fontanka river, and canals including the Griboyedov and Kryukov, the Moyka encircles the central portion of the city, effectively making that area an island or a group of islands. The river derives its name from the Ingrian word Muya for "slush" or "mire", having its original source in former swamp. It is long and wide. The river flows from the Fontanka river, which is itself a distributary of the Neva, near the Summer Garden past the Field of Mars, crosses Nevsky Prospect and the Kryukov Canal before entering the Neva river. It is also connected with the Neva by the Swan Canal and the Winter Canal. In 1711, Peter the Great ordered the consolidation of the banks of the river. After the Kryukov Canal linked it with the Fontanka River four years later, the river became so much cleaner that its name was changed from Muya to "Moyka", the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postoffice Bridge
Postoffice Bridge (, ''Pochtamtskiy most'') is a pedestrian bridge across Moika River in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It is located near the central Postoffice building, from which it takes the name. The bridge was built in 1823-1824 to designs by architects Wilhelm von Traitteur and Christianovich as a pedestrian bridge suspended by chains. There are only three such bridges left in Saint Petersburg today, the other two being Lions Bridge and Bank Bridge Bank Bridge (Russian: ''Bankovsky most'', ''Банковский мост'') is a long pedestrian bridge crossing the Griboedov Canal near the former Russian Assignation Bank in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Similar to other bridges across the canal .... With the time the construction became unstable, and it was reengineered in 1936 by setting the additional support underneath it, so the chains became merely a decoration. In 1981-1983 the bridge was reconstructed yet again, and restored as a suspended bridge. References St. Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspension Bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck (bridge), deck is hung below suspension wire rope, cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridges, which lack vertical suspenders, have a long history in many mountainous parts of the world. Besides the bridge type most commonly called suspension bridges, covered in this article, there are other types of suspension bridges. The type covered here has cables suspended between towers, with vertical ''suspender cables'' that transfer the Structural load#Live load, imposed loads, transient load, live and Structural load#Dead load, dead loads of the deck below, upon which traffic crosses. This arrangement allows the deck to be level or to arc upward for additional clearance. Like other suspension bridge types, this type often is constructed without the use of falsework. The suspension cables must be anchored at each end of the bridge, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |