|
Chanute Peak
Chanute Peak () is a peak in Korten Ridge on the east side of Lanchester Bay, south of Wennersgaard Point, Davis Coast in Graham Land. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Octave Chanute Octave Chanute (February 18, 1832 – November 23, 1910) was a French-American civil engineer and aviation pioneer. He provided many budding enthusiasts, including the Wright brothers, with help and advice, and helped to publicize their flying ..., an American designer of gliders who first introduced moveable planes for the purpose of control and stability in 1896–97. Map Trinity Peninsula.Scale 1:250000 topographic map No. 5697. Institut für Angewandte Geodäsie and British Antarctic Survey, 1996. References SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer Mountains of Graham Land Davis Coast {{DavisCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summit (topography)
A summit is a point on a surface that is higher in elevation than all points immediately adjacent to it. The topographic terms acme, apex, peak (mountain peak), and zenith are synonymous. The term (mountain top) is generally used only for a mountain peak that is located at some distance from the nearest point of higher elevation. For example, a big, massive rock next to the main summit of a mountain is not considered a summit. Summits near a higher peak, with some prominence or isolation, but not reaching a certain cutoff value for the quantities, are often considered ''subsummits'' (or ''subpeaks'') of the higher peak, and are considered part of the same mountain. A pyramidal peak is an exaggerated form produced by ice erosion of a mountain top. Summit may also refer to the highest point along a line, trail, or route. The highest summit in the world is Mount Everest with a height of above sea level. The first official ascent was made by Tenzing Norgay and Sir Edmund Hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korten Ridge
Korten Ridge ( bg, Кортенски хребет, ‘Kortenski Hrebet’ \'kor-ten-ski 'hre-bet\) is the ridge extending 18 km in south–north direction and 9 km wide, rising to 1864 mReference Elevation Model of Antarctica. Polar Geospatial Center. University of Minnesota, 2019 () on in Graham Land, Antarctica. It is bounded by |
Lanchester Bay
Lanchester Bay () is a bay wide lying east of Havilland Point, along the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. Its head is fed by Temple Glacier and Kasabova Glacier. The bay was photographed by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd in 1955–57 and mapped from these photos by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 for Frederick W. Lanchester, an aeronautical engineer who laid the foundations of modern airfoil An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or tur ... theory. References Bays of Graham Land Davis Coast {{DavisCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wennersgaard Point
Wennersgaard Point () is a point forming the northwest extremity of Svilengrad Peninsula on Davis Coast, the west coast of Graham Land in Antarctica. It is situated on both the east side of the entrance to Lanchester Bay and its sub-embayment Hvoyna Cove Hvoyna Cove ( bg, залив Хвойна, ‘Zaliv Hvoyna’ \'za-liv 'hvoy-na\) is the 1.7 km wide cove indenting for 1 km Davis Coast in Graham Land, Antarctica. It is part of Jordanoff Bay entered east of Wennersgaard Point and west ..., and the southwest side of the entrance to Jordanoff Bay . First charted by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition in Nov.-Dec. 1902 and named after Ole C. Wennersgaard, a seaman of the expedition who died while wintering on Paulet Island in 1903. Headlands of Graham Land Davis Coast {{DavisCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davis Coast
Davis Coast () is that portion of the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula between Cape Kjellman and Cape Sterneck. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Captain John Davis, the American sealer who claimed to have made the first recorded landing on the continent of Antarctica at Hughes Bay Hughes Bay is a bay lying between Cape Sterneck and Cape Murray along the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is wide and lies south of Chavdar Peninsula and north of Pefaur (Ventimiglia) Peninsula, indenting the Danco Coast on the west ... on this coast in the ''Cecilia'', February 7, 1821. Further reading * Ute Christina Herzfeld, Atlas of Antarctica: Topographic Maps from Geostatistical Analysis of Satellite Radar Altimeter Data', P 115 References * Coasts of Graham Land {{DavisCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graham Land
Graham Land is the portion of the Antarctic Peninsula that lies north of a line joining Cape Jeremy and Cape Agassiz. This description of Graham Land is consistent with the 1964 agreement between the British Antarctic Place-names Committee and the US Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names, in which the name "Antarctic Peninsula" was approved for the major peninsula of Antarctica, and the names Graham Land and Palmer Land for the northern and southern portions, respectively. The line dividing them is roughly 69 degrees south. Graham Land is named after Sir James R. G. Graham, First Lord of the Admiralty at the time of John Biscoe's exploration of the west side of Graham Land in 1832. It is claimed by Argentina (as part of Argentine Antarctica), Britain (as part of the British Antarctic Territory) and Chile (as part of the Chilean Antarctic Territory). Graham Land is the closest part of Antarctica to South America. Thus it is the usual destination for small ships taking pay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee
The UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee (or UK-APC) is a United Kingdom government committee, part of the Foreign and Commonwealth Office, responsible for recommending names of geographical locations within the British Antarctic Territory (BAT) and the South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI). Such names are formally approved by the Commissioners of the BAT and SGSSI respectively, and published in the BAT Gazetteer and the SGSSI Gazetteer maintained by the Committee. The BAT names are also published in the international Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica maintained by SCAR. The Committee may also consider proposals for new place names for geographical features in areas of Antarctica outside BAT and SGSSI, which are referred to other Antarctic place-naming authorities, or decided by the Committee itself if situated in the unclaimed sector of Antarctica. Names attributed by the committee * Anvil Crag, named for descriptive features *Anckorn Nunataks, named after J. F. Anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
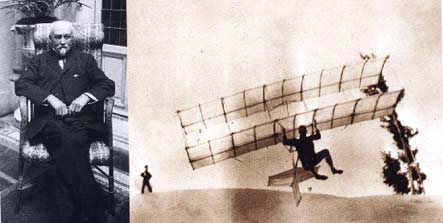
Octave Chanute
Octave Chanute (February 18, 1832 – November 23, 1910) was a French-American civil engineer and aviation pioneer. He provided many budding enthusiasts, including the Wright brothers, with help and advice, and helped to publicize their flying experiments. At his death he was hailed as the father of aviation and the initial concepts of the heavier-than-air flying machine. Biography Born in Paris, Chanute was the son of Elise and Joseph Chanut, professor at the Collège de France. He emigrated with his father to the United States of America in 1838, when the former was named Vice-President at Jefferson College in Louisiana. Octave attended private schools in New York. Civil engineer (railroads) Octave Chanute began his training as a budding civil engineer in 1848. He was widely considered brilliant and innovative in the engineering profession. During his career he designed and constructed the United States two biggest stockyards, Chicago Stock Yards (1865) and Kansas City ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Graham Land
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |