|
Cetraria Peruviana
''Cetraria peruviana'' is a rare species of fruticose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It is known from a single collection in a high-elevation locale in Cusco, Peru. Taxonomy ''Cetraria peruviana'' was first described by the lichenologists Ingvar Kärnefelt and Arne Thell in 1993. The holotype specimen was collected in Peru's Department of Cusco at an elevation of and is housed in the Farlow Herbarium (FH). The species was originally given the unpublished name "Platysma peruvianum" by George Knox Merrill. Morphologically, ''C. peruviana'' shares some characteristics with '' C. kamczatica'', though it has more curved and shorter lobes. It also bears some resemblance to '' C. nepalensis'', but can be distinguished by its less distinctly canaliculate and almost subtubular lobes. The species' placement within the genus ''Cetraria'' is supported by its anatomical and chemical features, though mature reproductive structures (ascomata and conidiomata) were not ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingvar Kärnefelt
Jan Eric Ingvar Kärnefelt (born 1944) is a Swedish lichenologist. Early life and education Kärnefelt was born in Gothenburg, Sweden in 1944. His initial goal in his higher-level studies at University of Cologne in 1966–1967 was to become a dentist. He changed courses in 1968, turning instead to biology at the University of Gothenburg in 1968. Gunnar Degelius, his first teacher during undergraduate studies in botany in 1968, inspired him and others. After Degelius' retirement in 1969, Ingvar continued his studies at Lund University, where Hans Runemark held a position in systematic botany. In 1971 he met Ove Almborn, who became his supervisor. In 1979, he defended his thesis titled "The brown fruticose species of ''Cetraria''". The thesis was later awarded a prize for the best doctoral dissertation in botany at Lund University during a 5-year period by the Royal Physiographic Society in Lund. Career Kärnefelt became associate professor at the Department of Systematic Botany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trebouxia
''Trebouxia'' is a unicellular green alga. It is a photosynthetic organism that can exist in almost all habitats found in polar, tropical, and temperate regions.Erokhina, L. G., Shatilovich, A. V., Kaminskaya, O. P., & Gilichinskii, D. A. (2004). Spectral Properties of the Green Alga ''Trebouxia'', a Phycobiont of Cryptoendolithic Lichens in the Antarctic Dry Valley. Microbiology,73(4), 420-424. doi:10.1023/b:mici.0000036987.18559Lukesova, A., & Frouz, J. (2007). Soil and Freshwater Micro-Algae as a Food Source for Invertebrates in Extreme Environments. Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology Algae and Cyanobacteria in Extreme Environments,265-284. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6112-7_14Seckbach, J. (2007). Algae and cyanobacteria in extreme environments. Dordrecht: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6112-7Seckbach, J. (2002). Symbiosis: Mechanisms and model systems. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic.John, D. M., Whitton, B. A., & Brook, A. J. (2002). The freshwater algal f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Ingvar Kärnefelt
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion, especially in the context of rank-based (" Linnaean") nomenclature (much less so under phylogenetic nomenclature). If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were presumably set forth in prehistoric times by hunter-gatherers, as suggested by the fairly sophisticated folk taxonomies. Much later, Aristotle, and later still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens Of Peru
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. . Lichens are the lifeform that first brought the term symbiosis (as ''Symbiotismus'') into biological context. Lichens have since been recognized as important actors in and producers which many higher trophic feeders feed on, such as reindeer, gastropods, nematodes, mites, and springtails. Lich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichens Described In 1993
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. . Lichens are the lifeform that first brought the term symbiosis (as ''Symbiotismus'') into biological context. Lichens have since been recognized as important actors in nutrient cycling and producers which many higher trophic feeders feed on, such as reindeer, gastropods, nematodes, mites, and springtails. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pycnidia
A pycnidium (plural pycnidia) is an asexual fruiting body produced by mitosporic fungi, for instance in the order Sphaeropsidales ( Deuteromycota, Coelomycetes) or order Pleosporales (Ascomycota, Dothideomycetes). It is often spherical or inversely pearshaped ( obpyriform) and its internal cavity is lined with conidiophore A conidium ( ; : conidia), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (: chlamydoconidia), is an Asexual reproduction, asexual, non-motility, motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word f ...s. When ripe, an opening generally appears at the top, through which the pycnidiospores escape. References {{reflist Further reading *Kulik, Martin M. "Symptomless infection, persistence, and production of pycnidia in host and non-host plants by Phomopsis batatae, Phomopsis phaseoli, and Phomopsis sojae, and the taxonomic implications." Mycologia(1984): 274–291. *Calpouzos, L., and D. B. Lapis. "Effects of l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apothecia
An ascocarp, or ascoma (: ascomata), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protolichesterinic Acid
Protolichesterinic acid is a naturally occurring γ-lactone compound found in various lichen species. Its structure consists of a combination of a lactone ring with a carboxylic acid group and a long aliphatic side chain. First isolated in the early 20th century, protolichesterinic acid has drawn scientific interest due to its diverse biological activities, including antimicrobial, antifungal, and anti-inflammatory properties. It is also noted for its potential as a therapeutic agent, particularly as a selective inhibitor of the 5-lipoxygenase enzyme, which is implicated in inflammatory diseases. Protolichesterinic acid is typically extracted from lichens such as ''Cetraria islandica'' using advanced chromatographic techniques and has been studied for its role in both natural product chemistry and pharmacology. History The study of lichen acids related to protolichesterinic acid began in 1845, when Schnedermann and Wilhelm Knop isolated lichesterinic acid from ''Cetraria is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spot Test (lichen)
A spot test in lichenology is a spot analysis used to help identify lichens. It is performed by placing a drop of a chemical reagent on different parts of the lichen and noting the colour change (or lack thereof) associated with application of the chemical. The tests are routinely encountered in dichotomous keys for lichen species, and they take advantage of the wide array of lichen products (secondary metabolites) produced by lichens and their uniqueness among taxa. As such, spot tests reveal the presence or absence of chemicals in various parts of a lichen. They were first proposed as a method to help identify species by the Finnish lichenologist William Nylander in 1866. Three common spot tests use either 10% aqueous KOH solution (K test), saturated aqueous solution of bleaching powder or calcium hypochlorite (C test), or 5% alcoholic ''p''-phenylenediamine solution (P test). The colour changes occur due to presence of particular secondary metabolites in the lichen. In ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
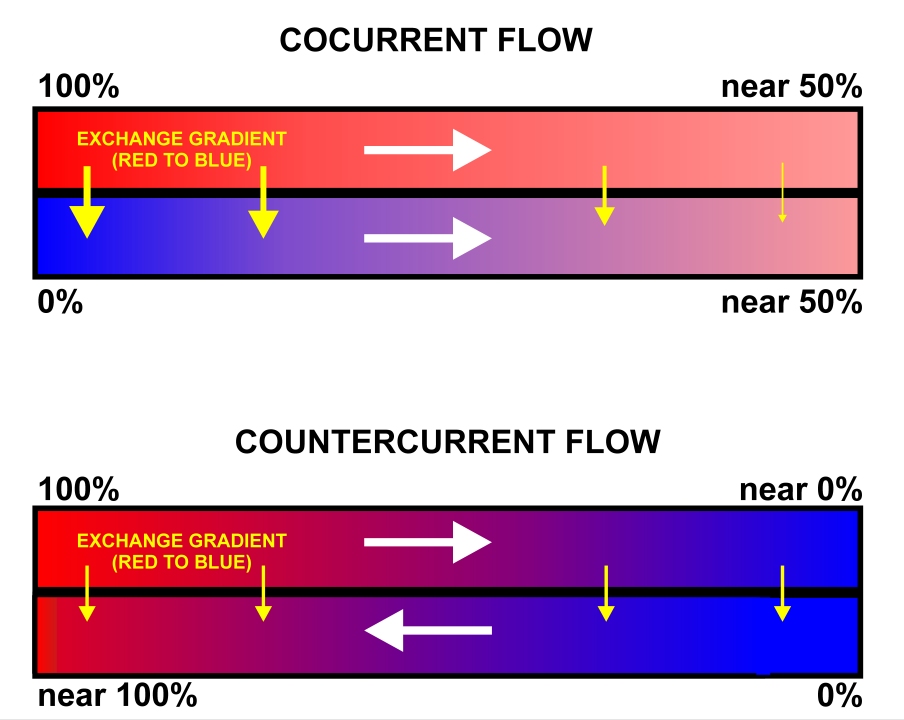
Gas Exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a biological membrane that forms the boundary between an organism and its extracellular environment. Gases are constantly consumed and produced by cellular and metabolic reactions in most living things, so an efficient system for gas exchange between, ultimately, the interior of the cell(s) and the external environment is required. Small, particularly unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and protozoa, have a high surface-area to volume ratio. In these creatures the gas exchange membrane is typically the cell membrane. Some small multicellular organisms, such as flatworms, are also able to perform sufficient gas exchange across the skin or cuticle that surrounds their bodies. However, in most larger organisms, which have small surface-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |