|
Charcot Cove
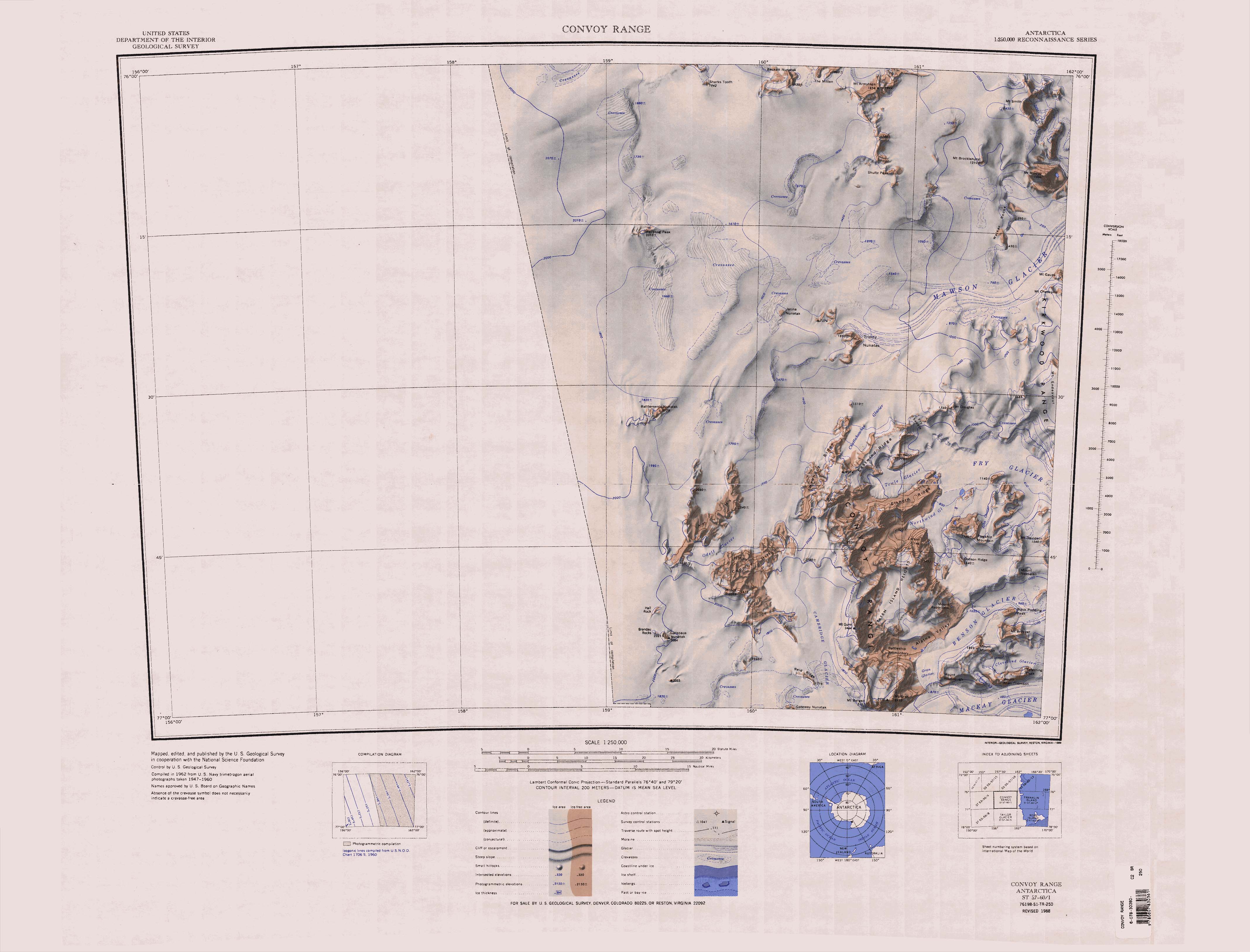
The Mawson Glacier () is a large glacier on the east coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica, descending eastward from the Antarctic Plateau to the north of Trinity Nunatak and the Kirkwood Range, to enter the Ross Sea, where it forms the Nordenskjöld Ice Tongue. The glacier was first mapped by the British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09) and named for Douglas Mawson, the expedition physicist, who later led two other Antarctic expeditions, 1911–14, and 1929–31. Glaciology After the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) there was dynamic retreat of the ice sheet covering the Ross Sea in the Mawson Glacier region. The glacier thinned abruptly between 7,500 and 4,500 years ago, then thinned more gradually until recently. This thinning was very similar to what happened at the Mackay Glacier to the south. Probably the ice sheet retreat and glacial ice drawdown were caused by ocean warming. Course The Mawson Glacier rises on the Antarctic Plateau. Features of the region of its head include B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78th parallel south, 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Victoria of the United Kingdom, Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. History Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 Meteorite, meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in Victoria Land. The meteorites appeared to have undergone little change since they were formed at what scientists believe was the birth of the Solar System. In 1981, Lichen, lichens fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross Sea
The Ross Sea is a deep bay of the Southern Ocean in Antarctica, between Victoria Land and Marie Byrd Land and within the Ross Embayment, and is the southernmost sea on Earth. It derives its name from the British explorer James Clark Ross who visited this area in 1841. To the west of the sea lies Ross Island and Victoria Land, to the east Roosevelt Island and Edward VII Peninsula in Marie Byrd Land, while the southernmost part is covered by the Ross Ice Shelf, and is about from the South Pole. Its boundaries and area have been defined by the New Zealand National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research as having an area of . The circulation of the Ross Sea is dominated by a wind-driven ocean gyre and the flow is strongly influenced by three submarine ridges that run from southwest to northeast. The circumpolar deep water current is a relatively warm, salty and nutrient-rich water mass that flows onto the continental shelf at certain locations. The Ross Sea is covered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Plateau
The Antarctic Plateau, Polar Plateau or King Haakon VII Plateau is a large area of East Antarctica that extends over a diameter of about , and includes the region of the geographic South Pole and the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station. This huge continental plateau is at an average elevation of about . Exploration This plateau was first sighted in 1903 during the '' Discovery'' Expedition to the Antarctic, which was led by Robert Falcon Scott. Ernest Shackleton became the first to cross parts of this plateau in 1909 during his '' Nimrod'' Expedition, which turned back in bad weather when it had reached a point from the South Pole. Shackleton named this plateau the King Edward VII Plateau in honour of the king of the United Kingdom. In December 1911, while returning from the first journey to the South Pole, the Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen decided to name this plateau the King Haakon VII Plateau in honour of the newly elected king of Norway. The Antarctic Plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkwood Range
The Kirkwood Range () is a massive coastal mountain range in Antarctica, extending north–south between Fry Glacier and Mawson Glacier. A broad low-level platform on the seaward side of the range is occupied by the Oates Piedmont Glacier. It is south of the Prince Albert Mountains and northeast of the Convoy Range. Exploration and naming The Kirkwood Range was named by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) for Captain Harry Kirkwood, Royal Navy, captain of the supply ship '' Endeavour'' during this period. Location The Kirkwood Range is just inland from the Oates Piedmont Glacier, which extends along the west coast of the Ross Sea from Mawson Glacier to the north to Fry Glacier to the south. Inland, the Convoy Range lies to the southwest, terminating in Mount Douglas at the head of the Fry Glacier. The Mawson Glacier extends to the northwest, forming near Trinity Nunatak and Jarina Nunatak. On a 1962 map, featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimrod Expedition
The ''Nimrod'' Expedition of 1907–1909, otherwise known as the British Antarctic Expedition, was the first of three expeditions to the Antarctic led by Ernest Shackleton and his second time to the Continent. Its main target, among a range of geographical and scientific objectives, was to be first to reach the South Pole. This was not attained, but the expedition's southern march reached a Farthest South latitude of 88° 23' S, just from the pole. This was by far the longest southern polar journey to that date and a record convergence on either Pole. A separate group led by Welsh Australian geology professor Edgeworth David reached the estimated location of the South magnetic pole, and the expedition also achieved the first ascent of Mount Erebus, Antarctica's second highest volcano. The expedition lacked governmental or institutional support, and relied on private loans and individual contributions. It was beset by financial problems and its preparations were h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Mawson
Sir Douglas Mawson (5 May 1882 – 14 October 1958) was a British-born Australian geologist, Antarctic explorer, and academic. Along with Roald Amundsen, Robert Falcon Scott, and Sir Ernest Shackleton, he was a key expedition leader during the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Mawson was born in England and was brought to Australia as an infant. He completed degrees in mining engineering and geology at the University of Sydney. In 1905 he was made a lecturer in petrology and mineralogy at the University of Adelaide. Mawson's first experience in the Antarctic came as a member of Shackleton's Nimrod Expedition, ''Nimrod'' Expedition (1907–1909), alongside his mentor Edgeworth David. They were part of the expedition's northern party, which became the first to attain the South magnetic pole and to climb Mount Erebus. After his participation in Shackleton's expedition, Mawson became the principal instigator of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (1911–1914). The expedit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackay Glacier
Mackay Glacier () is a large glacier in Victoria Land, descending eastward from the Antarctic Plateau, between the Convoy Range and Clare Range, into the southern part of Granite Harbour. It was discovered by the South magnetic pole party of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09, and named for Alistair Mackay, a member of the party. The glacier's glacier tongue, tongue is called Mackay Glacier Tongue. First mapped by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13 and named for Alistair F. Mackay, a member of the party. Its mouth is south of the Evans Piedmont Glacier and the Mawson Glacier. It is north of the Wilson Piedmont Glacier and the Ferrar Glacier. Course The Mackay Glacier forms on the Antarctic Plateau to the south of Gateway Nunatak and the north of Willett Range. It flows east to the north of Detour Nunatak and Pegtop Mountain, which separate it from Frazier Glacier to the south, which flows past the Clare Range further to the south. It is joined by Frazier Glacier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odell Glacier
The Odell Glacier () is a glacier draining northeast between Allan Hills and Coombs Hills into the upper Mawson Glacier in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) for Noel Odell, who was a mountaineer and was professor of geology at the University of Otago from 1950 to 1955. Location The Odell Glacier forms between the Allan Hills and the Coombs Hills, which contain Mount Brooke. To the southwest of its head are Hall Rock, Brandau Rocks and Carapace Nunatak. The glacier flows northeast past the Convoy Range to the Mawson Glacier. Field camp The United States set up an Antarctic field camp on the glacier during the summer of 2001 at . Tributary Irving Glacier . A glacier that flows northwest between Coombs Hills and Wyandot Ridge to enter Odell Glacier. Named in association with nearby Wyandot Ridge after Captain R.K. Irving, U.S. Navy (USN), commander of USS ''Wyandot'' (AKA-92), a cargo ship in the Ross Sea Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan Hills
The Allan Hills () are a group of hills, mainly ice free and about long, lying just north-west of the Coombs Hills near the heads of Mawson Glacier and Mackay Glacier in the Oates Land and Victoria Land regions of Antarctica. Exploration and naming The Allan Hills were mapped by the New Zealand party (1957–58) of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition and named for Professor Robin Allan, R. S. Allan of the University of Canterbury, New Zealand. Allan Hills is referred to as the ''Allan Nunatak'', and mapped north of Carapace Nunatak, in the memoirs of the Scott Base Leader Adrian Hayter. Both names are in the USGS listing. Location Allan Hills lie to the north of Odell Glacier, facing Coombs Hills to the south of the glacier. They are west of the Convoy Range, south of Battlements Nunatak and east of the Antarctic Plateau. Allan Hills are in the shape of the letter "Y", with the open end pointing roughly northwards, and encompassing the Shimmering Icefield. The southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fry Glacier
Fry Glacier () is a glacier draining the slopes at the northeast corner of the Convoy Range and flowing along the south end of the Kirkwood Range into Tripp Bay, Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was first charted by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09, and named for A.M. Fry, a contributor to the expedition. Location Fry Glacier rises to the west of the north end of the Convoy Range, south of the Kirkwood Range. At its head Fry Saddle drops down from the mouth of the Chattahoochee Glacier, between Mount Naab and Mount Douglas. The Towle Glacier joins the Fry Glacier from the west, to the north of Elkhorn Ridge. The Northwind Glacier and Atka Glacier join the head of Fry Glacier from the south. Fry Glacier flows past Shoulder Mountain to the north to enter Tripp Bay on the Ross Sea. Albrecht Penck Glacier converges with Fry Glacier in Tripp Bay. Features Tributaries and features of the terrain the glacier flows through include: Fry Saddle . Narrow ice saddle at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |