|
Cerebellar Cognitive Affective Syndrome
Cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome (CCAS), also called Schmahmann's syndrome is a condition that follows from lesions (damage) to the cerebellum of the brain. It refers to a constellation of deficits in the cognitive domains of executive function, spatial cognition, language, and affect resulting from damage to the cerebellum. Impairments of executive function include problems with planning, set-shifting, abstract reasoning, verbal fluency, and working memory, and there is often perseveration, distractibility and inattention. Language problems include dysprosodia, agrammatism and mild anomia. Deficits in spatial cognition produce visual–spatial disorganization and impaired visual–spatial memory. Personality changes manifest as blunting of affect or disinhibited and inappropriate behavior. These cognitive impairments result in an overall lowering of intellectual function. CCAS challenges the traditional view of the cerebellum being responsible solely for regulation of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
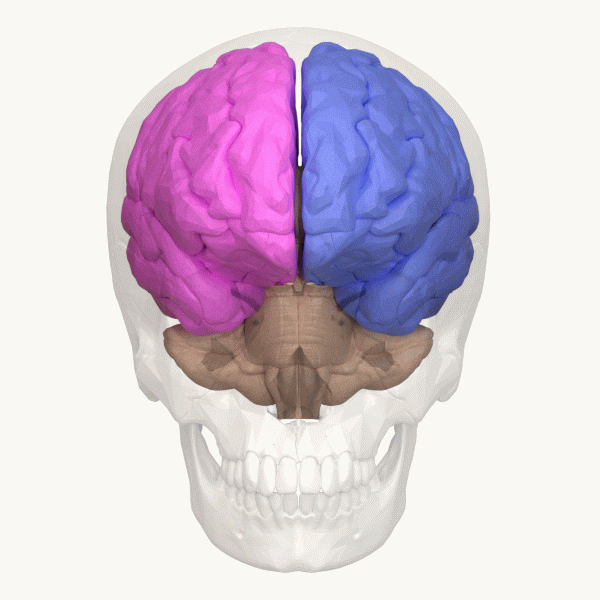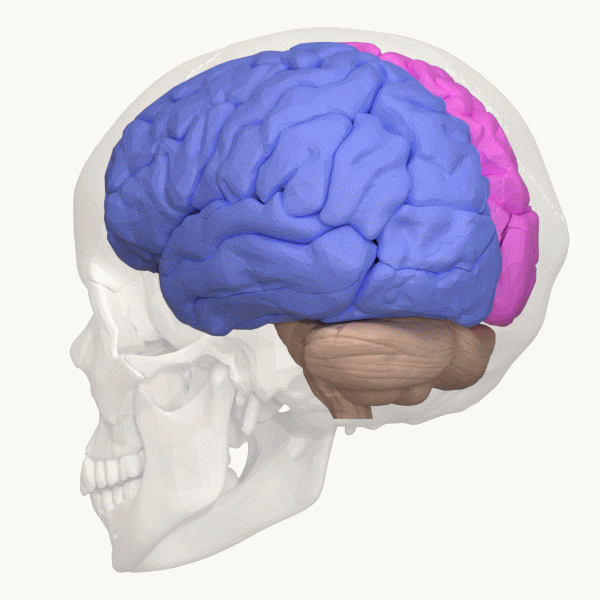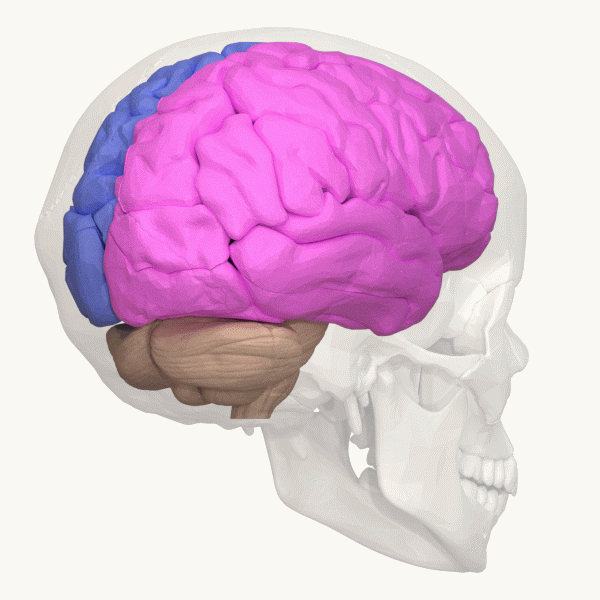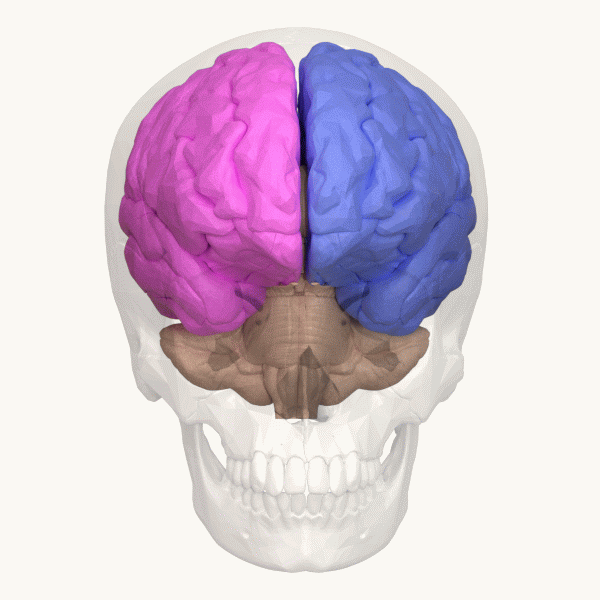
Cerebellum
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or even larger. In humans, the cerebellum plays an important role in motor control and cognition, cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as emotion, emotional control such as regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established. The human cerebellum does not initiate movement, but contributes to motor coordination, coordination, precision, and accurate timing: it receives input from sensory systems of the spinal cord and from other parts of the brain, and integrates these inputs to fine-tune motor activity. Cerebellar damage produces disorders in fine motor skill, fine movement, sense of balance, equilibrium, list of human positions, posture, and motor learning in humans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in some cases months. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called ''mania''; if it is less severe and does not significantly affect functioning, it is called ''hypomania''. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy, or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually, but not always, a Sleep deprivation, reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying, have a negative outlook on life, and demonstrate poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high. Over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, with about one-third Suicide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive neurostimulation technique in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current in a targeted area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. A device called a stimulator generates electric pulses that are delivered to a magnetic coil placed against the scalp. The resulting magnetic field penetrates the skull and induces a secondary electric current in the underlying brain tissue, modulating neural activity. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a safe, effective, and FDA-approved treatment for major depressive disorder (approved in 2008), chronic pain (2013), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (2018). It has strong evidence for certain neurological and psychiatric conditions—especially depression (with a large effect size), neuropathic pain, and stroke recovery—and emerging advancements like iTBS and image-guided targeting may improve its efficacy and efficiency. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that aims to reduce symptoms of various mental health conditions, primarily depression, PTSD, and anxiety disorders. Cognitive behavioral therapy focuses on challenging and changing cognitive distortions (thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes) and their associated behaviors in order to improve emotional regulation and help the individual develop coping strategies to address problems. Though originally designed as an approach to treat depression, CBT is often prescribed for the evidence-informed treatment of many mental health and other conditions, including anxiety, substance use disorders, marital problems, ADHD, and eating disorders. CBT includes a number of cognitive or behavioral psychotherapies that treat defined psychopathologies using evidence-based techniques and strategies. CBT is a common form of talk therapy based on the combination of the basic principles from behavioral and cognitive psychology. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateralization Of Brain Function
The lateralization of brain function (or hemispheric dominance/ lateralization) is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Both hemispheres exhibit Brain asymmetry, brain asymmetries in both structure and neuronal network composition associated with specialized function. Lateralization of brain structures has been studied using both healthy and split-brain patients. However, there are numerous counterexamples to each generalization and each human's brain develops differently, leading to unique lateralization in individuals. This is different from specialization, as lateralization refers only to the function of one structure divided between two hemispheres. Specialization is much easier to observe as a trend, since it has a stronger Anthropology, anthropological history. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Galbraith Heath
Robert Galbraith Heath (May 9, 1915 – September 21, 1999) was an American psychiatrist. He followed the theory of biological psychiatry, which holds that organic defects are the sole source of mental illness, and that consequently mental problems are treatable by physical means. He published 425 papers and three books. One of his first papers is dated 1946. He was profiled as a "famous American psychiatrist" in 1983 by '' Psychiatric Annals''. Heath founded the Department of Psychiatry and Neurology at Tulane University, New Orleans, in 1949 and remained its chairman until 1980. He performed many experiments there involving electrical stimulation of the brain via surgically implanted electrodes. He placed deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrodes into the brains of more than 54 patients. Indeed, he has been cited as the first, or one of the first, researcher(s) to have placed electrodes deep into the brains of living human patients. It has been suggested that this work was financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mossy Fiber (cerebellum)
Mossy fibers are one of the major inputs to cerebellum. There are many sources of this pathway, the largest of which is the cerebral cortex, which sends input to the cerebellum via the pontocerebellar pathway. Other contributors include the vestibular nerve and nuclei, the spinal cord, the reticular formation, and feedback from deep cerebellar nuclei. Axons enter the cerebellum via the middle and inferior cerebellar peduncles, where some branch to make contact with deep cerebellar nuclei. They ascend into the white matter of the cerebellum, where each axon branches to innervate granule cells in several cerebellar folia. In this case, the pathway is so named for a unique synapse formed by its projections, the ''mossy fiber rosette''. Fine branches of the mossy fiber axons twist through the granule cell layer, and slight enlargements giving a knotted appearance indicate synaptic contacts. These contacts have the appearance of a classic Gray's type 1 synapse, indicating they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysmetria
Dysmetria () is a lack of coordination of movement typified by the undershoot or overshoot of intended position with the hand, arm, leg, or eye. It is a type of ataxia. It can also include an inability to judge distance or scale. Hypermetria and hypometria are, respectively, overshooting and undershooting the intended position. Presentation Associated diseases Dysmetria is often found in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and persons who have had tumors or strokes. Persons who have been diagnosed with autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxia (SCAs) also exhibit dysmetria. There are many types of SCAs and though many exhibit similar symptoms (one being dysmetria), they are considered to be heterogeneous. Friedreich's ataxia is a relatively common cause of dysmetria. Cerebellar malformations extending to the brainstem can also present with dysmetria. Causes The actual cause of dysmetria is thought to be caused by lesions in the cerebe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple System Atrophy
Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by tremors, slow movement, muscle rigidity, postural instability (collectively known as parkinsonism), autonomic dysfunction and ataxia. This is caused by progressive degeneration of neurons in several parts of the brain including the basal ganglia, inferior olivary nucleus, and cerebellum. MSA was first described in 1960 by Milton Shy and Glen Drager and was then known as Shy–Drager syndrome. Many people affected by MSA experience dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which commonly manifests as orthostatic hypotension, impotence, loss of sweating, dry mouth and urinary retention and incontinence. Palsy of the vocal cords is an important and sometimes initial clinical manifestation of the disorder. A prion of the alpha-synuclein protein within affected neurons may cause MSA. About 55% of MSA cases occur in men, with those affected first showing symptoms at the age of 50–60 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a late-onset neurodegenerative disease involving the gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain, linked to 4-repeat tau pathology. The condition leads to symptoms including Balance disorder, loss of balance, Hypokinesia, slowing of movement, Ophthalmoparesis, difficulty moving the eyes, and cognitive impairment. PSP may be mistaken for other types of neurodegeneration such as Parkinson's disease, frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease. It is the second most common tauopathy behind Alzheimer's disease. The cause of the condition is uncertain, but involves the accumulation of tau protein within the brain. Medications such as L-DOPA, levodopa and amantadine may be useful in some cases. PSP was first officially described by Richardson, Steele, and Olszewski in 1963 as a form of progressive parkinsonism. However, the earliest known case presenting clinical features consistent with PSP, along with pathological co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body, such as: * Fluorodeoxyglucose ( 18F">sup>18FDG or FDG) is commonly used to detect cancer; * 18Fodium fluoride">sup>18Fodium fluoride (Na18F) is widely used for detecting bone formation; * Oxygen-15 (15O) is sometimes used to measure blood flow. PET is a common imaging technique, a medical scintillography technique used in nuclear medicine. A radiopharmaceutical—a radioisotope attached to a drug—is injected into the body as a tracer. When the radiopharmaceutical undergoes beta plus decay, a positron is emitted, and when the positron interacts with an ordinary electron, the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragile X Syndrome
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic neurodevelopmental disorder. The average IQ in males with FXS is under 55, while affected females tend to be in the borderline to normal range, typically around 70–85. Physical features may include a long and narrow face, large ears, flexible fingers, and large testicles. About a third of those affected have features of autism such as problems with social interactions and delayed speech. Hyperactivity is common, and seizures occur in about 10%. Males are usually more affected than females. This disorder and finding of fragile X syndrome has an X-linked dominant inheritance. It is typically caused by an expansion of the CGG triplet repeat within the '' FMR1'' (fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1) gene on the X chromosome. This results in silencing ( methylation) of this part of the gene and a deficiency of the resultant protein (FMRP), which is required for the normal development of connections between neurons. Diagnosis req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |