|
Cerebral Peduncle
The cerebral peduncles (In Latin, ''ped-'' means 'foot'.) are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending (sensory) and descending (motor) tracts that run to and from the cerebrum from the pons. Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cerebral cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum. The region includes the tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum. By this definition, the cerebral peduncles are also known as the basis pedunculi, while the large ventral bundle of efferent fibers is referred to as the cerebral crus (''crus'' means ‘leg’ in Latin.) or the pes pedunculi (''pes'' means 'foot' in Latin.). The cerebral peduncles are located on either side of the midbrain and are the frontmost part of the midbrain, and act as the connectors between the rest of the midbrain and the thalamic nuclei and thus the cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
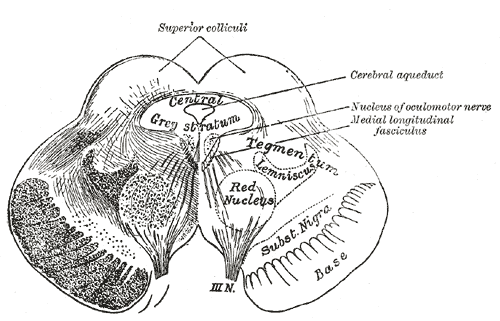
Superior Colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the tectum, roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the Homology (biology), homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectum, tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar in all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers (retinal nerve fiber layer, stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprioceptive
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinesthetic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other sensory systems, such as the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb movement and velocity (muscle length and the rate of change) are encoded by one group of se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience Information Framework
The Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/ genomic resources and provides many authoritative links throughout the neuroscience portal of Wikipedia. Description The Neuroscience Information Framework (NIF) is an initiative of the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research, which was established in 2004 by the National Institutes of Health. Development of the NIF started in 2008, when the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine obtained an NIH contract to create and maintain "a dynamic inventory of web-based neurosciences data, resources, and tools that scientists and students can access via any computer connected to the Internet". The project is headed by Maryann Martone, co-director of the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR), part of the multi-disciplinary Center for Research in Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Nerve
A motor nerve, or efferent nerve, is a nerve that contains exclusively efferent nerve fibers and transmits motor signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to the effector organs (muscles and glands), as opposed to sensory nerves, which transfer signals from sensory receptors in the periphery to the CNS. This is different from the motor neuron, which includes a cell body and branching of dendrites, while the nerve is made up of a bundle of axons. In the strict sense, a "motor nerve" can refer exclusively to the connection to muscles, excluding other organs. The vast majority of nerves contain both sensory and motor fibers and are therefore called mixed nerves. Structure and function Motor nerve fibers Transduction (physiology), transduce signals from the CNS to peripheral neurons of proximal muscle tissue. Motor nerve axon terminals innervate Skeletal muscle, skeletal and Smooth muscle tissue, smooth muscle, as they are heavily involved in muscle control. Motor nerves tend t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Neuron
A motor neuron (or motoneuron), also known as efferent neuron is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. There are two types of motor neuron – upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons. Axons from upper motor neurons synapse onto interneurons in the spinal cord and occasionally directly onto lower motor neurons. The axons from the lower motor neurons are efferent nerve fibers that carry signals from the spinal cord to the effectors. Types of lower motor neurons are alpha motor neurons, beta motor neurons, and gamma motor neurons. A single motor neuron may innervate many muscle fibres and a muscle fibre can undergo many action potentials in the time taken for a single muscle twitch. Innervation takes place at a neuromuscular junction and twitches can become superimpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Efferent Nerve Fiber
Efferent nerve fibers are axons (nerve fibers) of efferent neurons that exit a particular region. These terms have a slightly different meaning in the context of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS). The efferent fiber is a long process projecting far from the neuron's body that carries nerve impulses away from the central nervous system toward the peripheral effector organs (muscles and glands). A bundle of these fibers constitute an efferent nerve. The opposite direction of neural activity is afferent conduction, which carries impulses by way of the afferent nerve fibers of sensory neurons. In the nervous system, there is a "closed loop" system of sensation, decision, and reactions. This process is carried out through the activity of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. In the CNS, afferent and efferent projections can be from the perspective of any given brain region. That is, each brain region has its own unique set of affe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regions In The Human Brain
The human brain anatomical regions are ordered following standard neuroanatomy hierarchies. Functional, connective, and developmental regions are listed in parentheses where appropriate. Hindbrain (rhombencephalon) Myelencephalon * Medulla oblongata ** Medullary pyramids ** Arcuate nucleus ** Olivary body *** Inferior olivary nucleus ** Rostral ventrolateral medulla ** Caudal ventrolateral medulla ** Solitary nucleus (Nucleus of the solitary tract) **Respiratory center- Respiratory groups *** Dorsal respiratory group *** Ventral respiratory group or Apneustic centre **** Pre-Bötzinger complex **** Botzinger complex **** Retrotrapezoid nucleus **** Nucleus retrofacialis **** Nucleus retroambiguus **** Nucleus para-ambiguus ** Paramedian reticular nucleus ** Gigantocellular reticular nucleus ** Parafacial zone ** Cuneate nucleus ** Gracile nucleus ** Perihypoglossal nuclei *** Intercalated nucleus *** Prepositus nucleus *** Sublingual nucleus ** Area postrema **Medul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochlear Nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates a single muscle - the superior oblique muscle of the eye (which operates through the pulley-like trochlea). Unlike most other cranial nerves, the trochlear nerve is exclusively a motor nerve ( somatic efferent nerve). The trochlear nerve is unique among the cranial nerves in several respects: * It is the ''smallest'' nerve in terms of the number of axons it contains. * It has the greatest intracranial length. * It is the only cranial nerve that exits from the dorsal (rear) aspect of the brainstem. * It innervates a muscle, the superior oblique muscle, on the opposite side (contralateral) from its nucleus. The trochlear nerve decussates within the brainstem before emerging on the contralateral side of the brainstem (at the level of the inferior colliculus). An injury to the trochlear nucleus in the brainstem will result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpeduncular Fossa
The interpeduncular fossa is a deep depression of the ventral surface of the midbrain between the two cerebral crus, cerebal crura. It has been found in humans and macaques, but not in rats or mice, showing that this is a relatively new evolutionary region. Structure The interpeduncular fossa is a somewhat rhomboid-shaped area of the base of the brain. Features The lateral wall of the interpeduncular fossa bears a groove - the oculomotor sulcus - from which rootlets of the oculomotor nerve emerge from the substance of the brainstem and aggregate into a single fascicle. Anatomical relations The ventral tegmental area lies at the depth of the interpeduncular fossa. Boundaries The interpeduncular fossa is in front by the optic chiasma, behind by the antero-superior surface of the pons, antero-laterally by the converging optic tracts, and postero-laterally by the diverging cerebral peduncles. The floor of interpeduncular fossa, from behind forward, are the posterior perfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Capsule
The internal capsule is a paired white matter structure, as a two-way nerve tract, tract, carrying afferent nerve fiber, ascending and efferent nerve fiber, descending axon, fibers, to and from the cerebral cortex. The internal capsule is situated in the Anatomical terms of location#Medial and lateral, inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the subcortical basal ganglia. As it courses it separates the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways. The internal capsule is V-shaped in transection forming an anterior and posterior limb, with the angle between them called the genu. The corticospinal tract constitutes a large part of the internal capsule, carrying motor information from the primary motor cortex to the lower motor neurons in the spinal cord. Above the basal gangli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position. Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of proprioceptors, which detect distinct kinesthetic parameters, such as joint position, movement, and load. Although all mobile animals possess proprioceptors, the structure of the sensory organs can vary across species. Proprioceptive signals are transmitted to the central nervous system, where they are integrated with information from other Sensory nervous system, sensory systems, such as Visual perception, the visual system and the vestibular system, to create an overall representation of body position, movement, and acceleration. In many animals, sensory feedback from proprioceptors is essential for stabilizing body posture and coordinating body movement. System overview In vertebrates, limb movement and velocity (muscle length and the rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticobulbar Tract
The corticobulbar (or corticonuclear) tract is a two-neuron white matter motor pathway connecting the motor cortex in the cerebral cortex to the Medullary pyramids (brainstem), medullary pyramids, which are part of the brainstem's medulla oblongata (also called "bulbar") region, and are primarily involved in carrying the motor function of the non-oculomotor cranial nerves, like muscles of the face, head and neck. The corticobulbar tract is one of the pyramidal tracts, the other being the corticospinal tract. Structure The corticobulbar tract originates in the primary motor cortex of the frontal lobe, just superior to the lateral fissure and Anatomical terms of location#Rostral,cranial, and caudal, rostral to the central sulcus in the precentral gyrus (Brodmann area 4). The corticobulbar tract however also includes fibres from disparate regions from across the cerebral cortex (not limited to the frontal lobes). The tract descends through the corona radiata and then the Genu of int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |