|
Centurione I Zaccaria
Centurione I Zaccaria was one of the most powerful nobles of the Principality of Achaea in the 14th century. He was the firstborn son of Martino Zaccaria and Jacqueline de la Roche, last representant of the prestigious Burgundian house of the Duchy of Athens. In 1334 Centurione succeeded his brother, Bartolomeo Zaccaria as baron of Damala. After the death of Martino he rose as lord of one half of the Barony of Chalandritsa, and in 1359 he acquired the other half. In about 1370 he was named Grand Constable of Achaea and received also the Barony of Estamira. He also thrice held the post of ''bailli'' (viceroy) for the principality's Angevin rulers. Lord of Damala and prominence in Latin Morea On 1329 Martino Zaccaria, father of Centurione was imprisoned by Andronikos III Palaiologos and he was expelled from the administration of the island of Chios, however during his imprisonment and later it was Centurione that governed the Zaccaria estates in Morea. He was so successful in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barony Of Veligosti
The Barony of Veligosti or Veligosti–Damala was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, originally centred on Veligosti (; ; ; ) in southern Arcadia, but also came to include the area of Damala (, ) in the Argolid when it came under a cadet branch of the de la Roche family in the 1250s. After Veligosti was lost to the Byzantines towards 1300, the name was retained even though the barony was reduced to Damala. History Veligosti, near ancient Megalopolis, appears to have fallen to the Frankish Crusaders without resistance . The name's origin is obscure. The 19th-century historian Karl Hopf thought that the Greek name derived from the French form Véligourt, in turn possibly a corruption of Valaincourt/Walincourt, which Hopf proposed as the place of origin of the original baronial line of Mons. The Valaincourt family was indeed represented in the Fourth Crusade, but as the French medievalist Antoine Bon pointed out, there is nothing other than the simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capetian House Of Anjou
The Capetian House of Anjou, or House of Anjou-Sicily, or House of Anjou-Naples was a royal house and cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. It is one of three separate royal houses referred to as ''Angevin'', meaning "from Anjou" in France. Founded by Charles I of Anjou, the youngest son of Louis VIII of France, the Capetian king first ruled the Kingdom of Sicily during the 13th century. The War of the Sicilian Vespers later forced him out of the island of Sicily, leaving him with the southern half of the Italian Peninsula, known as the Kingdom of Naples. The house and its various branches would go on to influence much of the history of Southern and Central Europe during the Middle Ages until it became extinct in 1435. Historically, the house ruled the Counties of Anjou, Maine, Touraine, Provence and Forcalquier; the Principalities of Achaea and Taranto; and the Kingdoms of Sicily, Naples, Hungary, Croatia, Albania and Poland. Rise of Charles I and his sons A younge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
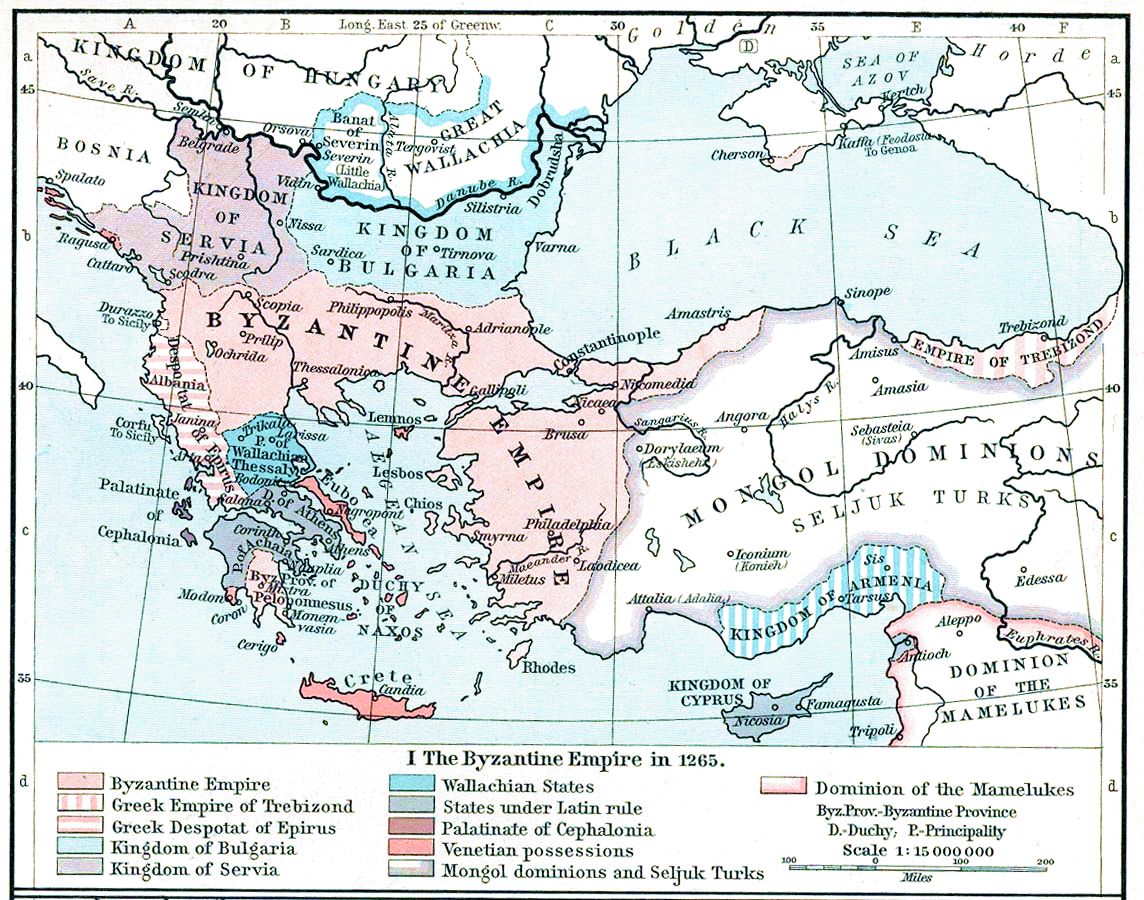
Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of the Palaiologos, Palaiologan dynasty that would rule the Byzantine Empire until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. He Reconquest of Constantinople, recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire in 1261 and transformed the Empire of Nicaea into a Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty, restored Byzantine Empire. His reign saw considerable recovery of Byzantine power, including the enlargement of the Byzantine army and Byzantine navy, navy. It also included the reconstruction of the city of Constantinople, and the increase of its population. His re-establishment of the University of Constantinople contributed to the Palaeologan Renaissance, a cultural flowering between the 13th and 15th centuries. It was also at this time that the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos II Palaiologos
Andronikos II Palaiologos (; 25 March 1259 – 13 February 1332), Latinization of names, Latinized as Andronicus II Palaeologus, reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1282 to 1328. His reign marked the beginning of the recently restored empire's final decline. The Turks conquered most of Byzantium's remaining Anatolian territories, and Andronikos spent the last years of his reign fighting his Andronikos III Palaiologos, own grandson in the First Palaiologan Civil War. The war ended in Andronikos' forced abdication in 1328, after which he retired to a monastery for the remainder of his life. Life Early life Andronikos was born on 25 March 1259, at Nicaea. He was the eldest surviving son of Michael VIII Palaiologos and Theodora Palaiologina (Byzantine empress), Theodora Palaiologina, grandniece of John III Doukas Vatatzes. Andronikos was acclaimed co-emperor in 1261, after his father Michael VIII recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire, but he was not crowned unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos Asen
Andronikos Asen (; died ) was the ''epitropos'' ("steward, overseer") of the Byzantine province of the Morea between 1316 and 1322. Life Andronikos Asen was the son of Bulgarian Tsar Ivan Asen III and Irene, who was the sister of Byzantine emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos. His father and mother escaped to Byzantine territory during the uprising of Ivaylo in 1280. After Michael Kantakouzenos' death in 1316, Andronikos II gave Andronikos Asen the position of ''epitropos'' of the small Byzantine province in the south-eastern part of the Morea. Kantakouzenos had already managed to consolidate the province, and enjoyed some success against the Frankish Principality of Achaea in the north. Asen continued in the same line, and taking advantage of internal strife in Achaea, he conquered much territory in the central Morea. In 1320, he took the castles of Akova, Polyphengos, Karytaina and Saint George in Skorta, and defeated a Frankish army near the latter fort in September.Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonardo I Tocco
Leonardo I Tocco (died 1375/1377) was the count palatine of the islands of Cephalonia and Zakynthos from 1357 until his death, and later lord of Ithaca, Lefkada, and the port of Vonitsa as well. He was the son of Guglielmo Tocco, the Angevin governor of Corfu in the 1330s, and his second wife Margaret Orsini, the daughter of John I Orsini, Count palatine of Cephalonia. Through his father, Leonardo was closely connected to the Angevin dynasty, and in particular Robert of Taranto. Leonardo was one of the witnesses to his marriage, and later was instrumental in securing Robert's release from captivity in Hungary in 1352. As a reward, in 1357, Robert named him Count palatine of Cephalonia, Zakynthos and possibly Ithaca as well. Probably by ca. 1362, and certainly before 1373, Leonardo also succeeded in gaining control over Lefkada and the port of Vonitsa on the Epirote mainland. In 1374, following the death of Philip II of Taranto, he was part of a delegation which went to Naples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barony Of Arcadia
The Barony of Arcadia was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located on the western coast of the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, and centred on the town of Arcadia (; ; ), ancient and modern Kyparissia. History The Barony of Arcadia was not one of the original twelve secular baronies of the Principality. Initially, Arcadia—the medieval name of Kyparissia on the western coast of Messenia—formed part of the princely domain of the Villehardouin family. It was created as a separate barony by Prince William II of Villehardouin shortly after the Byzantine reconquest of Constantinople in 1261, to recompense Vilain of Aulnay, one of the Frankish lords of the Latin Empire of Constantinople who sought refuge in Achaea. After Vilain's death in 1269 it was divided between his sons, Erard and Geoffrey. Erard disappears after 1279, when he was captured by the Byzantines, but Geoffrey did not manage to reclaim his brother's portion until 1293, due to the obstruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erard III Le Maure
Erard III Le Maure was Baron of Arcadia and Marshal of the Principality of Achaea in the mid-14th century. Life Erard III was the son of Stephen Le Maure, lord of the castle of Saint-Sauveur, and of Agnes of Aulnay, daughter of Vilain II of Aulnay, baron of Arcadia. Stephen and Agnes married in 1324. On Vilain's death, the barony of Arcadia had been divided into two, with Agnes inheriting one half, and the other going to her brother Erard II and eventually his widow, Balzana Gozzadini, and her second husband Peter dalle Carceri. Erard III succeeded his father sometime after 1330. Erard III is first mentioned among the Achaean barons who offered the principality to James II of Majorca in October 1344. It is likely that Erard was also the one chosen to travel and transmit the offer to James II, for which in November 1345—in James' only known act as Prince of Achaea—he received the title of Marshal of Achaea, and lands previously belonging to Nicholas Ghisi. Erard III managed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joanna I Of Naples
Joanna I, also known as Johanna I (; December 1325 – 27 July 1382), was Queen of Naples, and Countess of Provence and Forcalquier from 1343 to 1381; she was also Princess of Achaea from 1373 to 1381. Joanna was the eldest daughter of Charles, Duke of Calabria and Marie of Valois to survive infancy. Her father was the son of Robert the Wise, King of Naples, but he died before his father in 1328. Three years later, King Robert appointed Joanna as his heir and ordered his vassals to swear fealty to her. To strengthen Joanna's position, he concluded an agreement with his nephew, King Charles I of Hungary, about the marriage of Charles's younger son, Andrew, and Joanna. Charles I also wanted to secure his uncle's inheritance to Andrew, but King Robert named Joanna as his sole heir on his deathbed in 1343. He also appointed a regency council to govern his realms until Joanna's 21st birthday, but the regents could not actually take control of state administration after the K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Of Baux
James of Baux or James of Les Baux, or ''Jacopo del Balzo'' (died 7 July 1383) was the titular Latin Emperor of Constantinople from 1374 to 1383. He was the last Latin emperor to govern any imperial territory. James belonged to the noble House of Baux, specifically the branch settled in the Kingdom of Naples. He was the son of Francis, Duke of Andria, and Margaret, daughter of Prince Philip I of Taranto and his second wife, the Empress Catherine II, Princess of Achaea. His mother's brother was Prince Philip II of Taranto. In 1373, the childless Philip declared his nephew his universal heir. He thus stood to inherit the Principality of Taranto in the Neapolitan kingdom, and the Principality of Achaea in Greece, as well as a claim on the Latin Empire. On the death of Philip II of Taranto in 1374, most of the barons in the principality of Achaea recognized as his heir Queen Joanna I of Naples. She in turn confiscated all the Italian possessions of Francis and James of Baux and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Of Baux
Francis of Baux (, ; c. 1330Douglas Richardson. ''Plantagenet Ancestry: Plantagenet Ancestry: A Study In Colonial And Medieval Families,'' 2nd Edition, 2011. pg 401. – 23 April 1422) was the first Duke of Andria, Count of Montescaglioso and Squillace, and Lord of Berre, Mison, and Tiano. He was the son of Bertrand III of Baux, Count of Andria and Montescaglioso and his second wife, Marguerite d'Aulnay. Francis's father was a Senator of Rome, Captain General of Tuscany, and Justiciar of Naples. The half-royal Baux family was one of the greatest families of the kingdom after the Duke's marriage to Marguerite of Taranto in 1348.Kenneth Meyer Setton. ''A History of the Crusades: Fourteenth and fifteenth centuries,'' edited by Harry W. Hazard. Univ of Wisconsin Press, 1969. pg 142-46. Status In 1349, Francis was given an extensive grant by Louis, Prince of Taranto. Prince Louis had married Joanna I of Naples in 1346 as her second husband, and had become King of Naples; he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Of Villehardouin
William of Villehardouin (; Kalamata, 1211 – 1 May 1278) was the fourth prince of Achaea in Frankish Greece, from 1246 to 1278. The younger son of Prince Geoffrey I, he held the Barony of Kalamata in fief during the reign of his elder brother Geoffrey II. William ruled Achaea as regent for his brother during Geoffrey's military campaigns against the Greeks of Nicaea, who were the principal enemies of his overlord, the Latin Emperor of Constantinople Baldwin II. William succeeded his childless brother in the summer of 1246. Conflicts between Nicaea and Epirus enabled him to complete the conquest of the Morea in about three years. He captured Monemvasia and built three new fortresses, forcing two previously autonomous tribes, the Tzakones and Melingoi, into submission. He participated in the unsuccessful Egyptian crusade of Louis IX of France, who rewarded him with the right to issue currency in the style of French royal coins. In the early 1250s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |